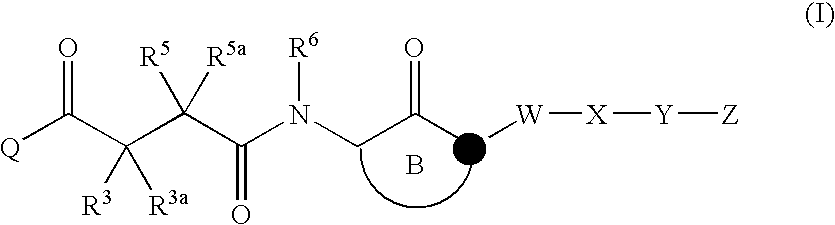
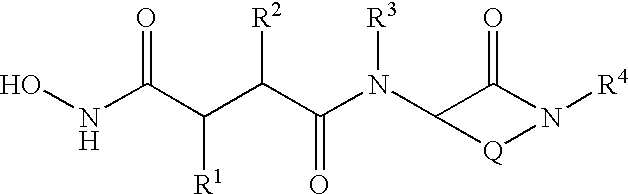
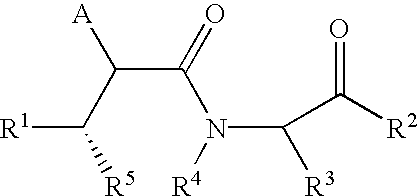
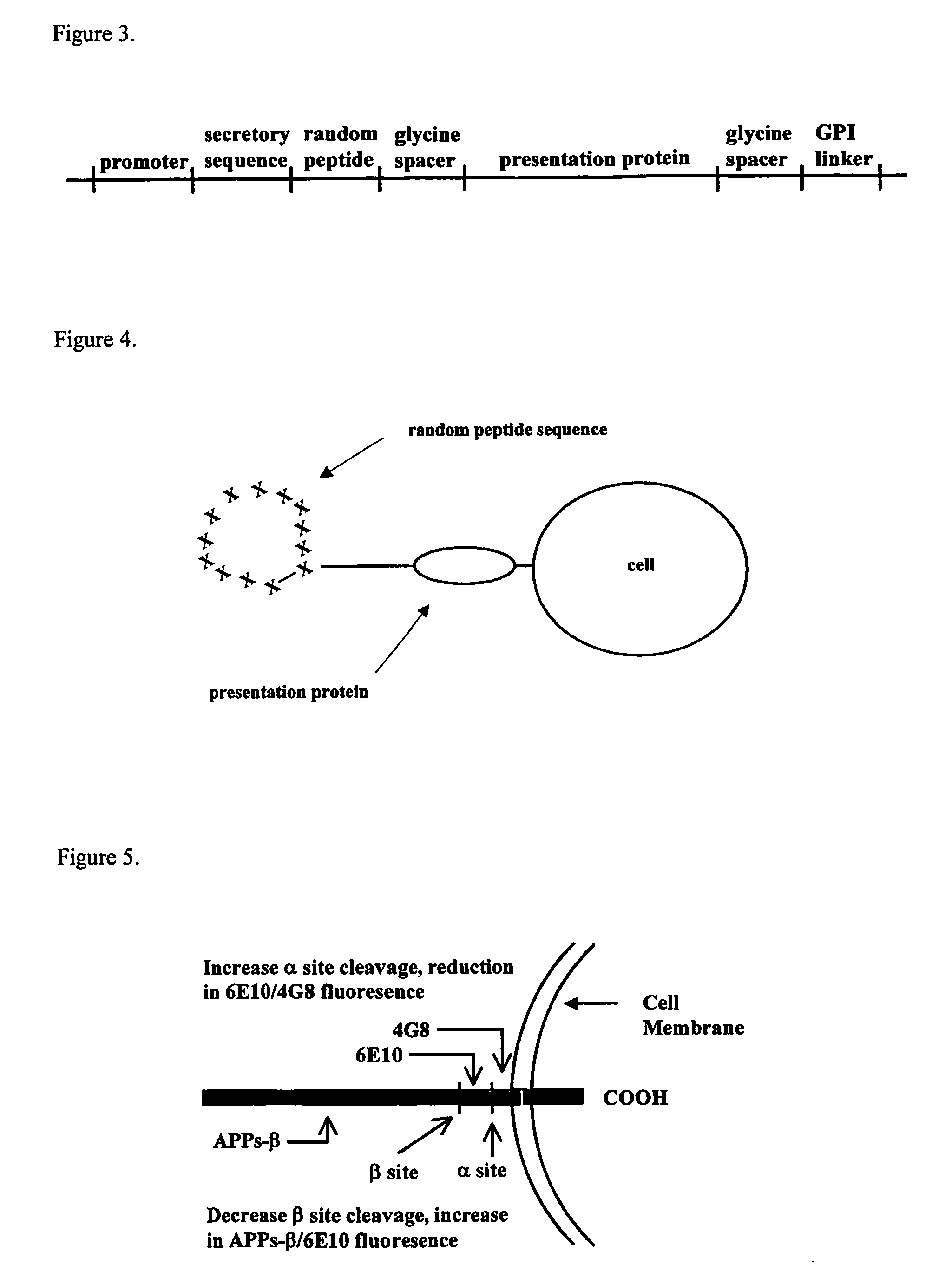
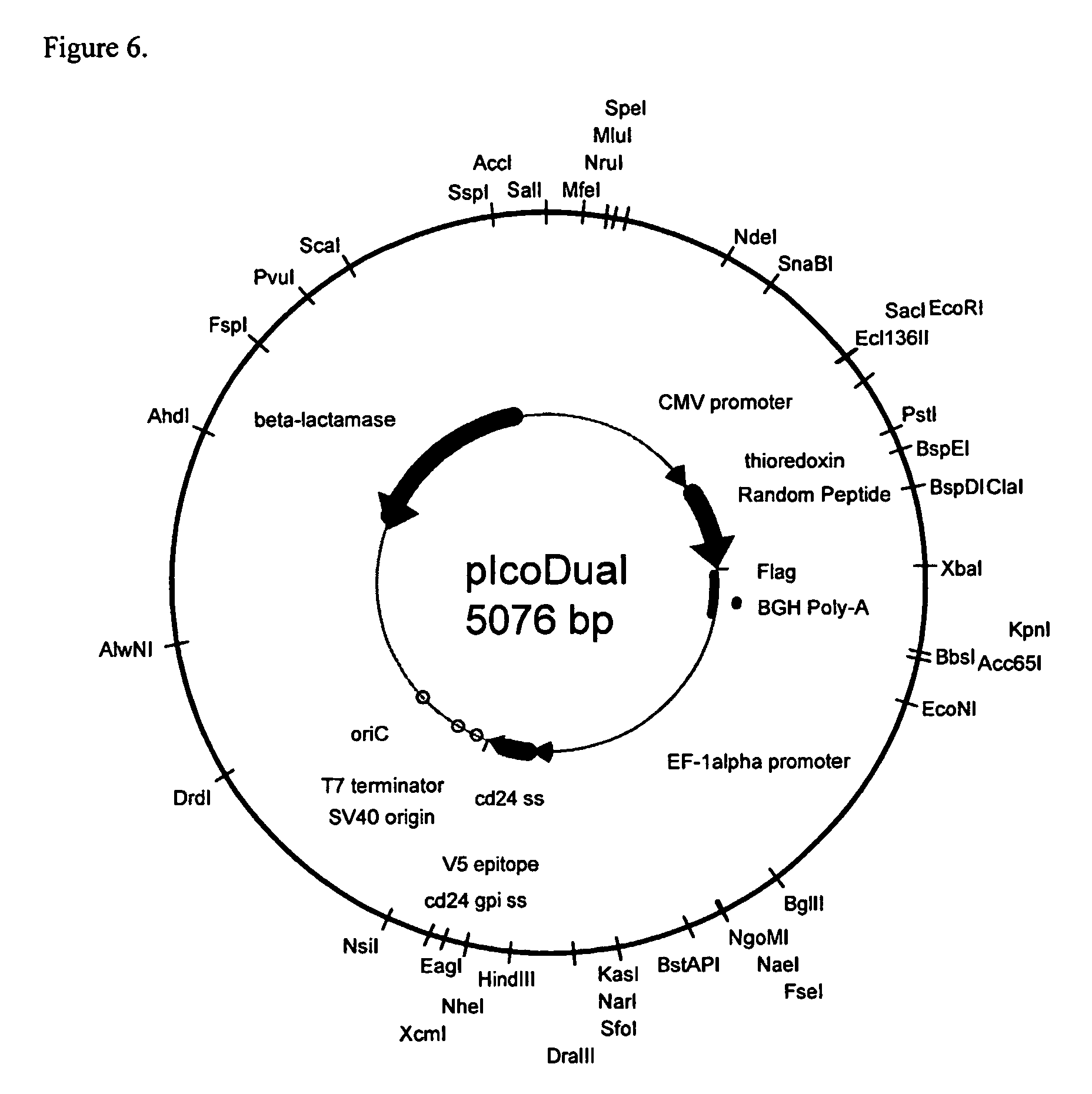
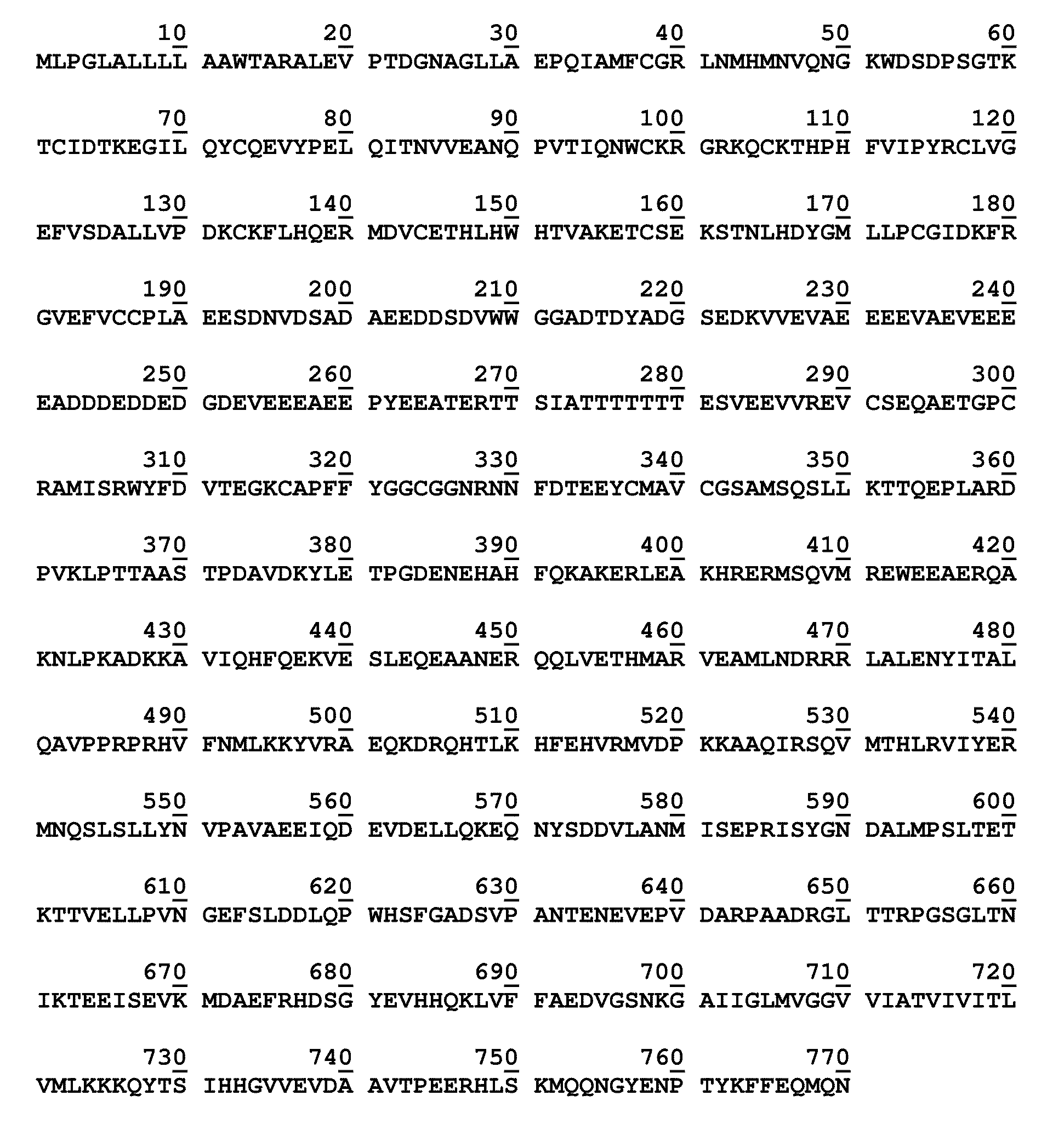
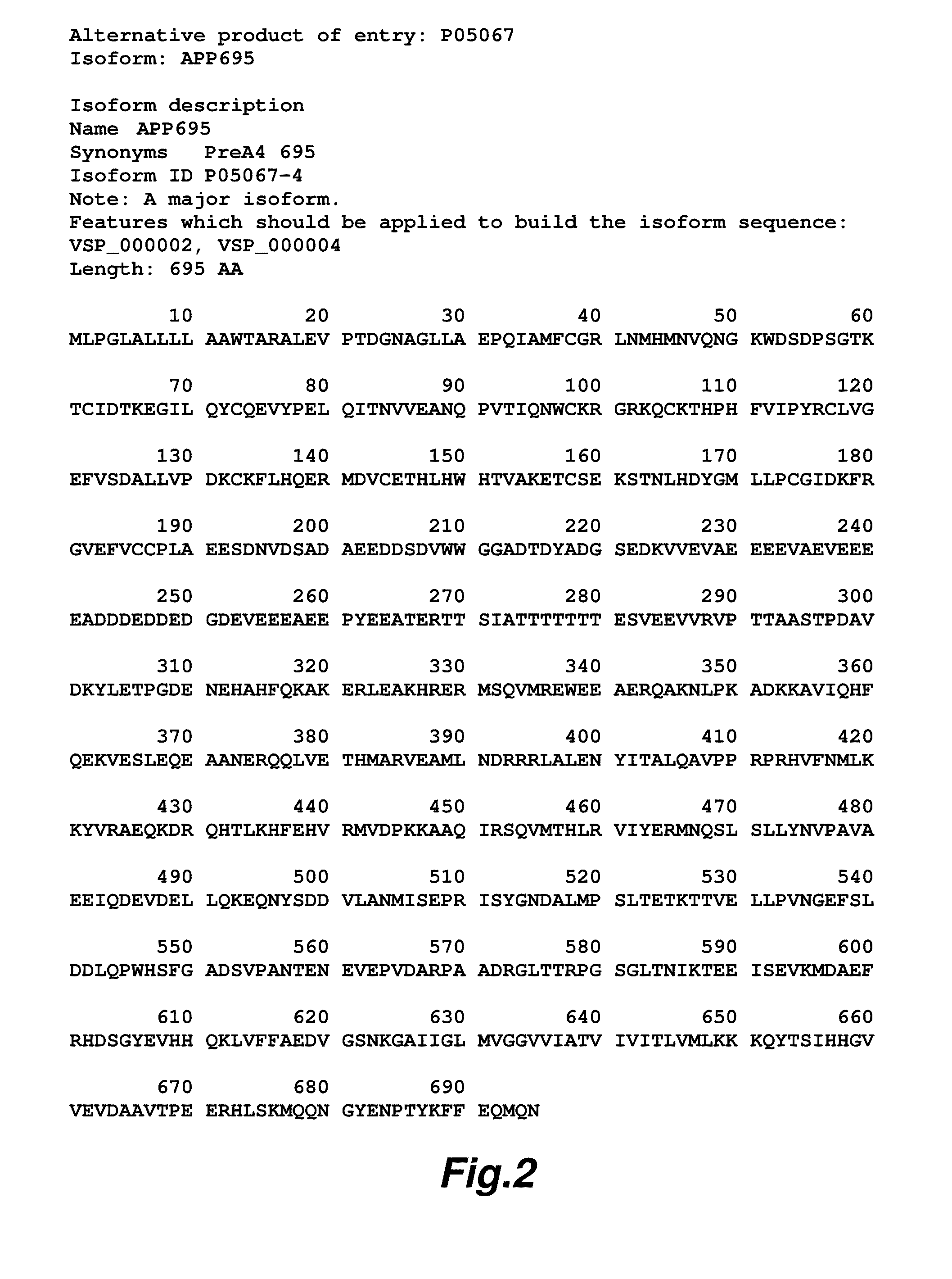
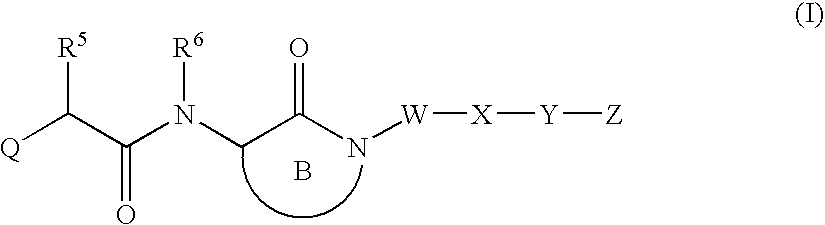Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
