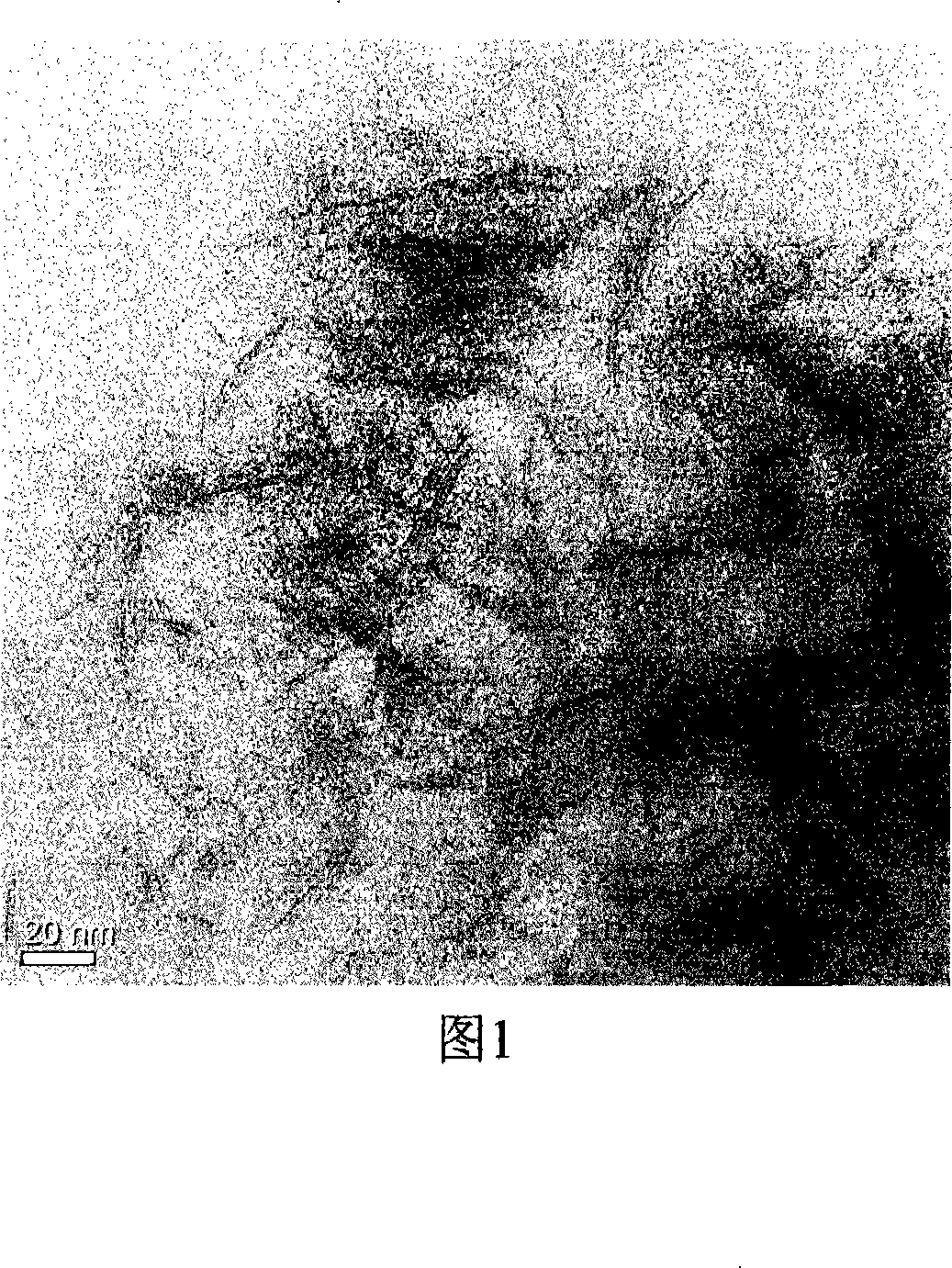
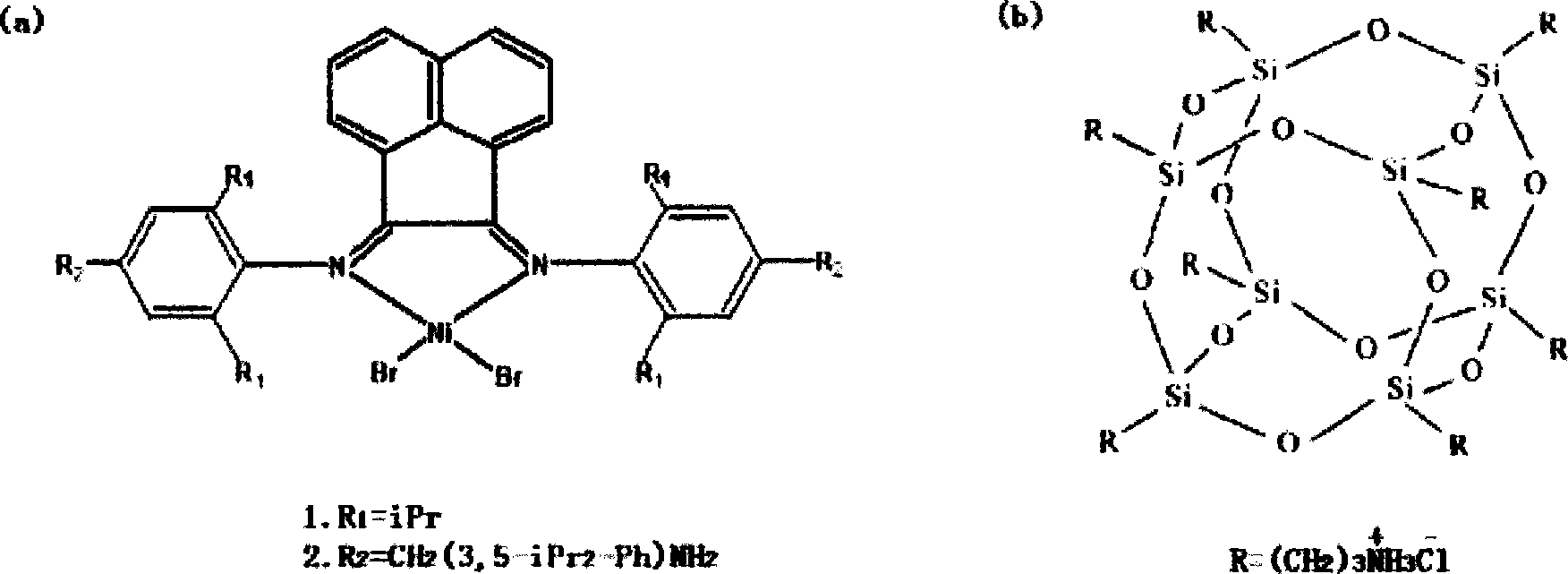
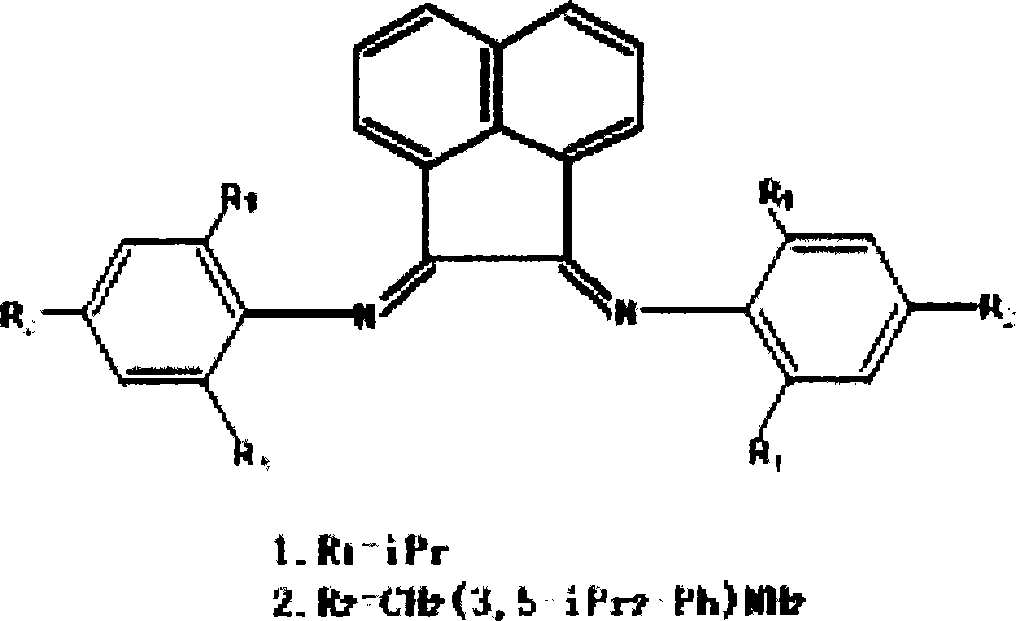
Method for producing polythene/POSS modified tough clay nano composite material
A technology of nanocomposite materials and polyethylene, which is applied in the field of preparation of polyethylene/POSS modified clay nanocomposites, can solve the problems of poor mechanical properties of composite materials, high temperature resistance, material processing and adverse effects on performance, etc., to achieve The preparation method is simple, avoiding thermal instability, thermal stability and the effect of improving the dynamic mechanical storage modulus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Preparation of acenaphthyldiimine ligand
[0032] 3.0 g of 4,4-methylene-bis(2,6-diisopropylaniline) and 0.54 g of acenaphthoquinone were dissolved in 50 ml of toluene solution, 2 ml of formic acid was added as a catalyst, and the mixture was refluxed for 14 hours. During the reflux process, a water separator was used to remove the moisture generated during the reaction. After the reflux was completed, the temperature of the solution was lowered to room temperature, and