Reclamation of germanium from chromium-germanium alloy waste material by wet method
A technology of germanium alloy and wet method, which is applied in the field of wet recovery of germanium from chromium-germanium alloy waste, can solve uneconomical problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
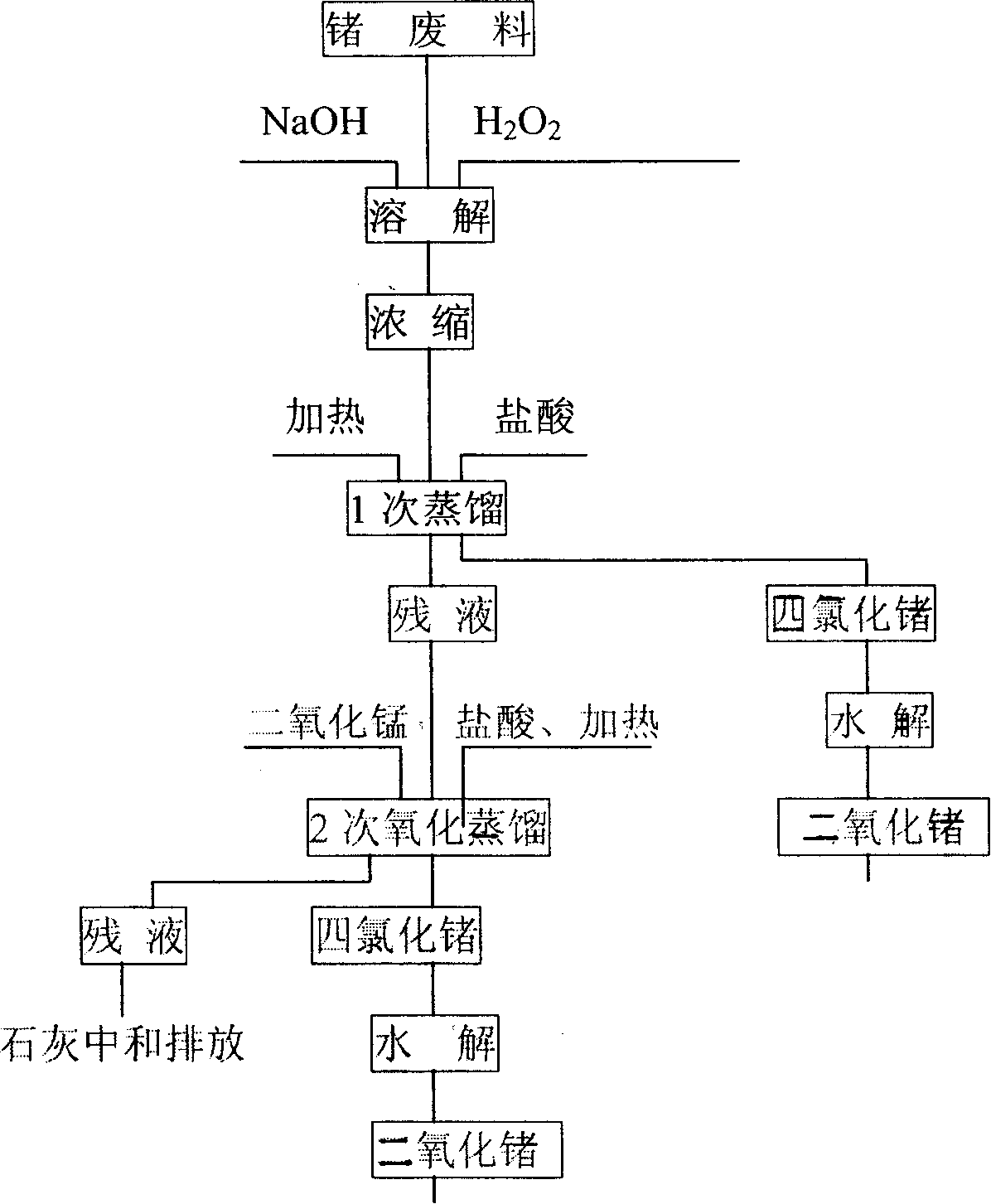
[0025] Embodiment 1, use level is that about 100g of chromium-germanium alloy waste material of 81.72% is divided into experiment 4 times, each about 25g, waste material is put into the flask of 2000ml, adds H 2 O125ml, stir, add 12.5-75g NaOH respectively, after it dissolves, add chromium-germanium alloy scrap, add the H of concentration 18-48% slowly respectively 2 o 2 75-200ml, H 2 o 2 The input speed is the first 1 / 4 period: the remaining time of the first half: the second half = 1: 2: 2.5-3.5; the reaction time is 8-12h, and then moved into the evaporator to evaporate to 125-150ml. Then transfer to a distillation bottle to cool to room temperature, add 500-850ml of HCl with a concentration of 10.5mol / L to react, slowly heat up to 84-100°C for distillation after 30 minutes, and receive it with a 5-stage receiving bottle. When the distilled solution was cooled to room temperature, MnO was added separately 2 25-125g, HCl 125-250ml to react, the reaction time is 4-7h, and...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2, take out 40kg from the chromium-germanium alloy cutting material of 83.87% from 400kg grade, carry out industrial test in 4 times, each time material 10kg, the amount of the NaOH that adds is 15kg, and concentration is 30% H 2 o2 98-100L, add 280L of HCl with a concentration of 10.5mol / L for the first distillation, and add 80L of HCl with a concentration of 10.5mol / L after the first distillation finishes cooling, MnO 2 20kg, the second distillation was carried out after 2 hours of reaction, the third addition of HCl reaction and the number of distillation were 30L, MnO 2 It is 6kg, adopts 7 grades of receiving bottles to receive, wherein, the 1st-5th grade is identical with embodiment 1 concentration, the 6th, 7th grade adopts 40% NaOH, according to the above-mentioned process step of regulation, reclaims the GeCl that obtains 4 As shown in Table 2, no germanium has been detected in the seventh-level receiving bottle, which is not listed in the table.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com