192 results about "Amyloid Protein Precursor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
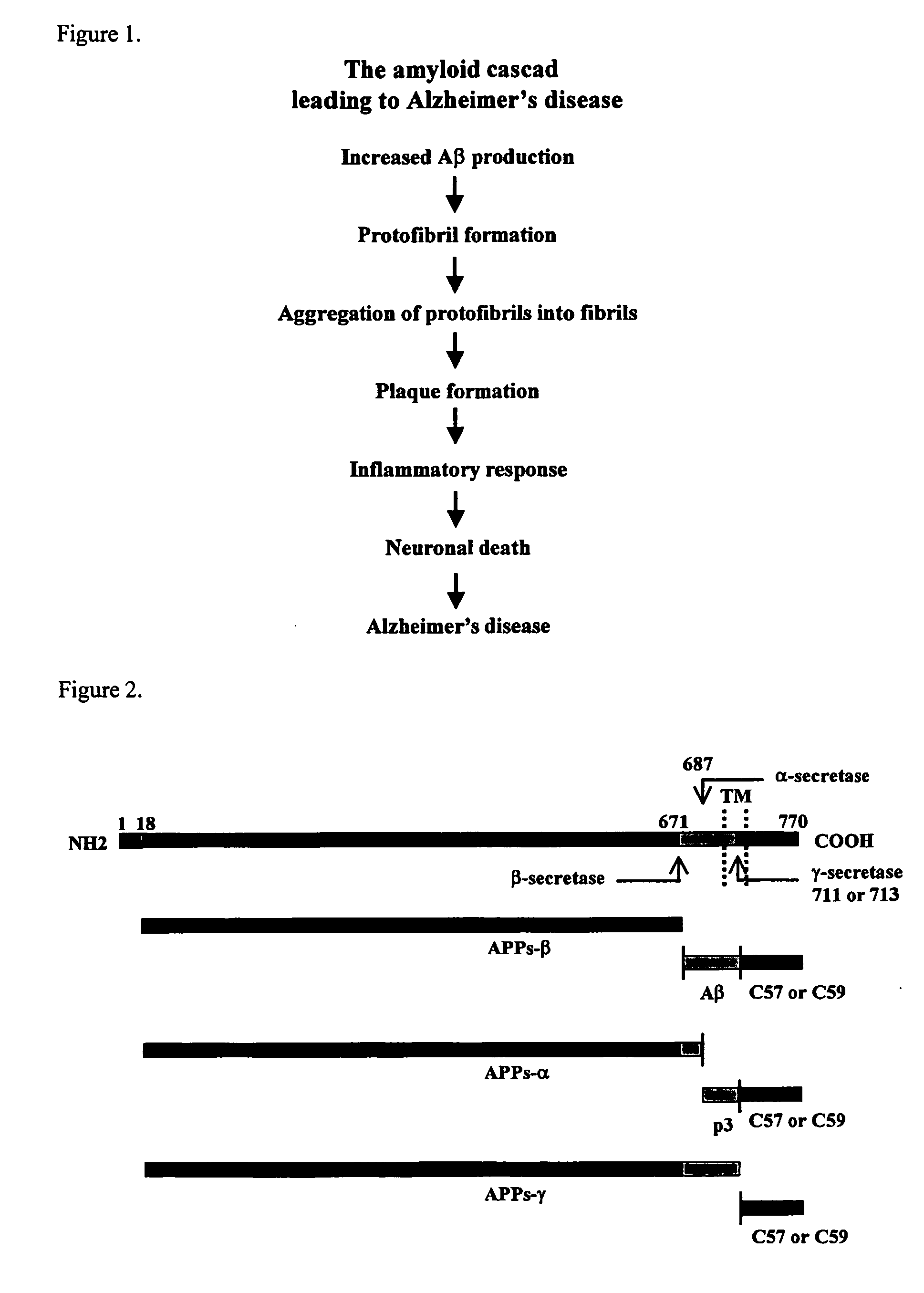
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is an integral membrane protein expressed in many tissues and concentrated in the synapses of neurons.
