Erasing method of single-gate non-volatile memory
A non-volatile memory, single-gate technology, used in electrical components, electrical solid-state devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of complex preparation, increased cost, and increased labor hours.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] In the following, specific embodiments are described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, so that it is easier to understand the purpose, technical content, features and effects of the present invention.
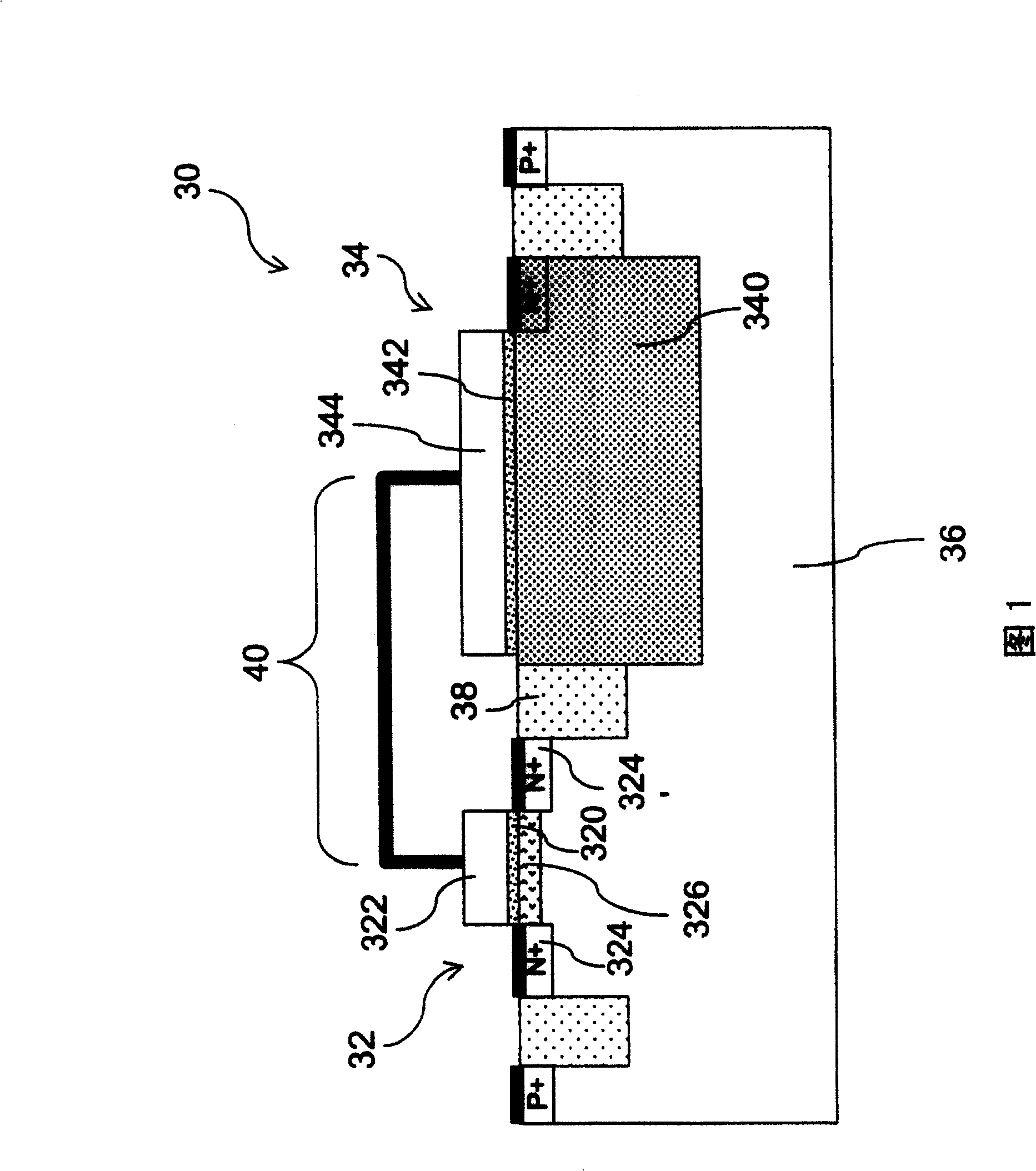
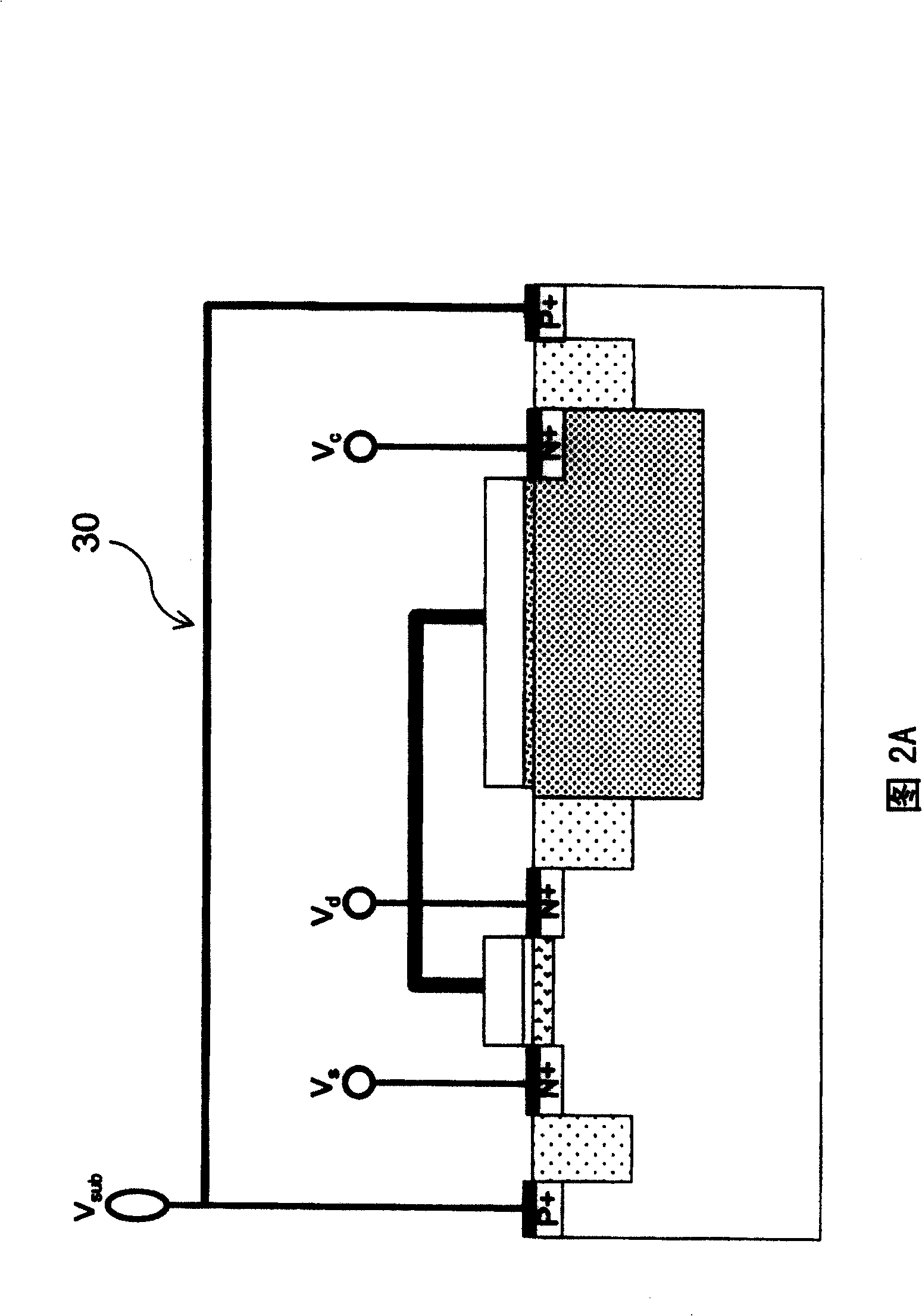
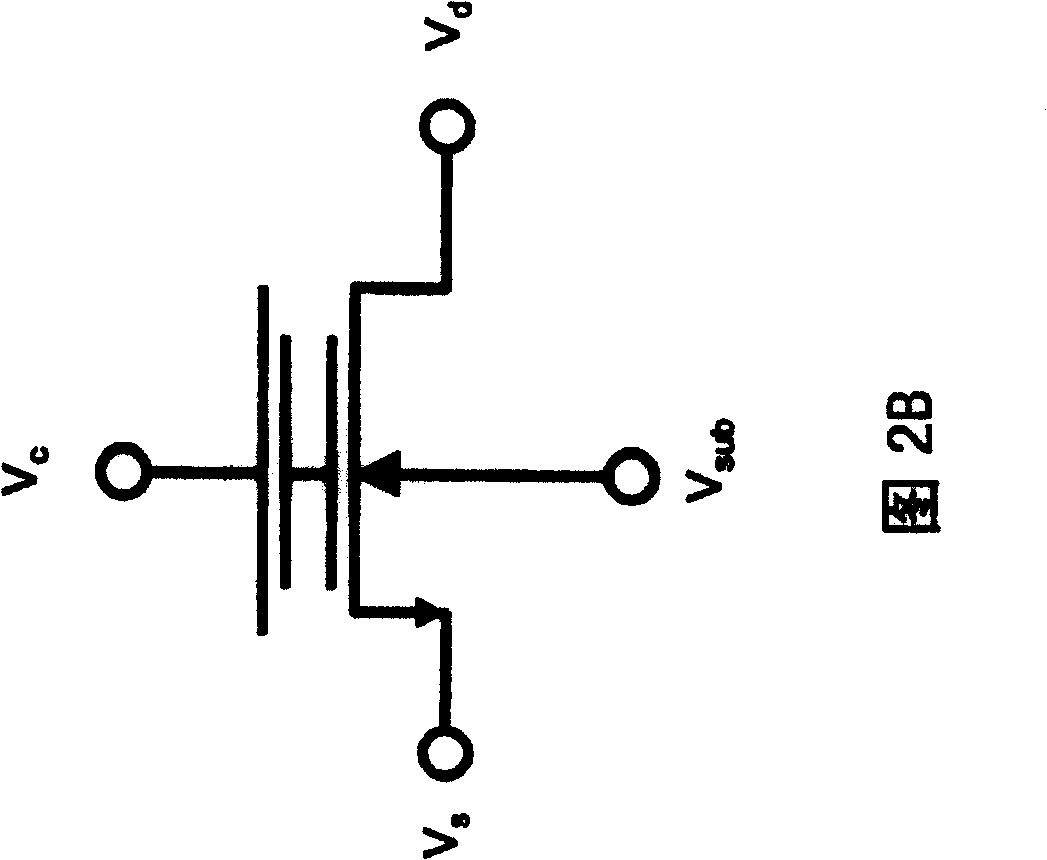
[0016] 1 is a cross-sectional view of a single-gate nonvolatile memory structure provided by the first embodiment of the present invention. The single-gate nonvolatile memory structure 30 includes an NMOS transistor (NMOSFET) 32 and an N well (N-well ) capacitor 34 in the P-type silicon substrate 36; the NMOS transistor 32 includes a first dielectric layer 320 located on the surface of the P-type silicon substrate 36, a first conductive gate 322 stacked above the first dielectric layer 320, and two N + The ion-doped region is located in the P-type silicon substrate 36, serving as its source 324 and drain 324' respectively, and a channel 326 is formed between the source 324 and the drain 324'; the N-well capacitor 34 includes the second ion-doped regi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com