Immunomodulatory fusion proteins and uses thereof
a technology of immunomodulatory fusion and fusion proteins, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, genetically modified cells, immunological disorders, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete remission, inability to fully remit, and inability to fully remit, and achieve the effect of increasing immune cell activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
CD200R-CD28 Fusion Protein Constructions
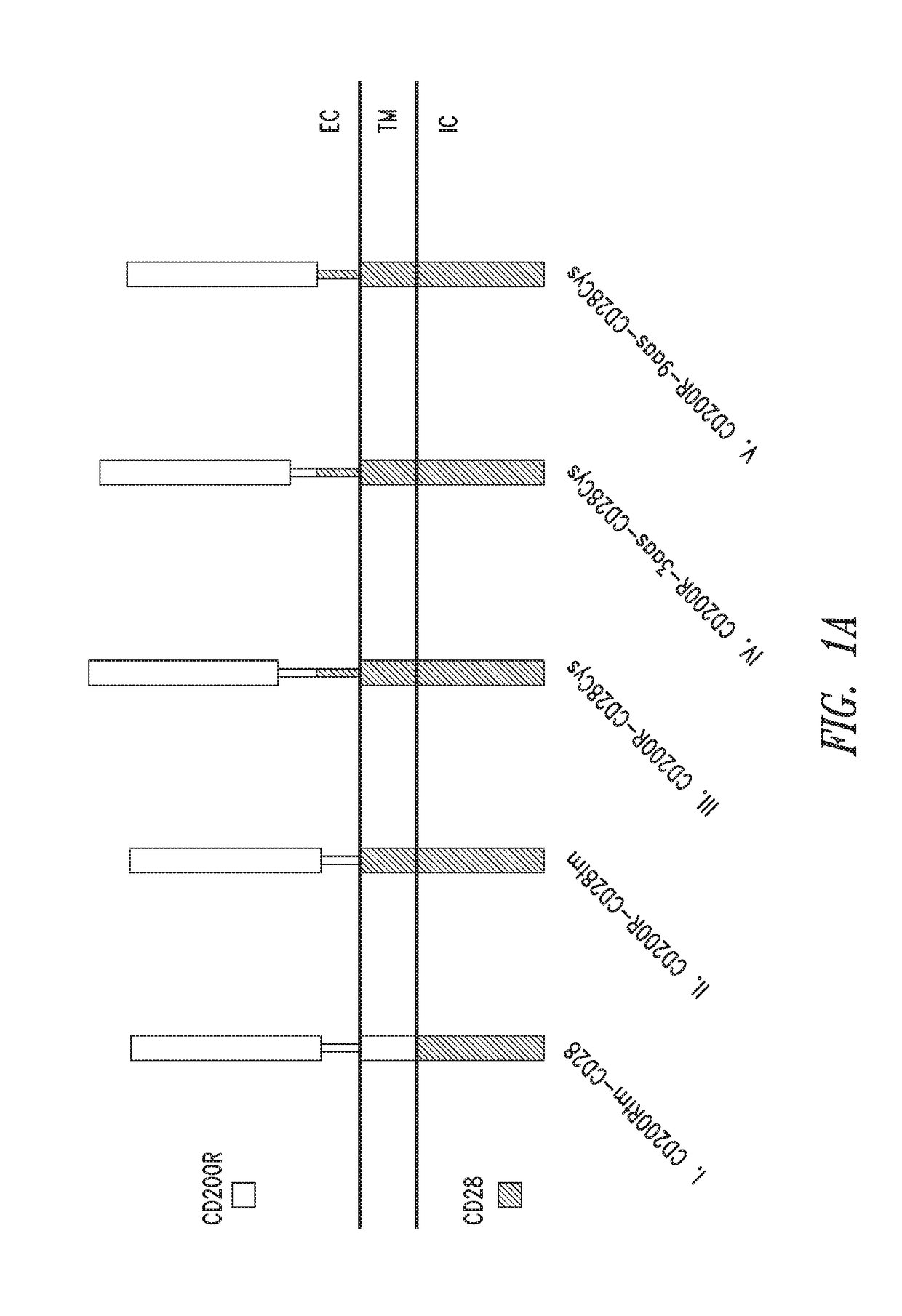
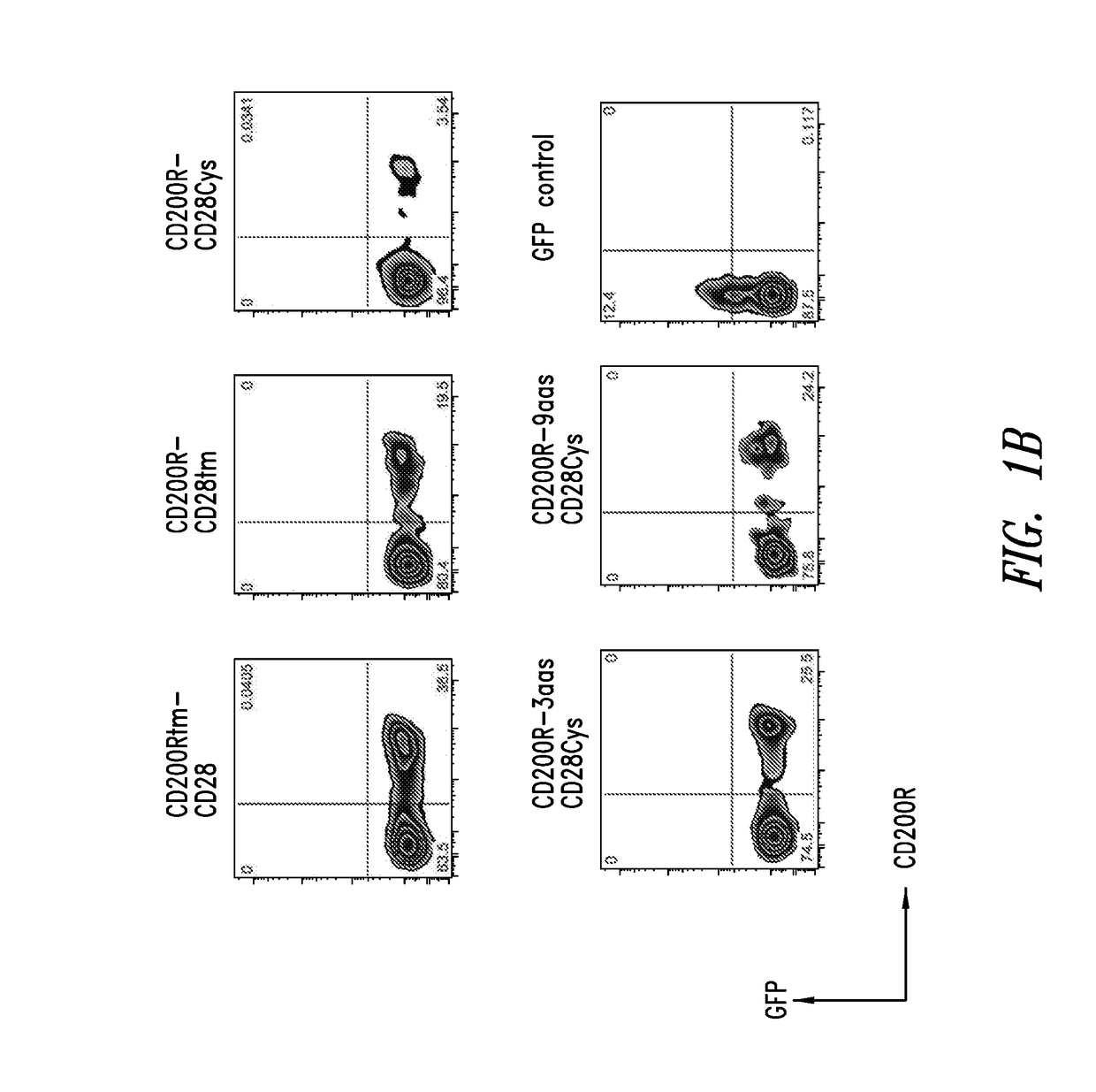
[0187]Exemplary fusion proteins as described herein are illustrated using schematic representations in FIG. 1A. Exemplary fusion proteins include immunomodulatory fusion proteins (IFPs) comprised of the extracellular domain of CD200R or a portion thereof, and an intracellular signaling domain of CD28 or a portion thereof (FIG. 1A, constructs I-V). The hydrophobic component may be comprised of the transmembrane domain of either CD200R (FIG. 1A, construct I) or CD28 (FIG. 1A, constructs II-V), or portions thereof. In some exemplary CD200R-CD28 fusion proteins, the hydrophobic component comprises the transmembrane domain of CD28 and the extracellular component further comprises an extracellular portion of CD28, particularly an extracellular cysteine residue adjacent to the hydrophobic component (e.g., FIG. 1A construct III, CD200R-CD28Cys; construct IV, CD200R-3aas-CD28Cys; and construct V, CD200R-9aas-CD28Cys). The extracellular component may co...