Translation enhancer element of the human amyloid precursor protein gene
The present invention is directed to a DNA element that enhances the translation of the human amyloid precursor protein (APP) gene. The enhancer may be incorporated into expression vectors to enhance recombinant protein production. In addition, the invention is directed to an assay that utilizes vectors containing the translation enhancer element for the purpose of identifying agents that modulate the expression of the human amyloid precursor protein. These agents will ultimately be used to suppress APP expression in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
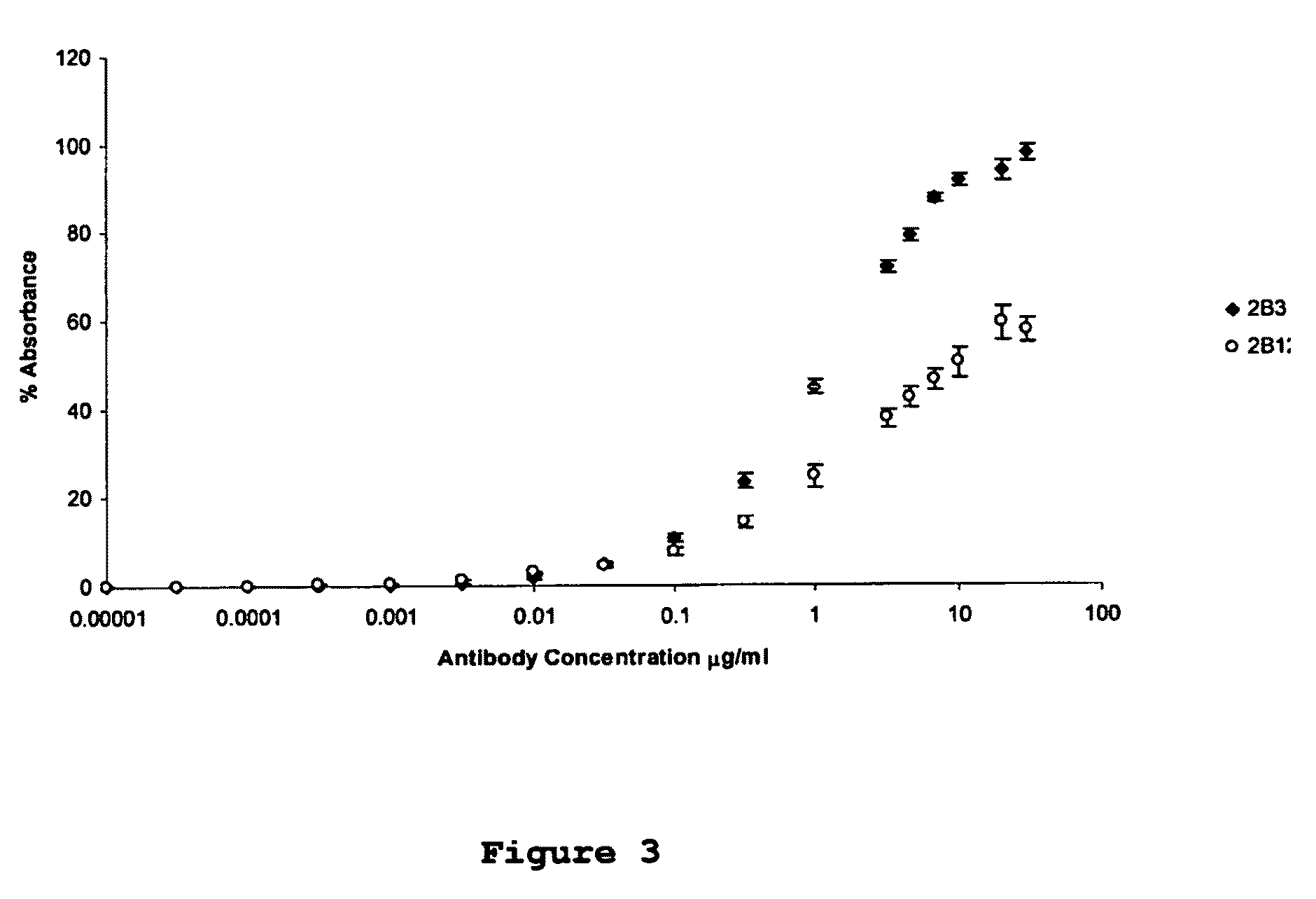
Antibodies specific for toxic amyloid beta protein oligomers
InactiveUS20050124016A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansOligomerMonoclonal antibody
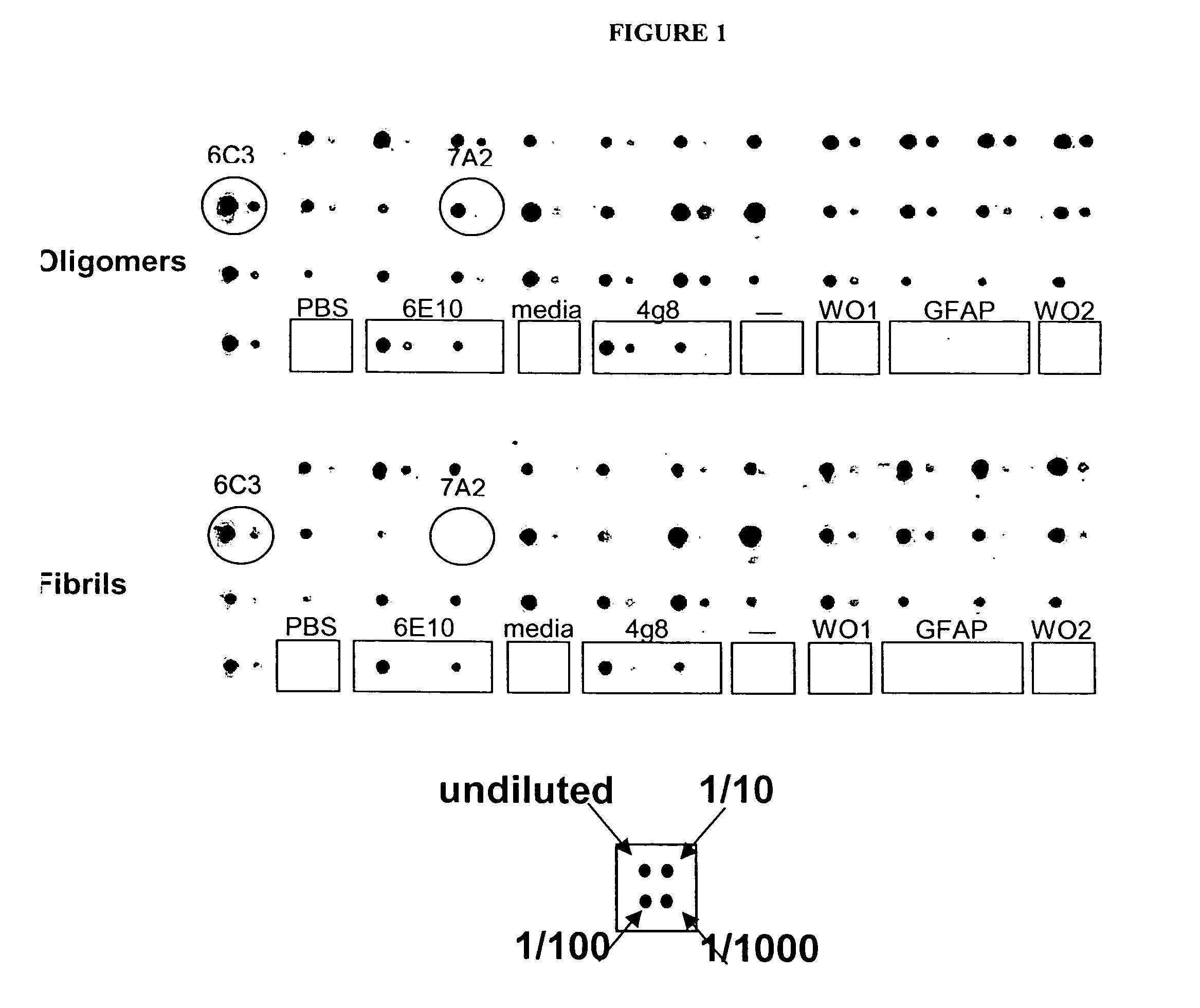
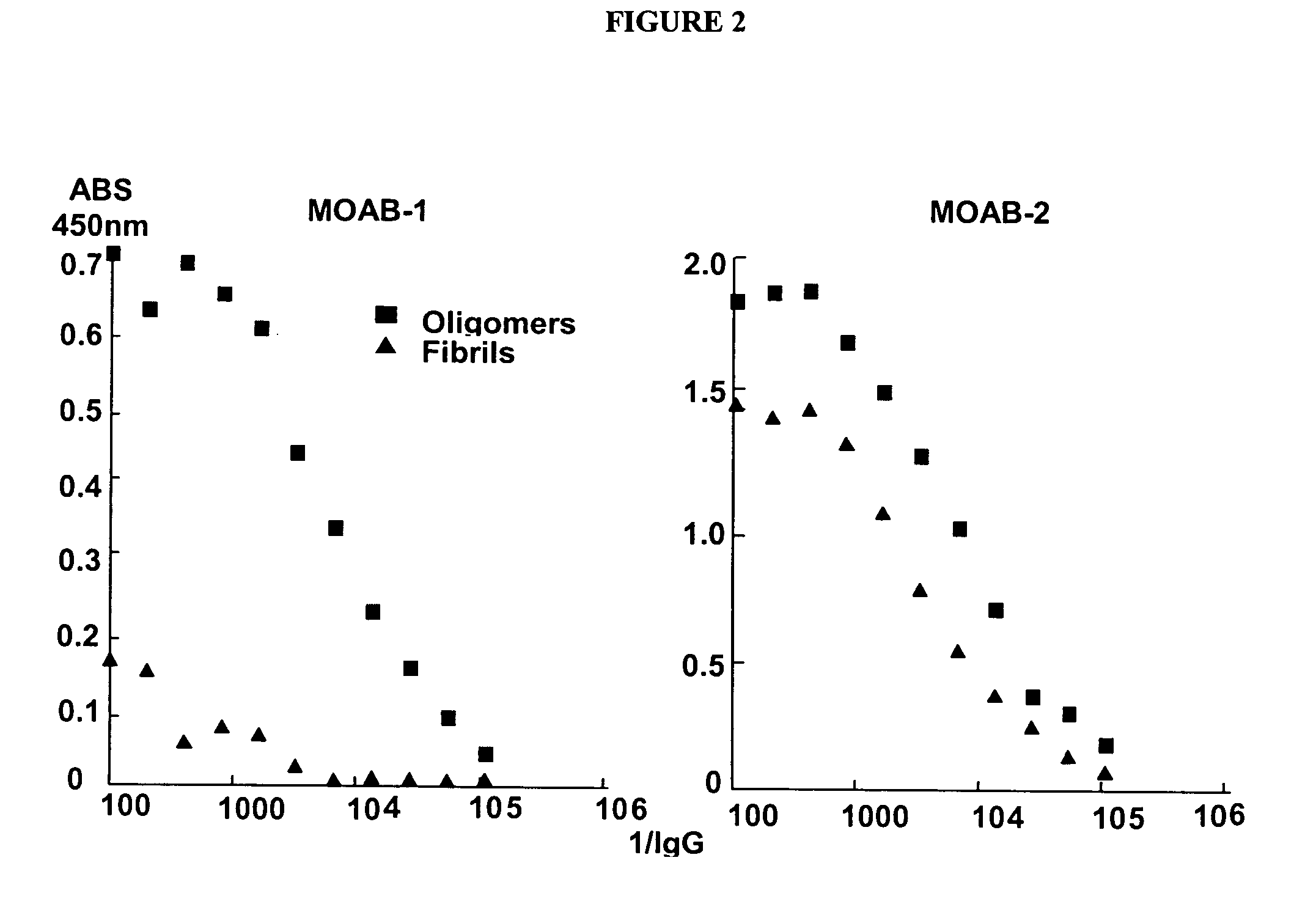
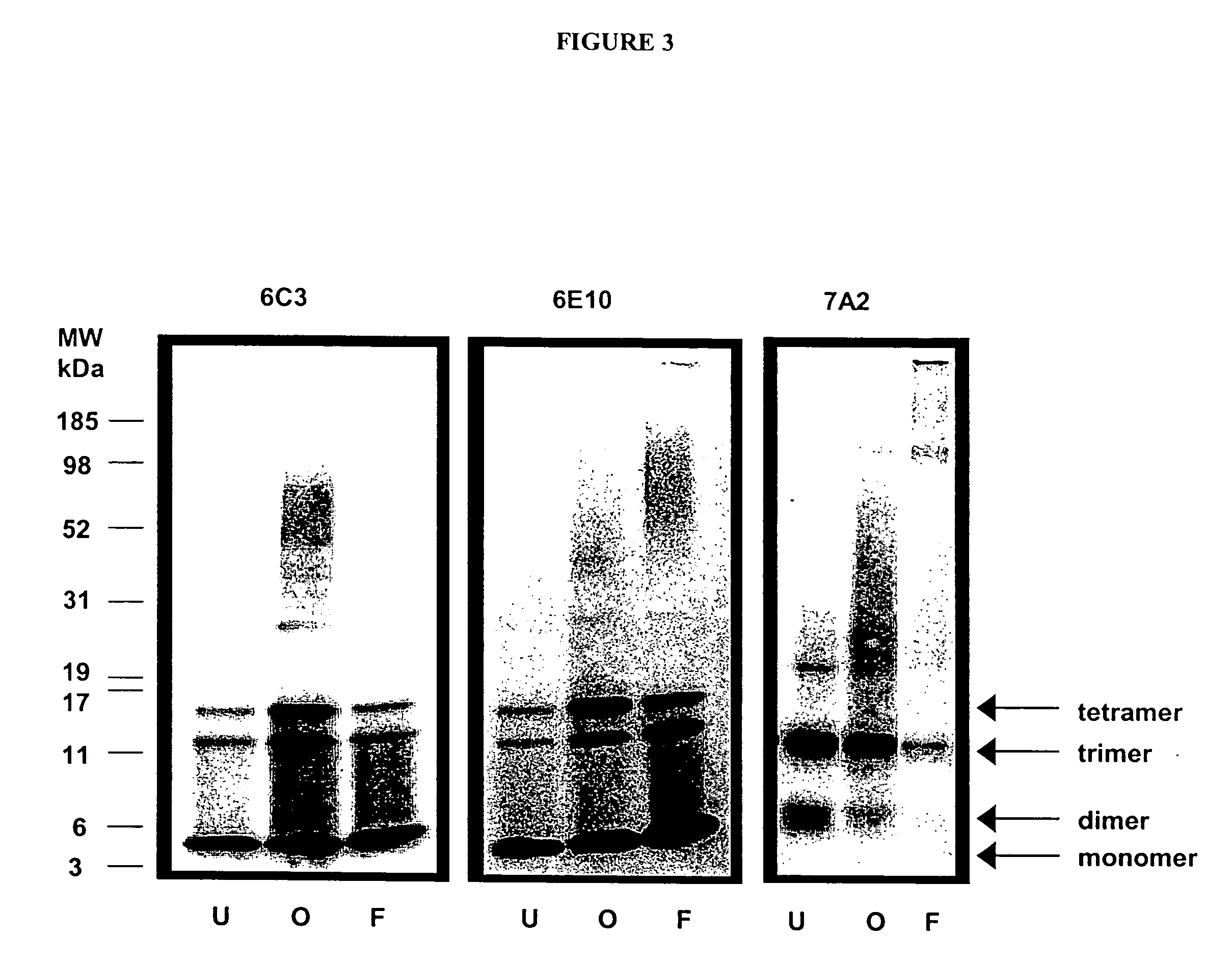
The present invention provides compositions and methods for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease (AD). In particular, the present invention provides monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to soluble, non-fibrillar oligomeric amyloid β protein assemblies proteolytically derived from the transmembrane amyloid precursor protein (APP) while not reacting with fibrillar amyloid β protein assemblies, monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to fibrillar amyloid β protein assemblies that do not react with soluble, non-fibrillar oligomeric amyloid β protein assemblies, and methods of use of these compositions in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, as well as methods to monitor treatment and / or disease progression of AD in patients.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Succinoylamino benzodiazepines as inhibitors of Aβ protein production
