Peptide fragments having cell death inhibitory activity
a technology of inhibitory activity and peptide fragments, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, peptide sources, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to afford sufficient clinical application, inability to control causal substances and factors that have been established, and inability to inhibit cell death
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
(Assay)
[0056]To 1 ml Dami cells (described in Greenberg S. M. et al., Blood, vol. 72, p. 1968–1977 (1988); 1×106 cells / dish / 3 ml), which can be subcultured in serum free medium SFO3 (manufactured by Sanko Jun-yaku K. K.) containing 0.05 μM 2ME and 0.1% BSA, was added 2 ml 1:2:2 mixed medium (SA medium) of RPMI 1640 / D-MEM / F-12. The cells were cultured for three days and recovered for assay. The cells were washed twice with 50% PBS / SA / 0.03% HSA (manufactured by SIGMA) and suspended in the same medium at 3×104 cells / ml. The cell suspension was added to a 96-well plate in each 200 μl for wells for sample addition or in each 100 μl for wells for serial dilution. To the wells for sample addition was added 2 μl assay sample and, after stirring, a serial dilution was made with the wells containing 100 μl cell suspension. The plate was incubated at 37° C. in CO2 incubator for 4 to 5 days followed by estimation.
[0057]For estimation, it was examined to what folds of dilution of tested samples ...
example 2
(Purification of Components Having Cell Death-Inhibitory Activity)
[0058]In the following purification procedure, the activity was estimated in accordance with the assay procedure described in Example 1.
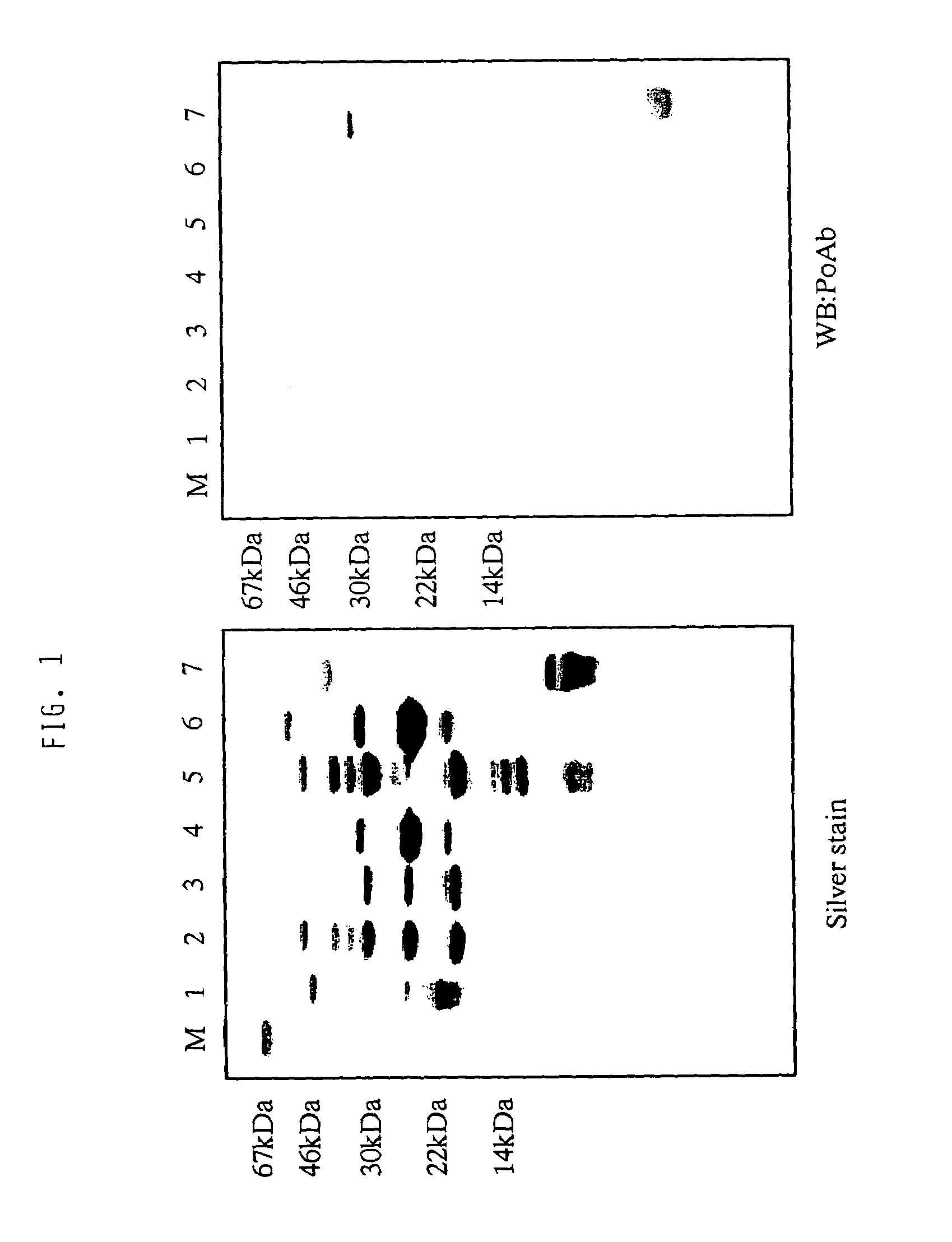
[0059]The cell death-inhibitory activity in plasma shows heparin-binding activity. Thus, fractionation with a heparin column was initially performed for collecting heparin-binding fractions from plasma. Using human plasma as starting material, heparin-binding proteins in plasma were adsorbed to a heparin column (Heparin Sepharose: manufactured by Pharmacia). After washing with 0.3 M sodium chloride, the adsorbed fractions were eluted with 2 M sodium chloride. Although most of the cell death-inhibitory activity of interest was recovered in the fractions after washing with 0.3 M sodium chloride, the fractions eluted with 2 M sodium chloride were used for purification of active substance.
