Nitric oxide-blocked cross-linked tetrameric hemoglobin
A technology of hemoglobin and nitric oxide, applied in hemoglobin/myoglobin, peptide/protein components, blood diseases, etc., can solve problems such as slow infusion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
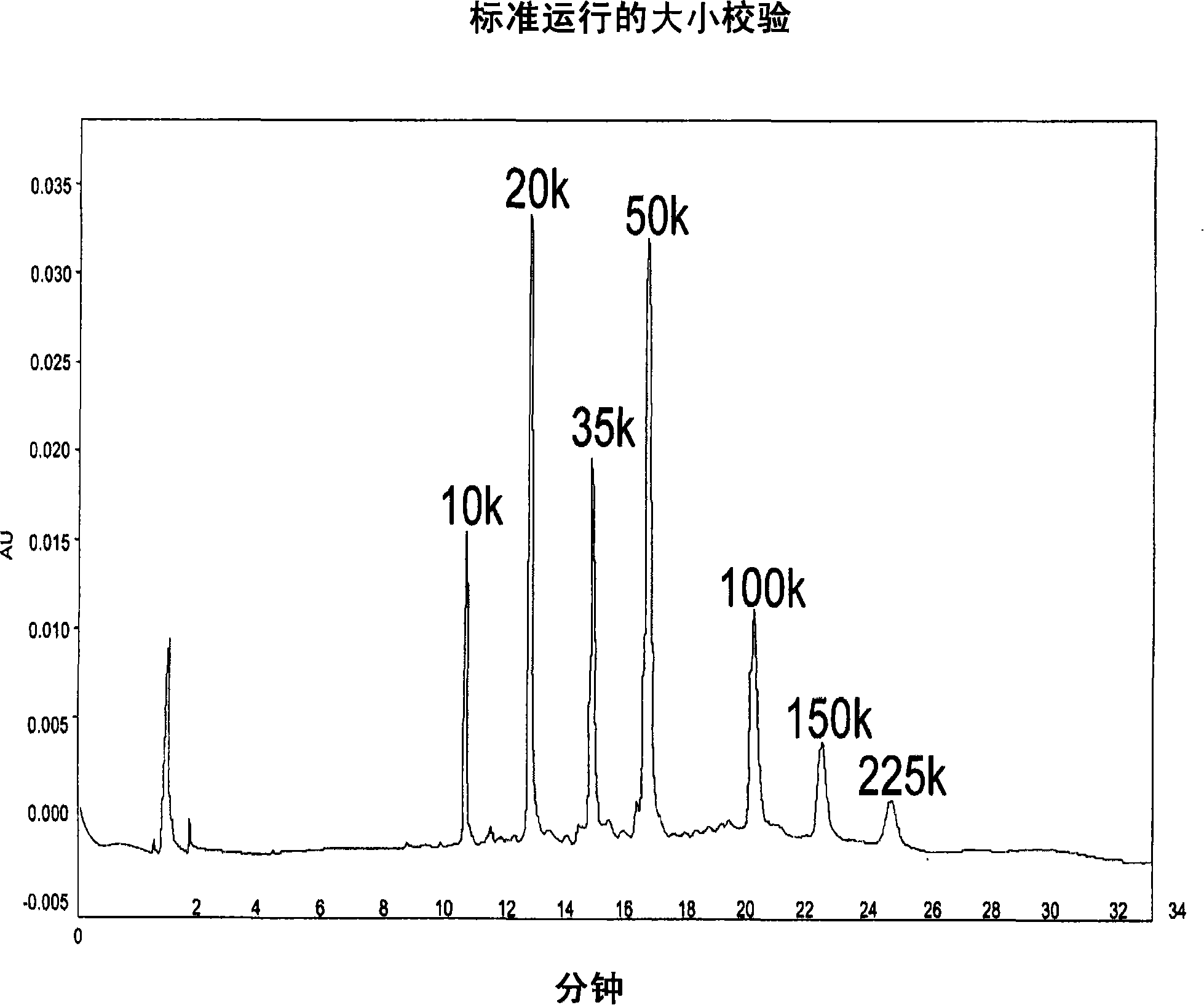
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0090] II. Preparation method of amidomethylated cross-linked hemoglobin
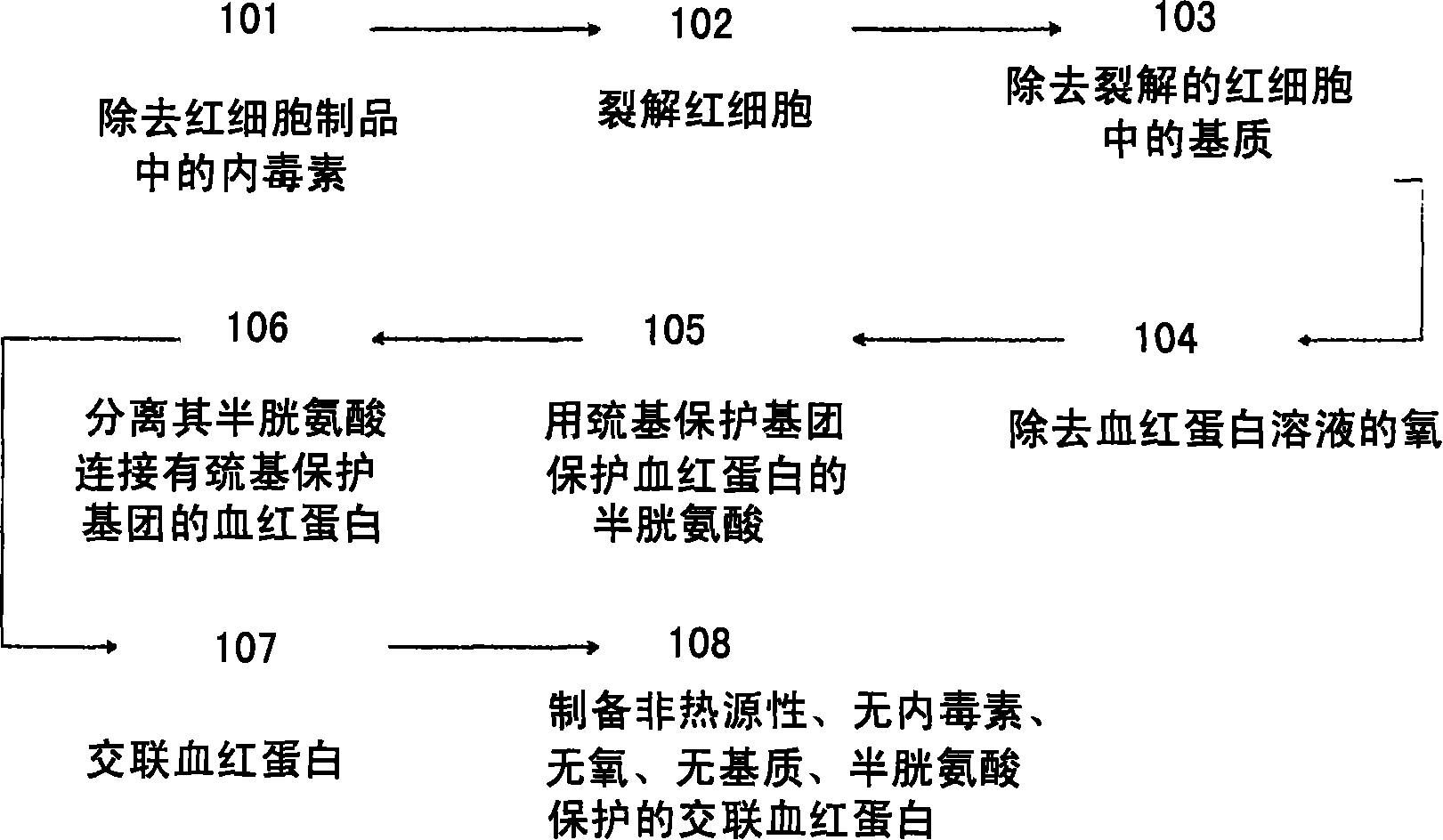
[0091] figure 1 The steps of some embodiments of the invention are described. These steps may be performed independently of each other or one after the other, which is not a limitation of the invention. The method of the present invention may omit one or more steps. The preparation method of hemoglobin of the present invention may include: step 101, which includes removing plasma proteins and endotoxins from products containing red blood cells by washing; step 102, which includes lysing these red blood cells; step 103, which includes removing endotoxins from the lysed red blood cells Matrix (comprising membrane and white blood cell) to separate hemoglobin; Step 104, comprises removing the oxygen in hemoglobin; Step 105, comprises adding the reagent that can provide sulfhydryl protecting group for cysteine of hemoglobin in hemoglobin solution; Step 106, comprises Isolating hemoglobin with a sulfhy...
Embodiment 1
[0238] Comparing two methods of primary processing of whole blood
[0239] Material: Bovine Blood Collection: The bovine blood was collected into a 1 gallon container that could hold 100 ml of a 6% sodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) solution and cooled on ice.
[0240] Whole bovine arterial blood was divided into batches A and B. Batch A consisted of 2200 ml whole blood, washed with a haemonetics cell saver (Cell Saver) 5 to obtain platelet-free, coagulation factor-free, extracellular potassium-free, anticoagulant-free and cell-matrix-free concentrated red blood cells (Method A). Batch B consisted of 1800 ml whole blood washed with Millipore 0.65 μm filter (Method B).
[0241] Method A. Removal of plasma proteins with a cell harvester 5: Red blood cells were concentrated from other fractions of freshly collected anticoagulated bovine blood using a Haemonetics cell harvester 5 . Do not burst white or red blood cells at this time.