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Aminoacetamide acyl guanidines as beta-secretase inhibitors
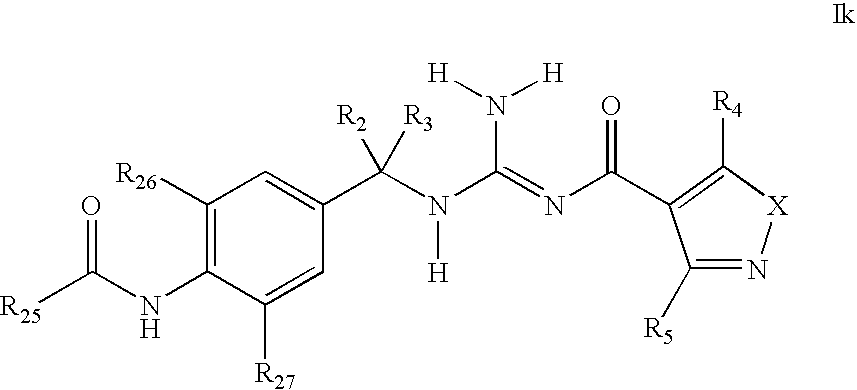
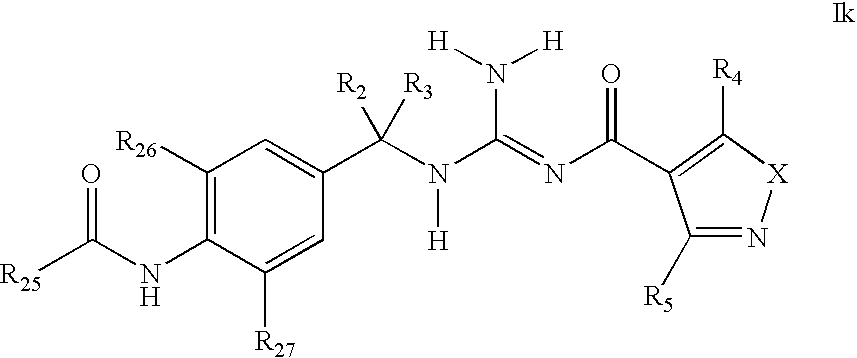
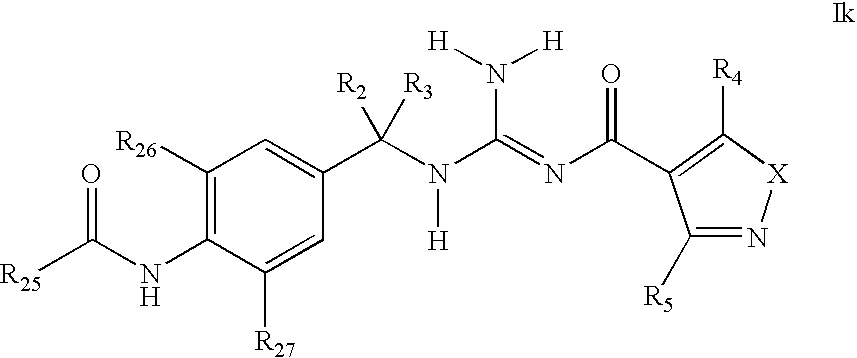
There is provided a series of substituted acyl guanidines of Formula (Ik) or a stereoisomer; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R2, R3, R4, R5, R25, R26 and R27 as defined herein, their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use. These compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide. The present disclosure is directed to compounds useful in the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production, such as Alzheimer's disease and other conditions affected by anti-amyloid activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Receptor for amyloid beta and uses thereof
Compositions and methods for identifying modulators of sortilin are described. The methods are particularly useful for identifying analytes that antagonize sortilin s effect on processing of amyloid precursor protein to Aβ peptide and thus useful for identifying analytes that can be used for treating Alzheimer disease.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
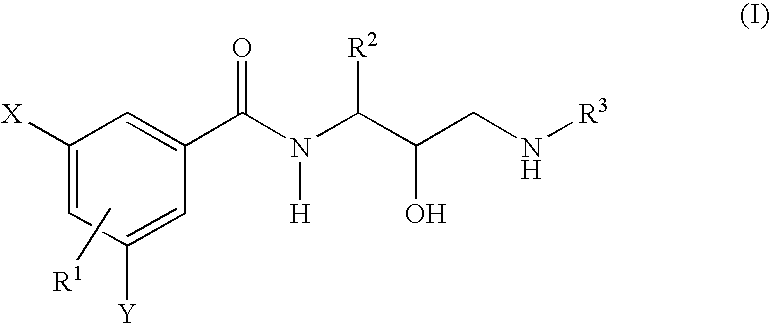
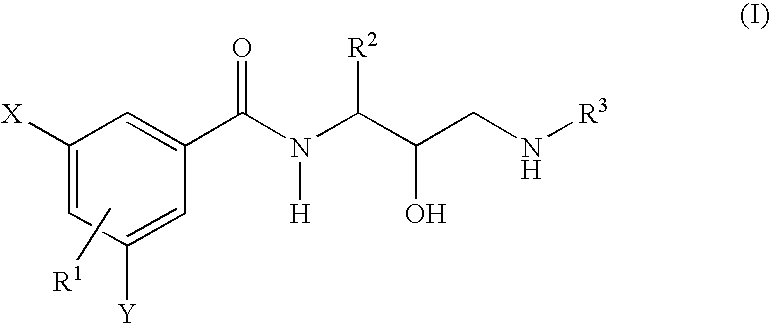
Novel phenylcarboxyamides as beta-secretase inhibitors
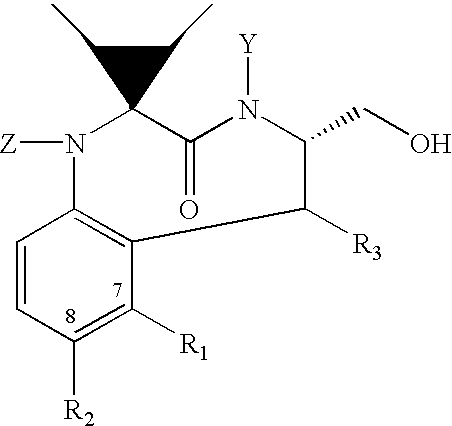
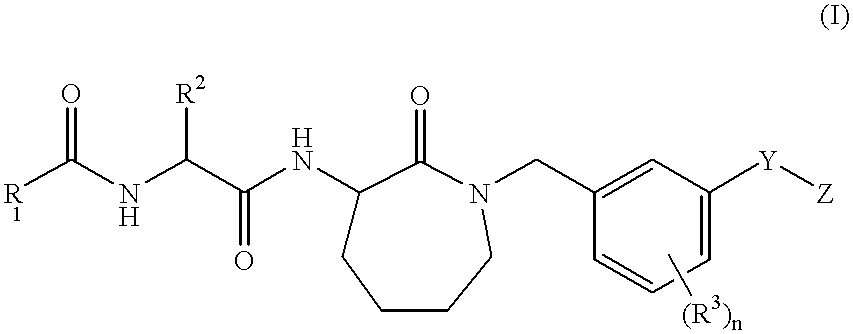
There is provided a series of novel phenylcarboxyamides of Formula (I) or a stereoisomer; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, X and Y as defined herein, their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use. These novel compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide. The present disclosure is directed to compounds useful in the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production, such as Alzheimer's disease and other conditions affected by anti-amyloid activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
