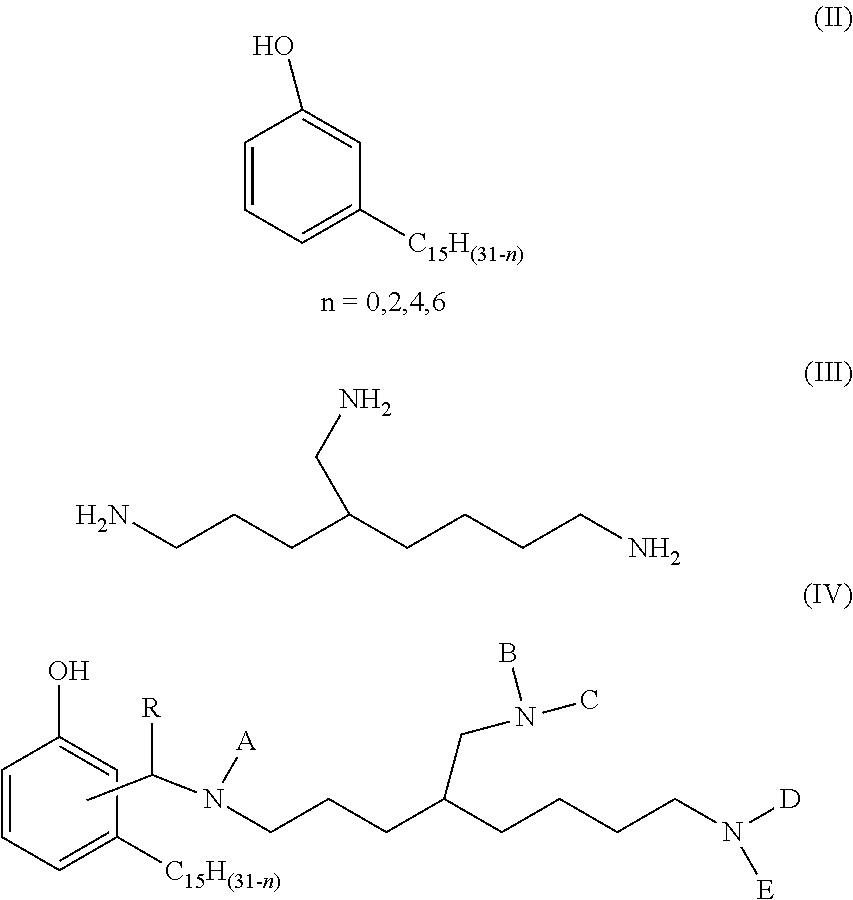
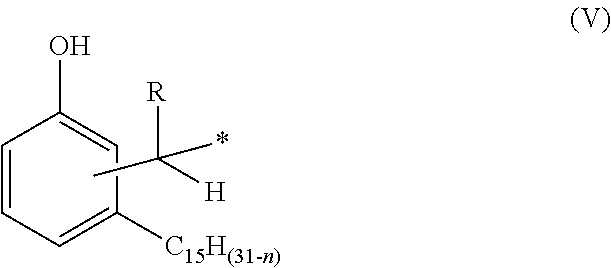
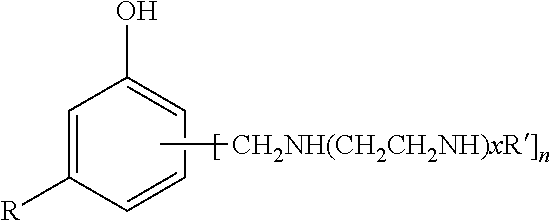Phenalkamine epoxy curing agents and epoxy resin compositions containing the same
a technology of epoxy resin and curing agent, which is applied in the direction of adhesive types, coatings, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to easily control the molecular weight distribution of these products, and achieve the effects of high gloss and clarity, low viscosity, and faster amine-epoxy reaction ra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
of the Phenalkamine of Triaminononane with Molar Ratio of Cardanol:Triaminononane:Formaldehyde (1:1:1)
[0053]A 3-neck 1 L round bottom flask equipped with N2 inlet, addition funnel and temperature probe was charged with cardanol (298 g, 1.0 mole) and triaminononane (TAN) (173.3 g, 1.0 mole). The mixture was heated to 80° C. A 37% solution of formaldehyde (81 g, 37 wt. %, 30 g, 1.0 mole) was added to maintain a reaction temperature of 80-90° C. After the addition the mixture was kept at 90-95° C. for 1 h. Water was distilled at 120° C. and the product was obtained as a light brown liquid.
example 2
of the Phenalkamine of Triaminononane with Molar Ratio of Cardanol:Triaminononane:Formaldehyde (1:1.3:1.3)
[0054]A 3-neck 1 L round bottom flask equipped with N2 inlet, addition funnel and temperature probe was charged with cardanol (298 g, 1.0 mole) and TAN (225.29 g, 1.30 mole). The mixture was heated to 80° C. A 37% solution of formaldehyde (105.40 g, 37 wt. %, 39 g, 1.3 mole) was added to maintain a reaction temperature of 80-90° C. After the addition the mixture was kept at 90-95° C. for 1 h. Water was distilled at 120° C. and the product was obtained as a light brown liquid.
examples 1a-3b
[0055]Curing agent mixtures were prepared by mixing the components given in the above examples. with the epoxy component of standard bisphenol-A based epoxy resin of (Epon 828, DER 331 type), EEW 190, unless specified otherwise. The formulations used are defined in Table 1. They were then mixed employing a stoichiometric level of 1:1 (amine:epoxy equivalents). The curing agents were tested neat and at 80% solids in a combination of xylene:n-butanol (3:1 by weight). Comparative Example (3) is a commercially available Phenalkamine Curing Agent Derived from Ethylenediamine [EDA] and was Used as a Reference.
TABLE 1Clear Coat Formulation Screening - TAN PhenalkaminesEx 1AEx2AEx3AEx 1BEx2BEx 3BPropertySolvent freeSolvent basedLiquid BADGE Epoxyg100100100100100100resin (EEW190)Curing agentg49——49——[Ex 1] (AHEW92)Curing agentg—51——51—[Ex 2] (AHEW97)Commercial [EDA]g——65.6——65.6phenalkamine[Ex 3] (AHEW125)Xylene / n-butanolg—0012.312.716.4(3:1 by wt)Total solids%10010010092.392.290.9Total mixg...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com