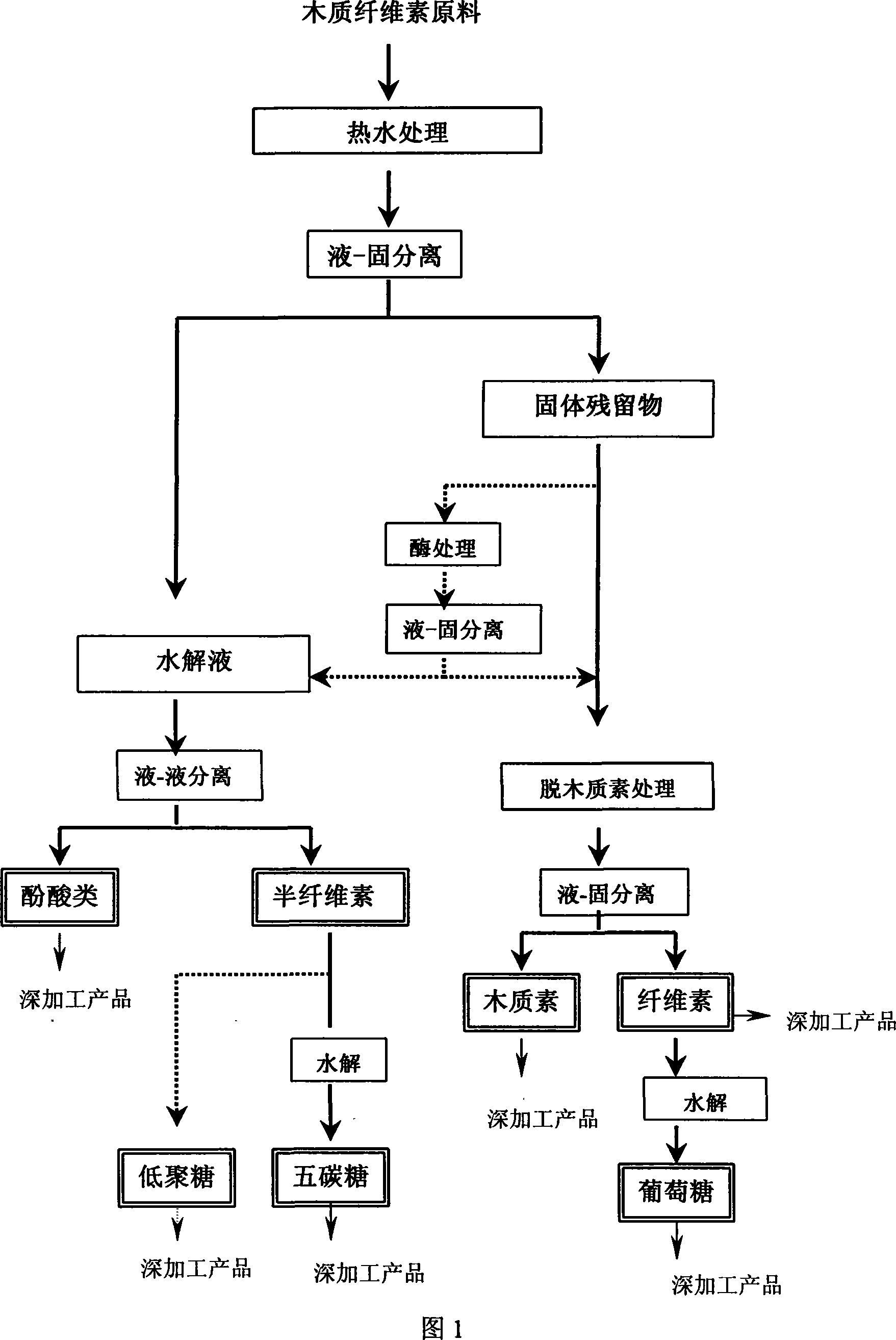
Method for synchronously extracting hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin and reclaiming phenolic acid compounds
A technology of hemicellulose and lignocellulose, which is applied in the field of processing lignocellulosic biomass, can solve the problems of poor economic benefits and insufficient utilization of biomass raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] 80 grams (absolute dry weight) air-dried pulverized cornstalk raw material is packed into a stainless steel pressure reactor (capacity is 1 liter), adds the deionized water of 800 milliliters. Start stirring and heating, and use the preset heating speed to raise the reactor from room temperature to 180 degrees Celsius within 30 minutes, and keep it at 180 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes, then use the coil cooling device in the reactor to reduce the temperature of the reactor Rapidly drop to about 50 degrees Celsius, open the reactor, transfer the reactant to a funnel for liquid-solid separation, and wash the fiber solid several times with hot water. Recover all filtrate and fiber solids, record the total amount and sample for chemical analysis.
[0072] Get 50 grams (absolute dry weight) above the fiber solid that obtains and pack in identical reactor, add the ammonium hydroxide solution (15% concentration of NH of 500 milliliters) 3 weight), heated to 170 degrees Celsi...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Reaction apparatus and operation method are identical with example 1.
[0076] Raw material is wheat straw
[0077] The first paragraph processing: the same as example 1
[0078] The second stage of treatment: add 1% sulfuric acid (by weight of raw materials) with 50% ethanol aqueous solution, and the incubation time at 170 degrees Celsius is 30 minutes.
[0079] The hemicellulose dissolved in the first stage hydrolyzate was about 70% of the total amount in the raw material.
[0080] The recovered lignin in the second treatment liquid accounts for about 75% of the total amount in the raw material.
[0081] The conversion rate of enzymatic hydrolysis of the fiber residue obtained in the second stage into glucose is 96%
Embodiment 3
[0083] Reaction apparatus and operation method are identical with example 1.
[0084] The raw material is wheat straw.
[0085] The first stage of treatment: 0.5N sulfuric acid aqueous solution, 100 degrees Celsius, 60 minutes.
[0086] The second stage of treatment: 75% ethanol aqueous solution (1N sulfuric acid concentration), 120 degrees Celsius, 90 minutes.
[0087] The first stage treatment yielded 72% hemicellulose.
[0088] The second stage treatment yielded 69% lignin and 97% cellulose.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com