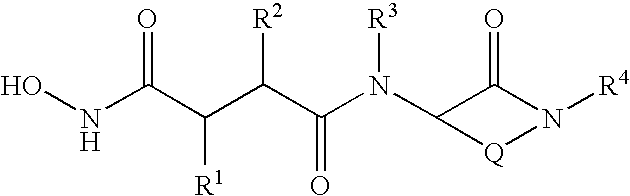
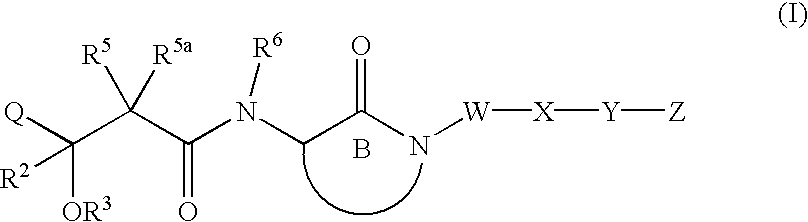
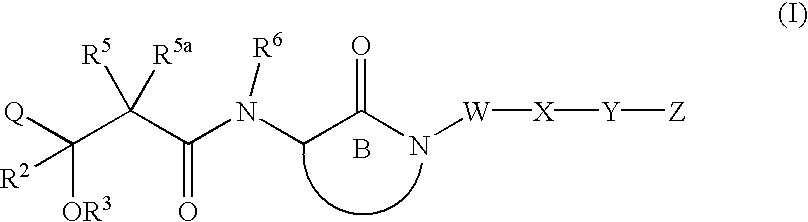
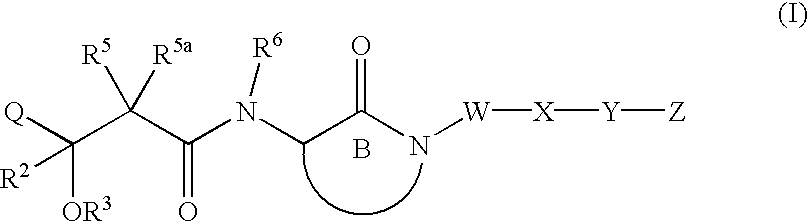
LACTAMS SUBSTITUTED BY CYCLIC SUCCINATES AS INHIBITORS OF Abeta PROTEIN PRODUCTION
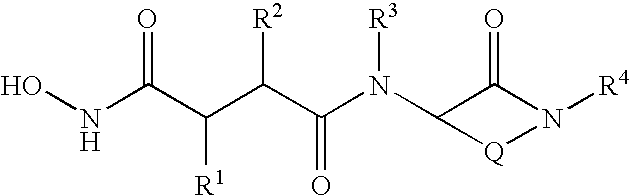
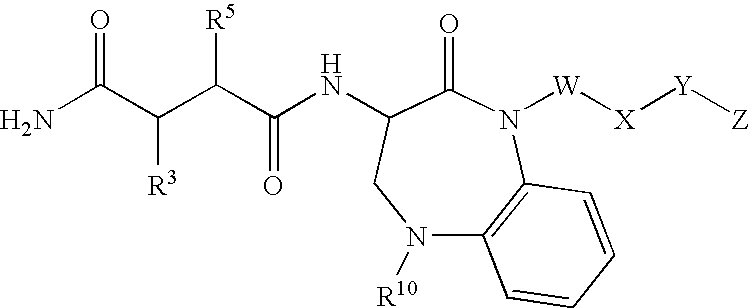
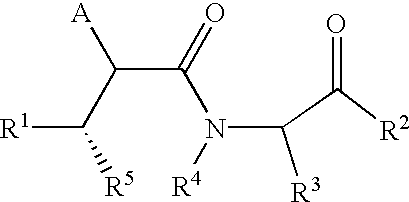
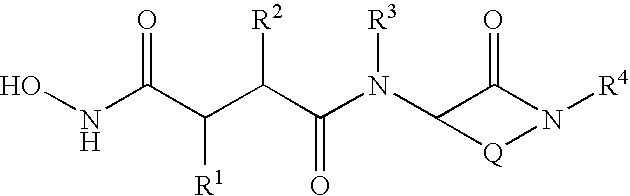
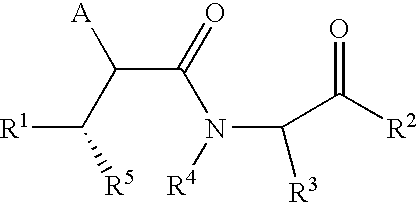
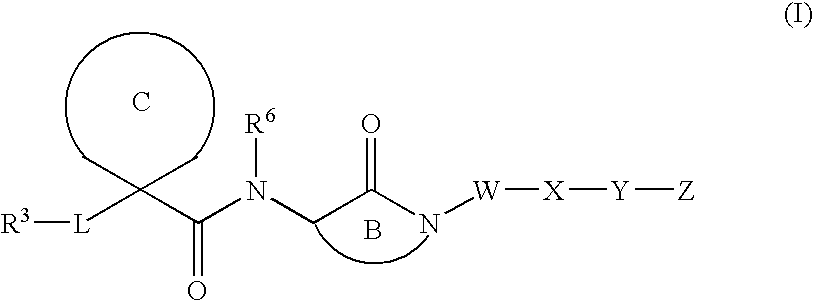
This invention relates to novel lactams having the Formula (I):to their pharmaceutical compositions and to their methods of use. These novel compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide, thereby acting to prevent the formation of neurological deposits of amyloid protein. More particularly, the present invention relates to the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production such as Alzheimer's disease and Down's Syndrome.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Reagents and methods for identification of binding agents
InactiveUS20050221391A1Reduce the binding forceCompound screeningNervous disorderThreonineProtein Fragment
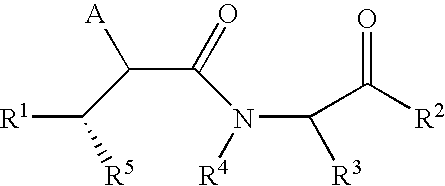
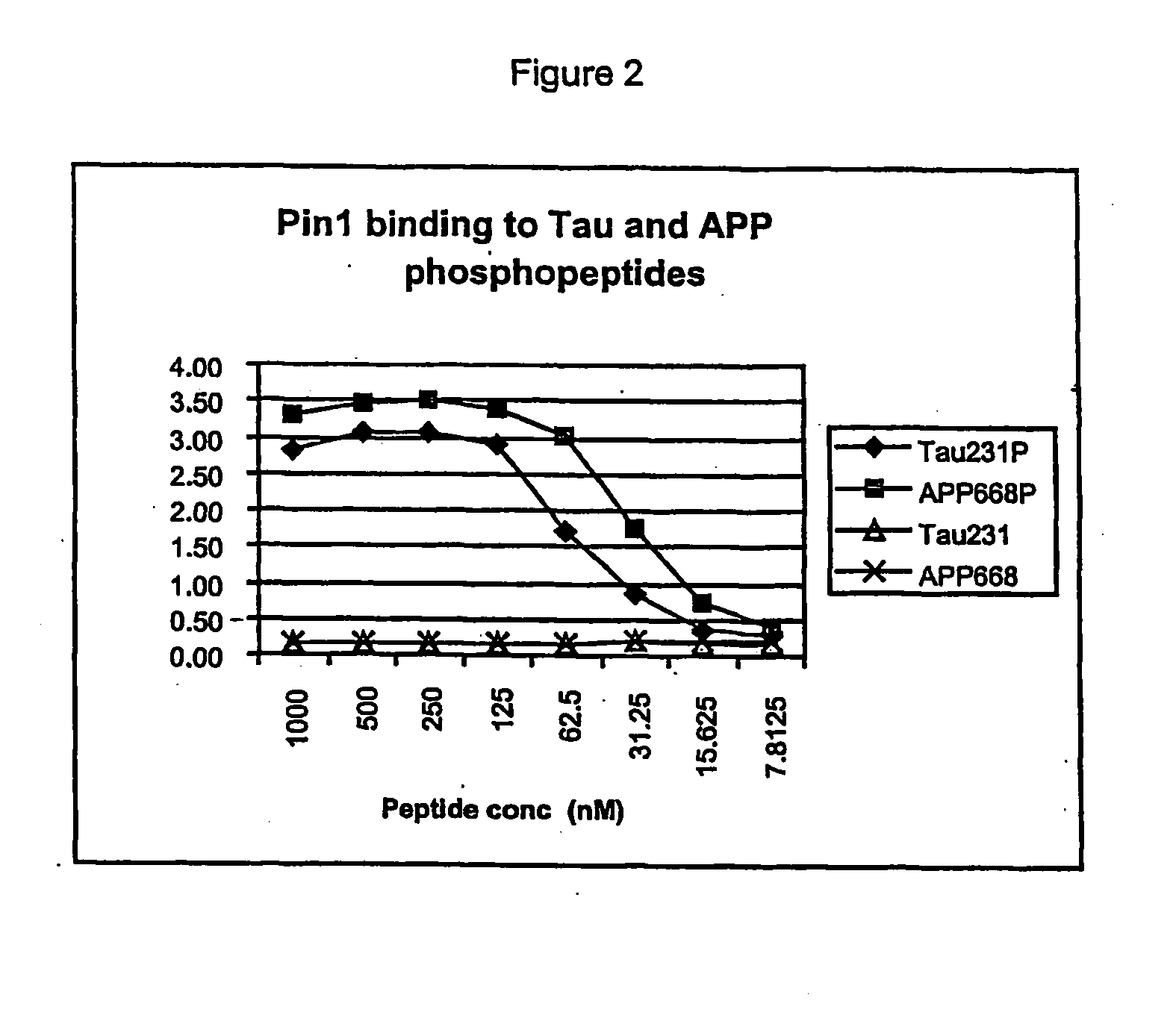
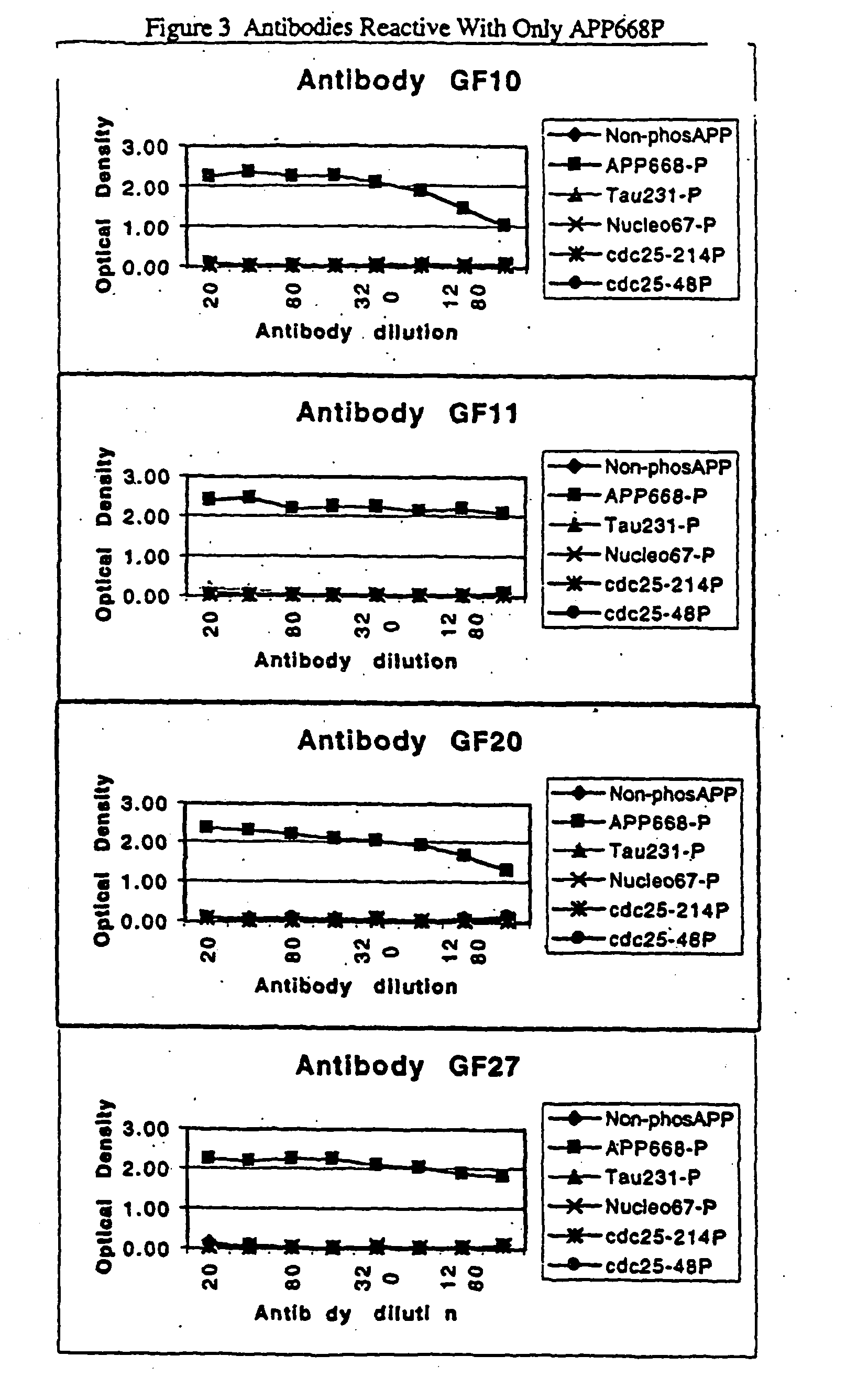
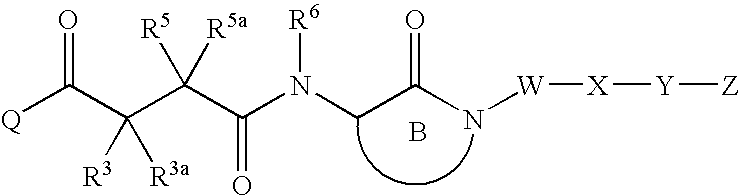
A method for identifying a desired binding agent that interferes with the interaction between a protein, protein fragment, polypeptide or a peptide and a binding surrogate. The method comprises combining the protein, protein fragment, polypeptide or peptide, the binding surrogate and a binding agent. Detecting a decrease in the interaction between the protein, protein fragment, polypeptide or peptide