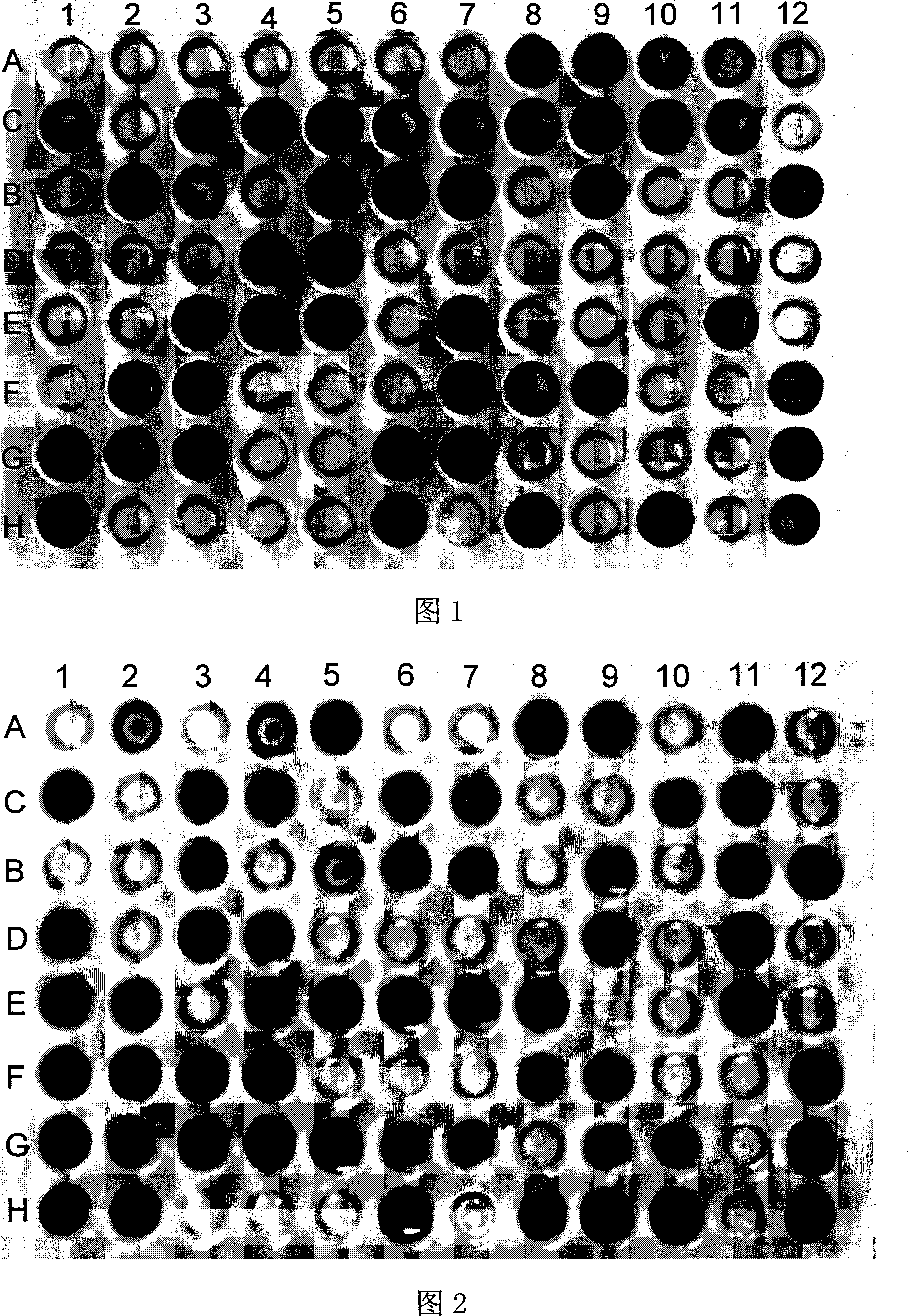Bacterium identification reagent kit as well as preparation method and uses thereof
A technology of bacterial identification and kit, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of low comparability of results and high price, and achieve simple and convenient use, short identification time, and improved The effect of comparability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Activate the Enterobacter cloacae model strain Enterobacter cloacae ATCC 13047 with a medium plate for 1-2 times;
[0040](2), collect its fresh thallus, wash thalline 2 times with the centrifugation of 0.9% normal saline, wash with sterile water, dilute thalline, make OD 600 Bacterial suspension with a value of 1.5;
[0041] (3), take step 2 bacterial suspension 0.5ml, OD 600 =1.5, add 15ml of sterile semi-solid 0.2% agar-deionized water, shake well and mix completely;
[0042] (4) Use an eight-channel pipette to take 150 μL of the bacterial suspension in step 3 and add it to each well of the kit;
[0043] (5) Put the kit with the added bacterial suspension into a 37°C constant temperature bacterial incubator for cultivation, and determine the cultivation temperature according to the optimal growth temperature of the bacteria;
[0044] (6) After culturing for 20 hours, observe the kit, and use A1 as the control well to determine the utilization of bacterial carb...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Same as Example 1, after activating the Rhizobium japonicum type strain NZP 2213 with LB plates, collect its fresh bacteria, wash with sterile water, and prepare the bacteria suspension according to the above steps. Add 150 μL of bacterial suspension to each well of the kit with a pipette. Put the kit with the added bacterial suspension into a constant temperature bacterial incubator at 37°C for cultivation, observe the kit after 4 days, and use A1 as the control well to determine the utilization of bacterial carbon sources. The observation results are shown in Figure 2. It can be seen that the rhizobia type strain NZP2213 can utilize dextrin, Tween 40, Tween 80, sucrose, D-glucose, D-mannose, D-galactose, L-fructose, D-fructose, D-xylose, xylose , D-ribose, D-trehalose, D-mannitol, L-arabitol, D-sorbitol, hexyl alcohol, m-inositol and other 57 carbon sources, specifically A2 shown in Figure 2 , A4, A5, A8, A9, A11, C1, C3, C4, C6, C7, C10, C11, B3, B5~7, B9, B11, B12...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com