the solvent was evaporated in vacuo. The resulting crude product was purified by column (silica gel, ethyl acetate:petroleum ether=1:9) to obtain 1.2 g of N,N'-bis[4-(4-amino-3,5-diisopropylbenzyl )-2,6-diisopropylphenyl] acenaphthylenediimine ligand L, yellow powder. Ligand L 1 H-NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 ) results: 7.89(d, 2H), 7.37(t, 2H), 7.01(s, 4H), 6.87(s, 4H), 6.74(s, 2H), 3.84(d, 4H), 3.53(s, 4H ), 2.19(s, 12H), 2.06(s, 12H); ligand L 13 C-NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 )结果:161.016,145.358,140.787,137...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The other conditions of this embodiment are the same as in Example 1: the polymerization reaction time in step (6) is 80min. Under the above polymerization conditions, the branching degree, melting point, crystallinity and molecular weight of the obtained polyethylene are shown in Table 1. The POSS modified clay content is 6.2%. The thermal decomposition temperature of polyethylene / POSS modified clay nanocomposites is shown in Table 2. When 50% thermal weight loss is used as a comparison point, the degradation temperature of polyethylene composites is 471.9 ° C, which is higher than that of pure Polyethylene is 56.0°C higher. The storage modulus of polyethylene / POSS modified clay nanocomposites is shown in Table 3. At 20°C, the storage modulus of polyethylene composites is 989% higher than that of pure polyethylene.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The other conditions of this embodiment are the same as in Example 1: the polymerization reaction time in step (6) is 45min. Under the above polymerization conditions, the branching degree, melting point, crystallinity and molecular weight of the obtained polyethylene are shown in Table 1. The POSS modified clay content is 9.8%. The thermal decomposition temperature of polyethylene / POSS modified clay nanocomposites is shown in Table 2. When 50% thermal weight loss is used as a comparison point, the degradation temperature of polyethylene composites is 477.8 ° C, which is higher than that of pure Polyethylene is 61.9°C higher. The storage modulus of polyethylene / POSS modified clay nanocomposites is shown in Table 3. At 20°C, the storage modulus of polyethylene composites is 1226% higher than that of pure polyethylene.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com