from the binding surrogate indicates that the binding agent interferes with the interaction. Proteins useful in the method include the tau protein phosphorylated at threonine (231), the Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) phosphorylated at threonine (668 and cdc25 phosphorylated at threonine (48). Compounds identified by the method are useful in the treatment of Alzheimers' disease and cancer.
Owner:MOLECULAR GERIATRICS
Tetrazolylpropionamides as inhibitors of Abeta protein production
This invention relates to novel tetrazolyl-propionamides in which the amide group comprises an aminoazepinone, and related structures, of Formula (I): or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug forms thereof, their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use. These novel compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide, thereby resulting in prevention and treatment of the neuropathology associated with production of Aβ-peptide. More particularly, the present invention relates to the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production such as Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Treatment of conditions associated with amyloid processing using PKC activators
InactiveUS20030050302A1Increase secretionHigh selectivityBiocideAnimal repellantsBiological activationAmyloid aggregation
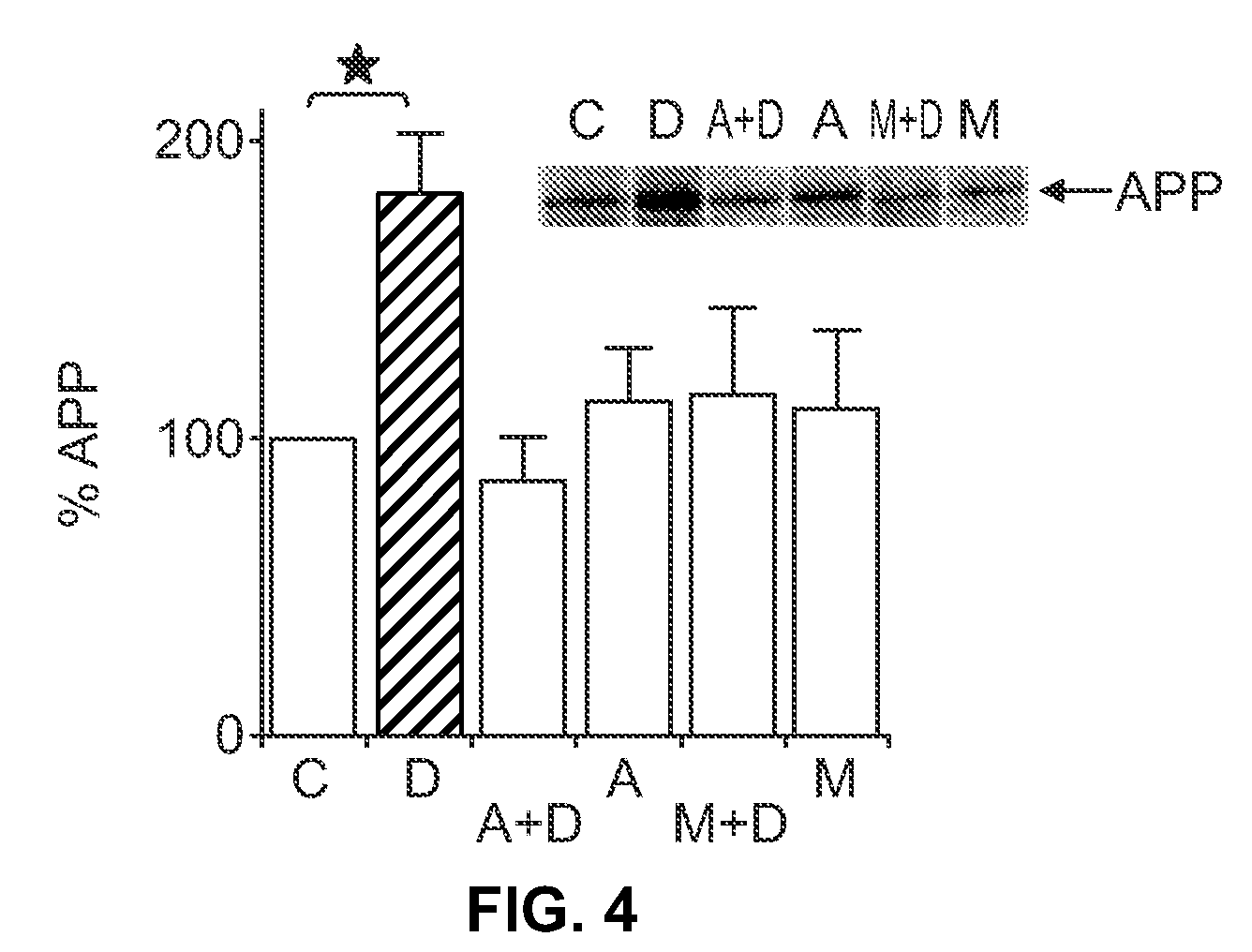
A method for increasing the generation of non-amyloidogenic soluble APP comprising activation of protein kinase C (PKC) by administering an effective amount of at least one PKC activator. Also provided is a method for altering conditions associated with amyloid processing in order to enhance an alpha-secretase pathway to generate soluble alpha-amyloid precursor protein (alpha-APP) so as to prevent beta-amyloid aggregation comprising administering an effective amount of a benzolactam.
