Apparatus and method for forming silica glass elements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029]An embodiment of the invention will be described below by referring to the drawings.
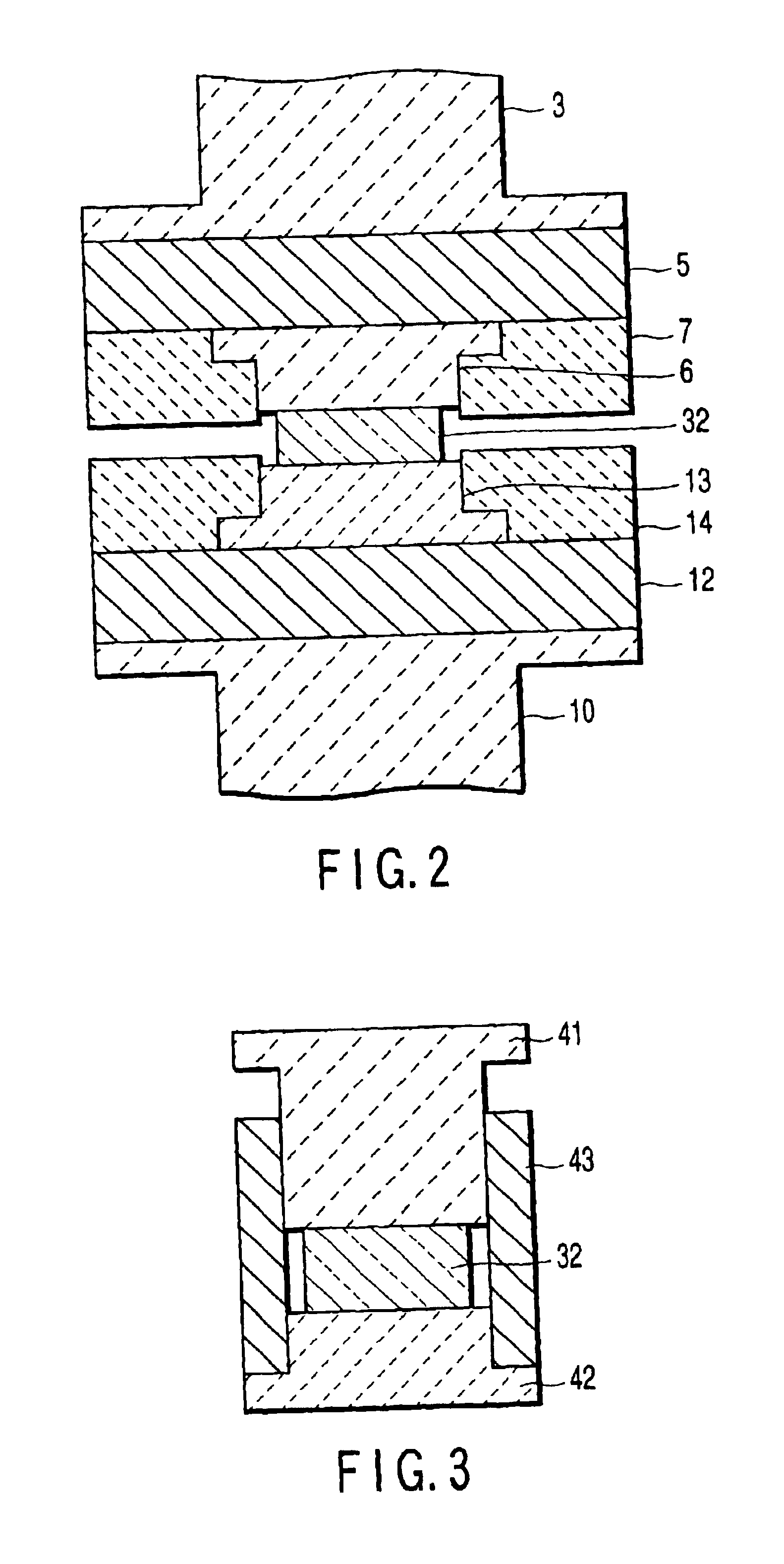
[0030]An example of an apparatus for forming a silica glass element related to the invention is shown in FIG. 1 (a general view) and FIG. 2 (a partial enlarged view). In this apparatus, a fixed shaft 2 extends downward from the upper part of a frame 1 and at the bottom end of the fixed shaft 2 is attached a top die assembly 4 by a bolt, etc. (not shown) through a heat insulating cylinder 3 made of ceramics. The top die assembly 4 comprises a top die plate 5 made of metal or ceramic carbon, a top core mold 6 for forming a figure of a silica glass element to be formed and made of vitrified carbon and a top mold die 7 surrounding a periphery of the top core mold and made of isotropic carbon. The top mold die 7 and top core mold 6 are attached to top die plate 5, and the top die plate 5 is attached to a heat insulating cylinder 3.
[0031]A drive unit 8, such as a screw jack, which uses a servomotor 8...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Torque | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com