[0060]For crude fractionation of the heparin-bound cell death-inhibitory activity, fractionation with...
example 3
(Analysis of N-Terminal Sequence of Active Components)
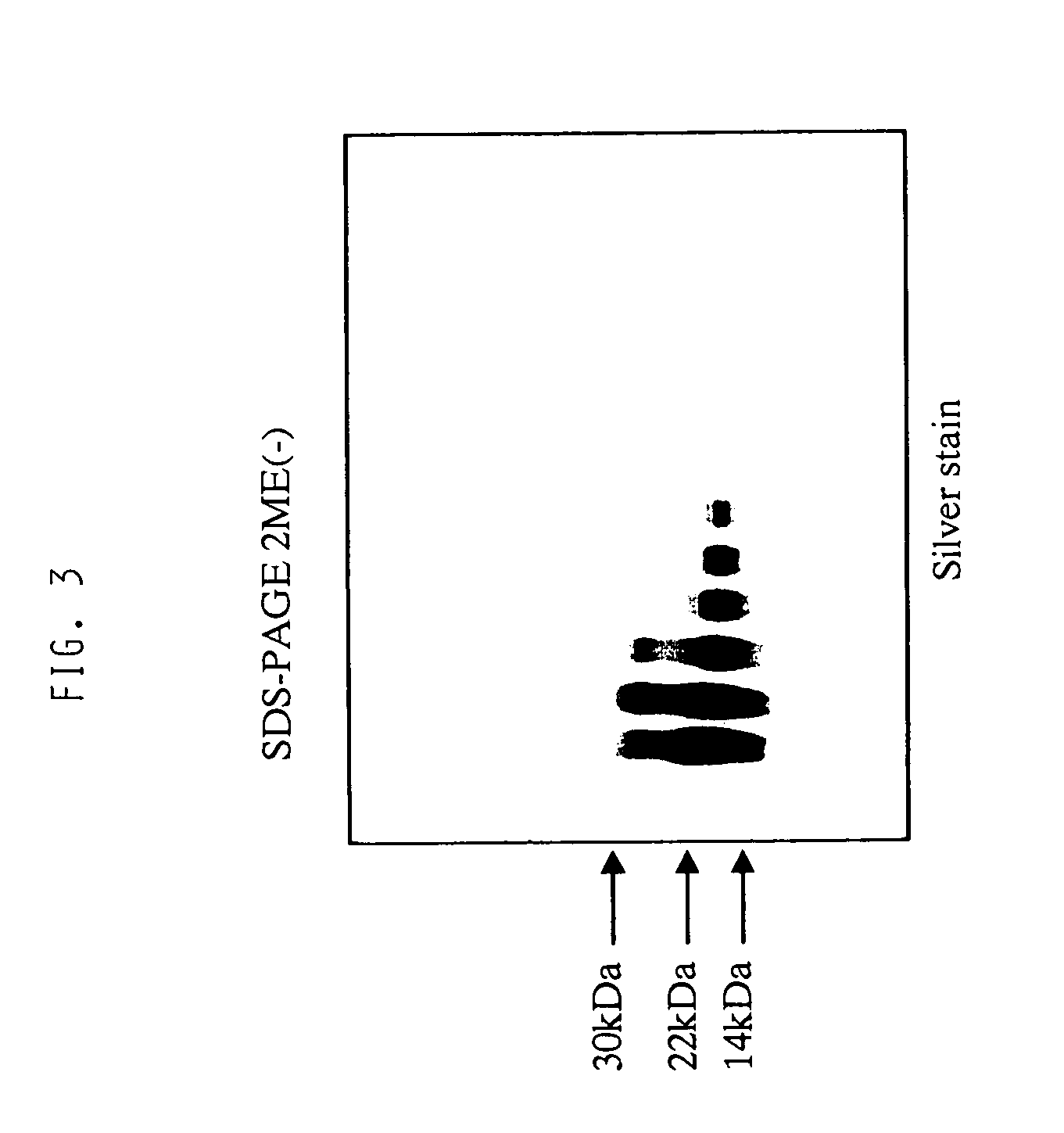
[0071]Amino acid sequence analysis with a gas phase sequencer revealed that the active components of the present invention consisted of a peptide comprising the amino acid sequence: Lys Arg Cys Ile Asn Gln Leu Leu Cys Lys Leu Pro Thr Asp Ser Glu Leu Ala Pro Arg Ser Xaa Cys Cys His Cys Arg His Leu (SEQ ID NO: 1) and a peptide comprising the amino acid sequence: Thr Gly Ser Ala Ile Thr Xaa Gln Cys Lys Glu Asn Leu Pro Ser Leu Cys Ser Xaa Gln Gly Leu Arg Ala Glu Glu Asn Ile, wherein Xaa is selenocysteine (SEQ ID NO: 2). A ratio of these peptides was in a range of from 1:1 to 2:1 as estimated from an amount of amino acid residues recovered while sequencing of this fraction. A recovery of amino acid residues from other proteins than these two peptides was 5% or less. These two peptides were separated by gel filtration chromatography and C4 reverse phase HPLC under reduced condition to suggest the presence of molecular species formed by...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| isoelectric points | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com