Owner:NEUROLOGICS
Heterocyclic derivatives
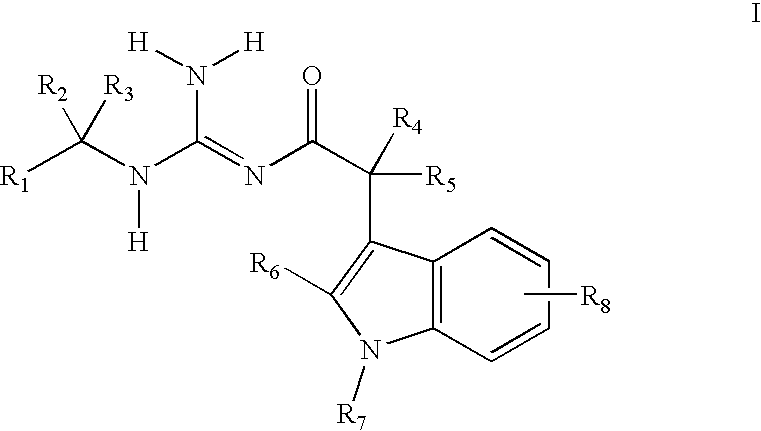
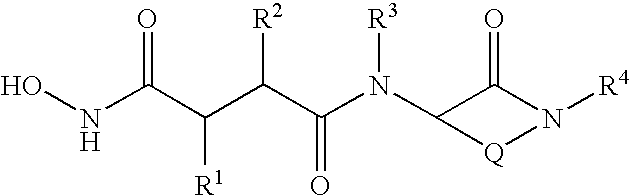
The object of the present invention is to provide soluble β-amyloid precursor protein secretory stimulators, which are effective in treating neurodegenerative diseases as well as cerebrovascular disorder-induced neuronopathy. More specifically, the present invention provides a novel compound of the following Formula (I) or a salt or prodrug thereof: [wherein R1 and R2 each represent a hydrogen atom or a lower alkyl group, etc., Ar1 and the ring B each represent an optionally substituted aromatic group, the ring A represents an optionally substituted benzene ring, the ring C represents an optionally substituted 4- to 8-membered ring which may further be condensed with an optionally substituted ring, X represents CH or N, and Y represents CH or N].
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Assays using amyloid precursor proteins with modified beta-secretase cleavage sites to monitor beta-secretase activity
InactiveUS7196163B2More productiveOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeAmyloid
Provided are methods of identifying inhibitors of β-secretase that employ modified β-secretase substrates. The modified β-secretase substrates have β-secretase cleavage sites that are altered from wild type. The amino acid sequences of the altered β-secretase cleavage sites contain different amino acids in at least one of the positions P2-P1-P1′-P2′ of the β-secretase cleavage site. Many of the modified β-secretase substrates are more efficient substrates for β-secretase than are corresponding substrates having wild-type sequences, that is, these modified substrates are more susceptible to enzymatic breakdown by β-secretase. Recombinant polynucleotide molecules encoding the modified β-secretase substrates are provided. Antibodies that recognize cleavage products of the modified β-secretase substrates are provided. Stable cell lines expressing the modified β-secretase substrates are provided. Transgenic animals expressing the modified β-secretase substrates are provided.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Benzo-1,4-diazepin-2-ones as inhibitors of Abeta protein production
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Testing compounds for effects on synaptophysin in transgenic mice expressing an Alzheimer's disease FAD DNA sequence
InactiveUS7186881B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAnimals/human peptidesSynaptophysinElectroporation
The construction of transgenic animal models of human Alzheimer's disease, and methods of using the models to screen potential Alzhe## disease therapeutics, are described. The models are characterized by pathologies similar to pathologies observed in Alzheimer's disease, based on expression of all three forms of the β-amyloid precursor protein (APP), APP695, APP751, and APP770, as well as various point mutations based on naturally occurring mutations, such as the London and Indiana familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD) mutations at amino acid 717, predicted mutations in the APP gene, and truncated forms of APP that contain the Aβ region. Animal cells can be isolated from the transgenic animals or prepared using the same constructs with standard techniques such as lipofection or electroporation. The transgenic animals, or animal cells, are used to screen for compounds altering the pathological course of Alzheimer's disease as measured by their effect on the amount of APP, β-amyloid peptide, and numerous other Alzheimer's disease markers in the animals, the neuropathology of the animals, as well as by behavioral alterations in the animals.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
Lactams substituted by cyclic succinates as inhibitors of A-β protein production
This invention relates to novel lactams having the Formula (I): to their pharmaceutical compositions and to their methods of use. These novel compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide, thereby acting to prevent the formation of neurological deposits of amyloid protein. More particularly, the present invention relates to the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production such as Alzheimer's disease and Down's Syndrome.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Methods for the identification of agents that modulate the structure and processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein
The present invention provides methods for the screening and identification of agents from a large library of molecular structures that can alter the cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (AP). Agents identified by the methods of the present invention that modify the cleavage of APP can be used in the treatment and prevention of Alzheimer's disease. The methods select for and identify effector agents that bind to APP causing a structural change in the structure of APP in such a way that the efficiency of the cleavage of a secretase is modulated. Further, the methods are carried out in an in vivo system that provides for physiological conditions similar or identical to conditions for APP processing. Agents can be selected for their ability to cause a decrease in the amount of B-secretase or β-secretase cleavage of APP, or for an increase in a-secretase cleavage of APP. The agents can be, particularly peptide agents, can be converted into a peptidominetic, an isosteric replacement compound, a D-amino acid analog, or non-peptidyl compound for treating Alzheimer's disease or any other amyloid related or prion related disease. The agents or derivatives thereof can be formulated for intravenous, parenteral, topical, sustained release, intranasal, or inhalation use.
Owner:ICOGENEX CORP
eAPP AND DERIVATIVES FOR TREATMENT OF ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
InactiveUS20100099609A1Lower Level RequirementsNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNetrinMutant
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
Neuronal differentiation-inducing peptide and use thereof
A neuronal differentiation inducer provided by the present invention contains an artificially synthesized peptide which includes an amino acid sequence constituting a signal peptide in amyloid precursor protein (APP), or a partial sequence of the amino acid sequence constituting this signal peptide.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD
Agents useful for reducing amyloid precursor protein and treating demantia and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides compounds and methods of administering compounds to a subject that can reduce βAPP production and that is not toxic in a wide range of dosages. The present invention also provides non-carbamate compounds and methods of administering such compounds to a subject that can reduce βAPP production and that is not tocix in a wide range of dosages. It has been discovered that either the racemic or enantiomerically pure non-carbamate compounds can be used to decrease βAPP production.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH THE +1
Lactams as inhibitors of A-beta protein production
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
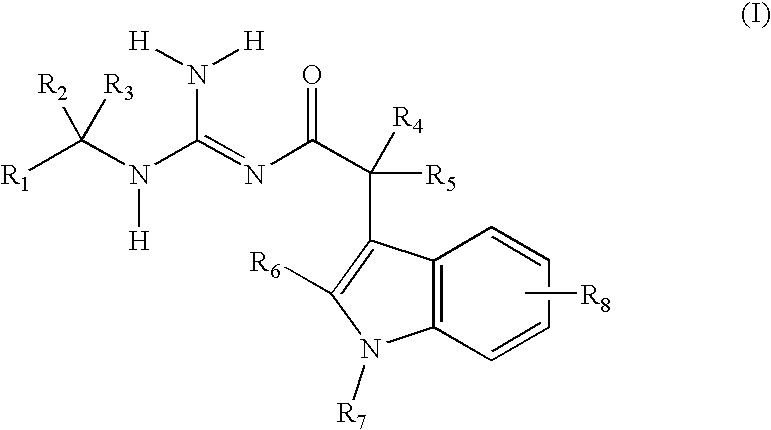
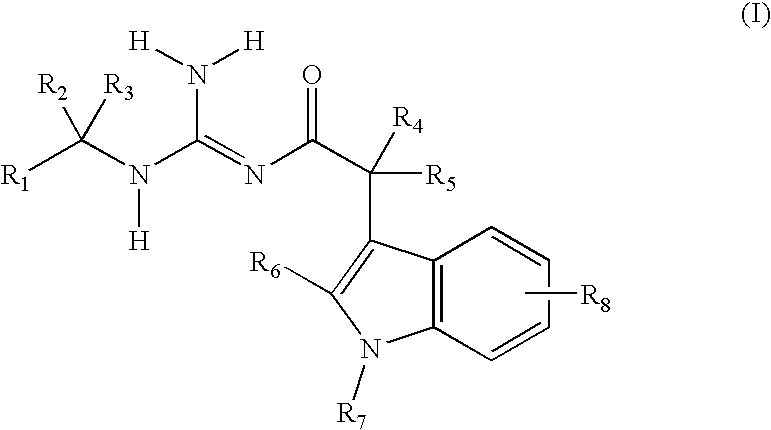
Indole acetic acid acyl guanidines as beta-secretase inhibitors
There is provided a series of substituted acyl guanidines of Formula (I) or a stereoisomer; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, and R8 as defined herein, their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use. These compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide. The present disclosure is directed to compounds useful in the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production, such as Alzheimer's disease and other conditions affected by anti-amyloid activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Monoclonal antibody for APP
InactiveUS8337848B2Reduce accumulationReduce releaseAnimal cellsNervous disorderMonoclonal antibodyΒ amyloid
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CARDIFF CONSULTANTS LTD
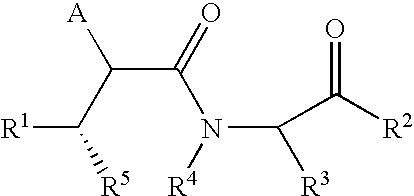
Succinoylamino lactams as inhibitors of Aβ protein production
This invention relates to novel lactams having drug and bio-affecting properties, their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use. These novel compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide, thereby acting to prevent the formation of neurological deposits of amyloid protein. More particularly, the present invention relates to the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production such as Alzheimer's disease and Down's Syndrome.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Hydroxyalkanoylaminolactams and related structures as inhibitors of Aβ protein production
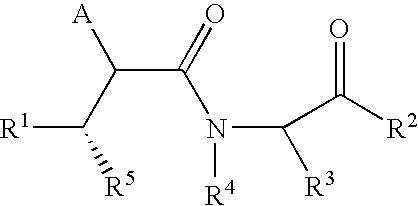
This invention relates to novel lactams having the formula (I): to their pharmaceutical compositions and to their methods of use. These novel compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide, thereby acting to prevent the formation of neurological deposits of amyloid protein. More particularly, the present invention relates to the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production such as Alzheimer's disease and Down's Syndrome.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Cell growth-promoting peptide and use thereof
ActiveUS20130079273A1Improve stabilityReduce usagePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSenses disorderSequence signalBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The pharmaceutical composition includes at least one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and an active ingredient including an artificially synthesized peptide includes: (A) an amino acid sequence constituting a cell-penetrating peptide and (B) an amino acid sequence constituting the signal peptide in amyloid precursor protein (APP) or an N-terminal partial amino acid sequence or C-terminal partial amino acid sequence from the amino acid sequence constituting that signal peptide.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD
Substituted lactams as inhibitors of Aβ protein production
This invention relates to novel lactams of Formula (I): having drug and bio-affecting properties, their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use. These novel compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide, thereby acting to prevent the formation of neurological deposits of amyloid protein. More particularly, the present invention relates to the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production such as Alzheimer's disease and Down's Syndrome.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Methods for Inhibiting Amyloid Precursor Protein and Beta-Amyloid Production and Accumulation
InactiveUS20090239888A1Ameliorating neurological disorderReduced activityBiocideNervous disorderDiseasePhysiology
Compositions and uses of mGluR5 antagonists for the treatment and inhibition of amyloid precursor protein (APP), Aβ protein, and APP proteolytic products in Alzheimer's disease, Fragile X Syndrome, autism, and Down's Syndrome are provided. The invention provides methods for diagnosing Fragile X Syndrome via the assessment of Aβ1-42 levels in blood plasma.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cyclic malonamides as inhibitors of A-beta protein production
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
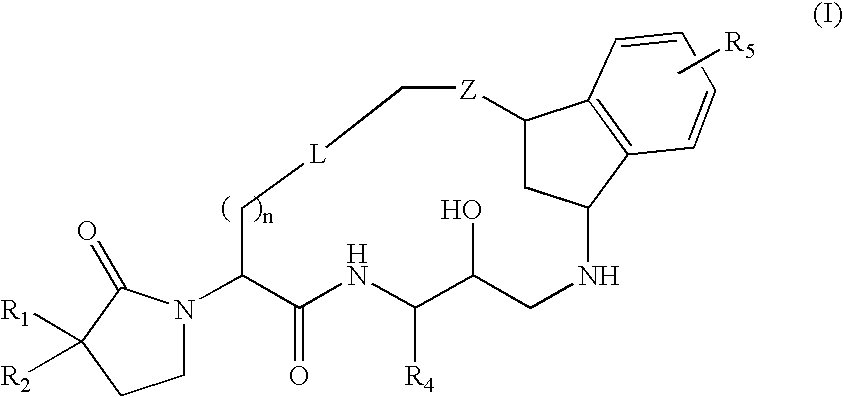
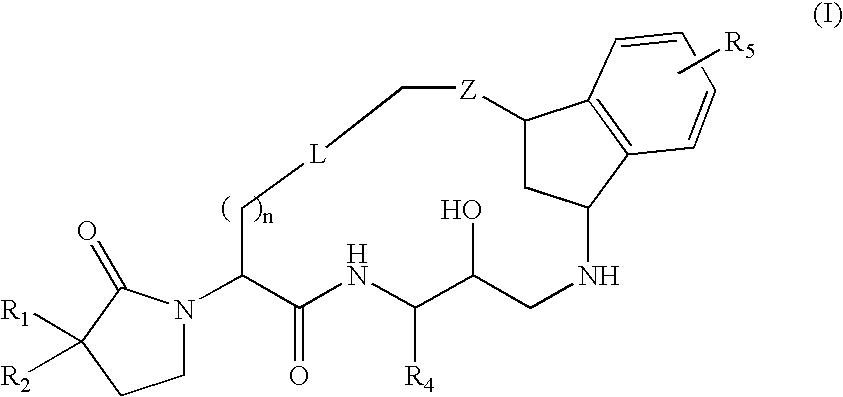
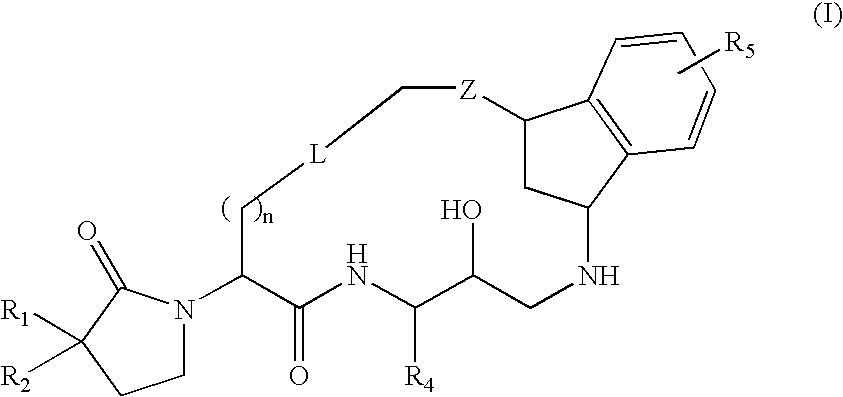
Macrocyclic diaminopropanes as beta-secretase inhibitors
There is provided a series of novel macrocyclic diaminopropanes of Formula (I) or a stereoisomer; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R4, R5, n, L, Z, and as defined herein, their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use. These novel compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide. The present disclosure is directed to compounds useful in the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production, such as Alzheimer's disease and other conditions affected by anti-amyloid activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
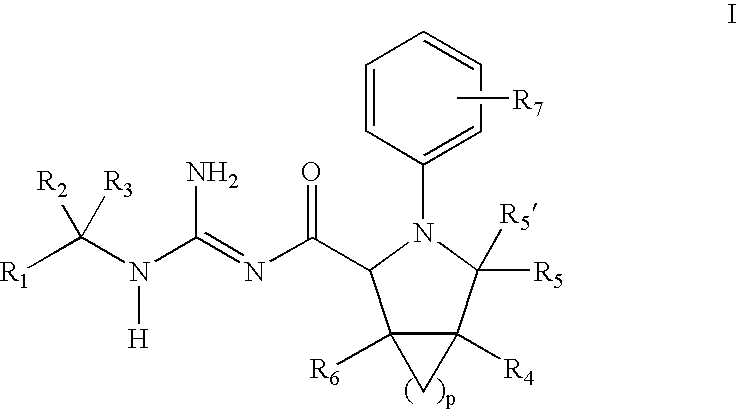
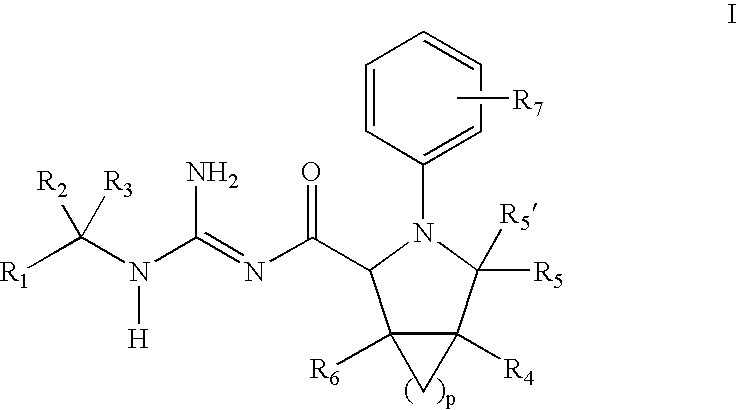
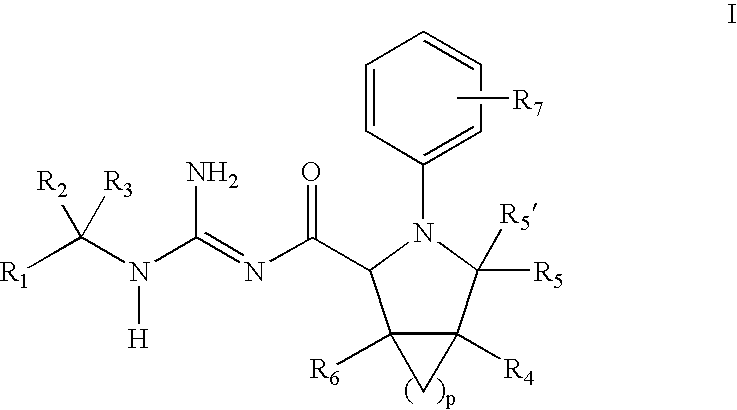
N-Aryl Pyrrolidine Derivatives as Beta-Secretase Inhibitors
There is provided a series of substituted N-aryl pyrrolidine derivatives of Formula (I)or a stereoisomer; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R5′, R6, R7, and p as defined herein, their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use. These compounds inhibit the processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase and, more specifically, inhibit the production of Aβ-peptide. The present disclosure is directed to compounds useful in the treatment of neurological disorders related to β-amyloid production, such as Alzheimer's disease and other conditions affected by anti-amyloid activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com