example 2
Transgenic Expression of CD200R-CD28 Constructs
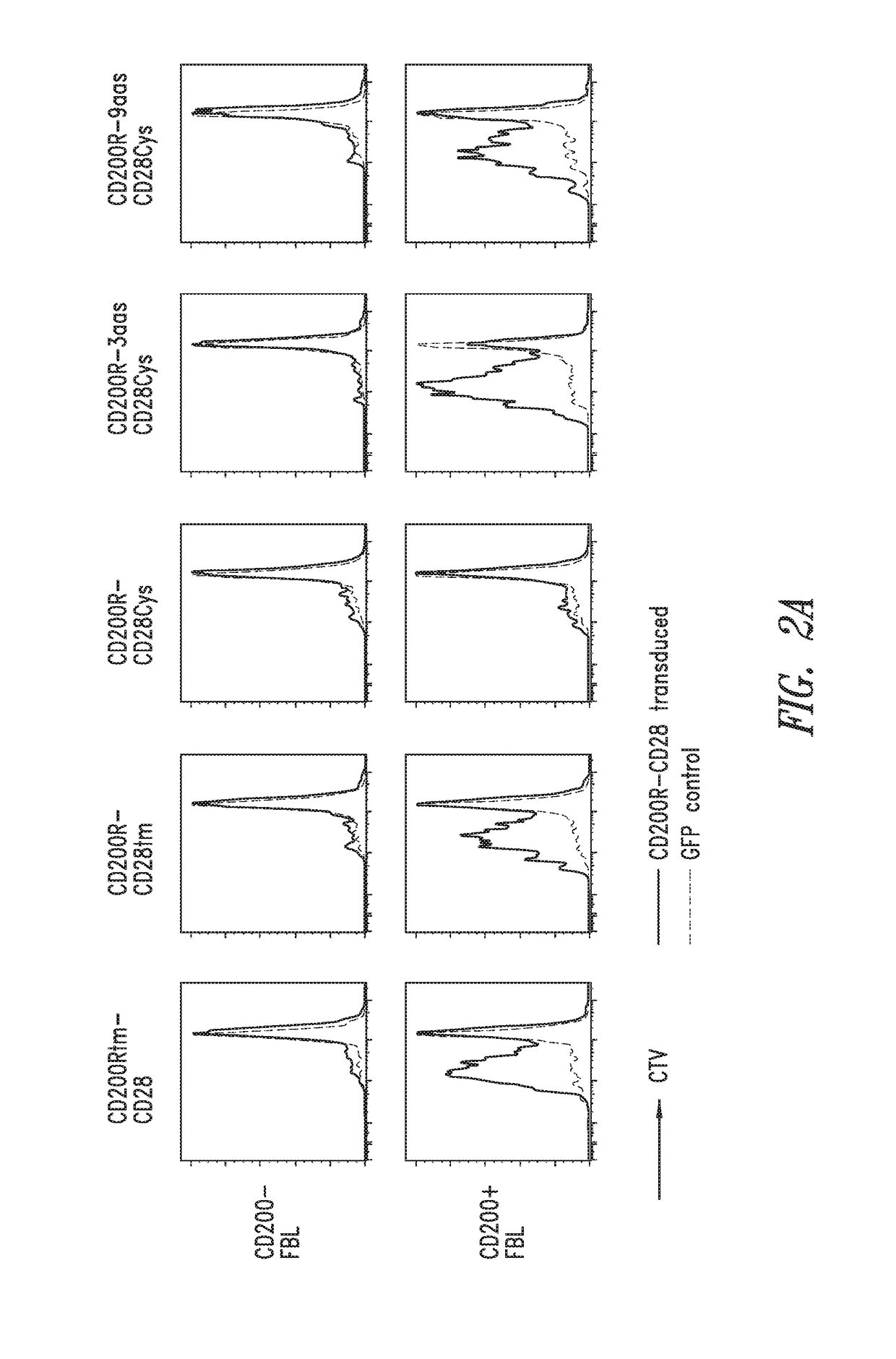
[0190]A preclinical mouse model for disseminated leukemia, based on the murine C57BL / 6 Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia (FBL) and TCRgag transgenic mice, was used to determine if CD200R-CD28 chimeric receptors can improve T cell function.
[0191]TCR transgenic mice were generated to produce CD8+ T cells specific for the gag epitope (TCRgag). C57BL / 6 (B6) mice were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory. TCRgag transgenic mice express a TCR transgene specific for the Friend virus gag epitope in CD8+ T cell (Ohlen et al., J. Immunol. 166: 2863-2870, 2001). All animal studies performed were approved under the University of Washington Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee protocol (Protocol #2013-01). The murine B6 Friend virus induced erythroleukemia (FBL) expresses the F-MuLV encoded gag epitope (peptide CCLCLTVFL).
[0192]CD200R-CD28 chimeric constructs based on murine genes were inserted into the pMP71 retroviral vector and used to...
example 3
CD200R-CD28 Constructs Promote In Vitro Proliferation, Accumulation, and Effector Function of Transduced T Cells
[0195]The CD200R-CD28 constructs described in Examples 1 and 2 were assessed for their abilities to promote proliferation, accumulation, and effector function of TCRgag T cells.
[0196]Expansion of Effector Cells In Vitro
[0197]TCRgag effector cells were generated in vitro as previously described (Stromnes et al., J. Clin. Invest. 120: 3722-34, 2010). Irradiated antigen presenting splenocytes (5×106), irradiated FBL (3×106), and TCRgag tg cells (106) were cultured together with IL-2 (50 U / mL) in 10 mL of culture media (IMDM supplemented with non-essential amino acids, 2 μM glutamine, 100 U / mL penicillin / streptomycin, 10% FBS, and 50 μM 2-mercapatoethanol). T cells were restimulated weekly and assessed by flow cytometry 5-7 days after the last stimulation.
[0198]In Vitro T Cell Proliferation Assay
[0199]TCRgag T cells were transduced as in Example 2. To assess T cell proliferati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Nanoscale particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Nanoscale particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com