[0242] After passing through a...
Embodiment 2
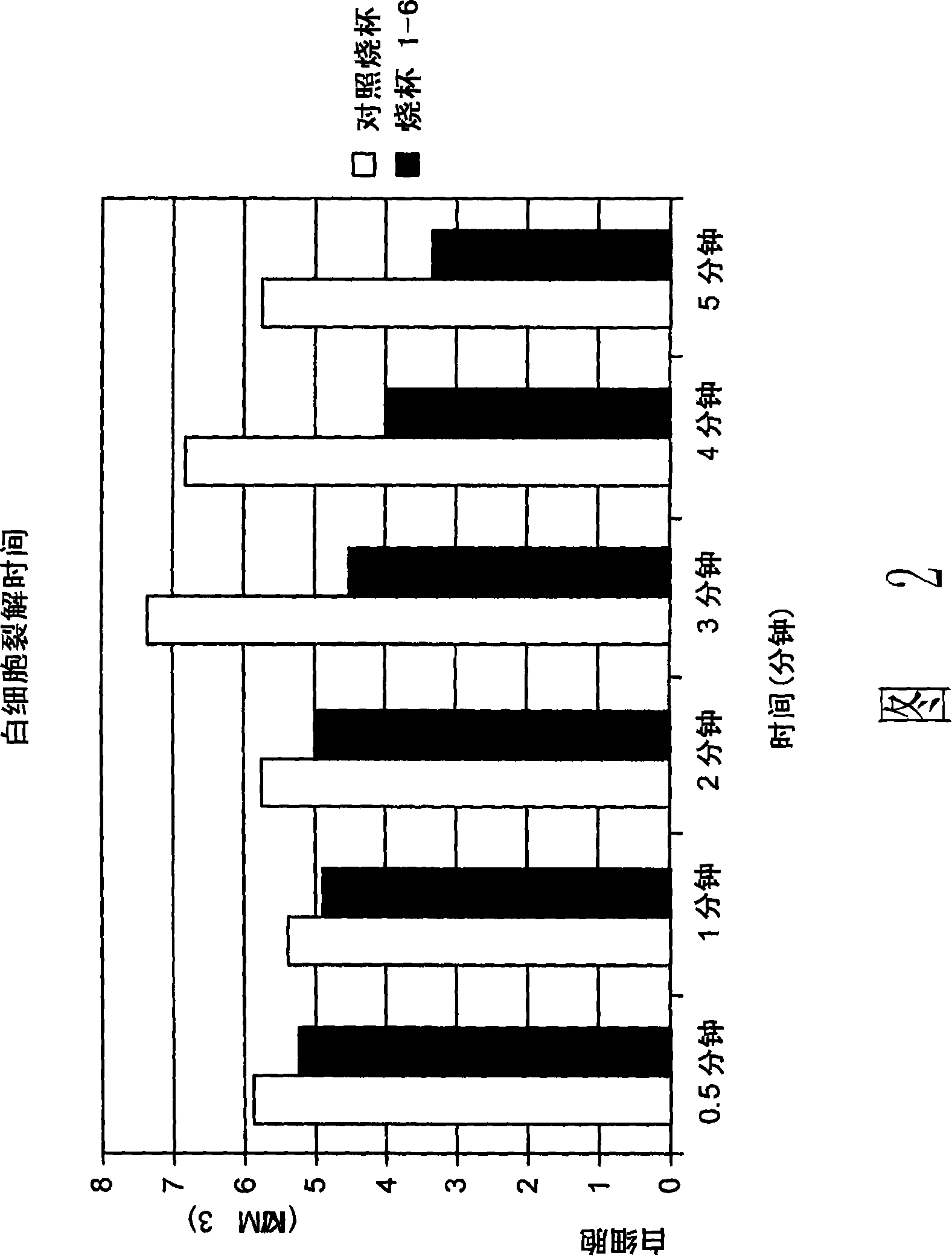
[0260] lysed white blood cells
[0261] This example shows that the relative time to WBC lysis was determined. Preferential lysis of RBCs compared to WBCs optimizes erythrocyte lysis for maximum hemoglobin and does not introduce proteases to lysed WBCs.
[0262] Method: 2000ml of whole blood was only filtered through the 100μ reservoir filter of the cell harvester 5 . Then 200ml of blood was injected into 7 beakers. One beaker was designated as control. Then specify specific lysis times for the remaining 6 beakers: 30 s, 1 min, 2 min, 3 min, 4 min, 5 min. Add 910ml of 0.9% saline solution to the control beaker and start timing. At times increasing to 30 seconds, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 minutes, 10 ml samples were taken for white blood cell analysis.
[0263] For the remaining 6 beakers, add 800ml DI water. After 30 seconds, 110 ml of 9% saline was added to the first beaker to stop lysis. After stirring for about 30 seconds, a 10 ml sample was taken for leukocyte analysis. A...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com