Magnetoresistive effect element and magnetic memory
A technology of magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory, which is applied to devices applying electro-magnetic effect, static memory, digital memory information, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in realizing large capacity, large writing current value, and insulation damage of tunnel insulating layer. Component damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
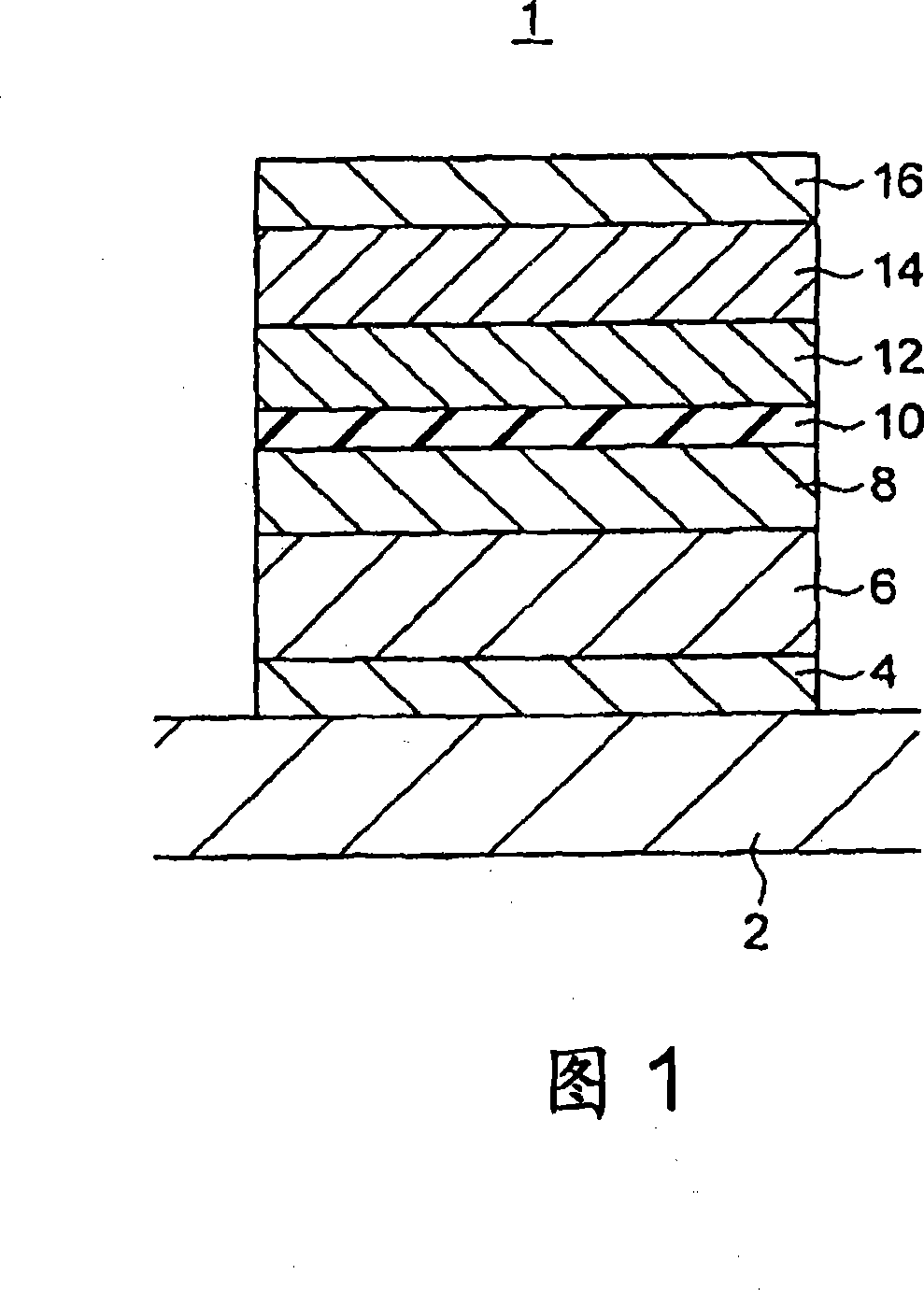
[0029] FIG. 1 shows a cross section of a magnetoresistance effect element according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The magnetoresistance effect element 1 of this embodiment is a lower fixed (bottom pin) type magnetoresistance effect element, comprising: a bottom layer 4 arranged on the lower electrode 2; an antiferromagnetic layer 6 arranged on the bottom layer 4; magnetization fixed layer 8 on the magnetic layer 6 and composed of a magnetization fixed ferromagnetic layer; tunnel insulating layer 10 provided on the magnetization fixed layer 8; provided on the tunnel insulating layer 10 and composed of a ferromagnetic layer whose magnetization direction is variable The magnetization free layer (magnetic recording layer) 12; the antiferromagnetic layer 14 provided on the magnetization free layer 12; the top cover (cap) layer 16 provided on the antiferromagnetic layer 14; and the cap layer 16 provided on the upper electrode (not shown). In addition, in this embo...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0054]Next, a magnetic memory according to a second embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 7 . The magnetic memory of this embodiment has at least one memory cell provided in the intersection region of the bit line 30 and the word line 40 . The above-mentioned memory cell has the lower fixed magnetoresistance effect element 1 of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 and the select transistor 60 for both writing and reading, and forms one bit. The selection transistor 60 has a source region 61 , a gate region 62 and a drain region 63 . One terminal of the magnetoresistance effect element 1 is connected to the extraction electrode 20 , and the other terminal is connected to the bit line 30 via the metal hard mask or the via 25 . The extraction electrode 20 is connected to the source region 61 of the selection transistor 60 via the connection portion 50 . The word line 40 is connected to the drain region 63 of the selection transistor 60 . In addition, the selecti...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0060] Next, a magnetic memory according to a third embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 11 . The magnetic memory of this embodiment has at least one memory cell, and the memory cell is provided on the bit line 30 1 、30 2 in the intersection region with the word line 40 . The above-mentioned memory cell has the bottom pinned magnetoresistance effect element 1 of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 1 ,1 2 The select transistor 60 used for both writing and reading forms 1 bit. The selection transistor 60 has a source region 61 , a gate region 62 and a drain region 63 . Magnetoresistance effect element 1 1 One terminal of is connected to the lead-out electrode 20, and the other terminal is connected via a metal hard mask or a via 25 1 with bit line 30 1 connect. The extraction electrode 20 is connected to the source region 61 of the selection transistor 60 via the connection portion 50 . The word line 40 is connected to the drain region 63 of the selecti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com