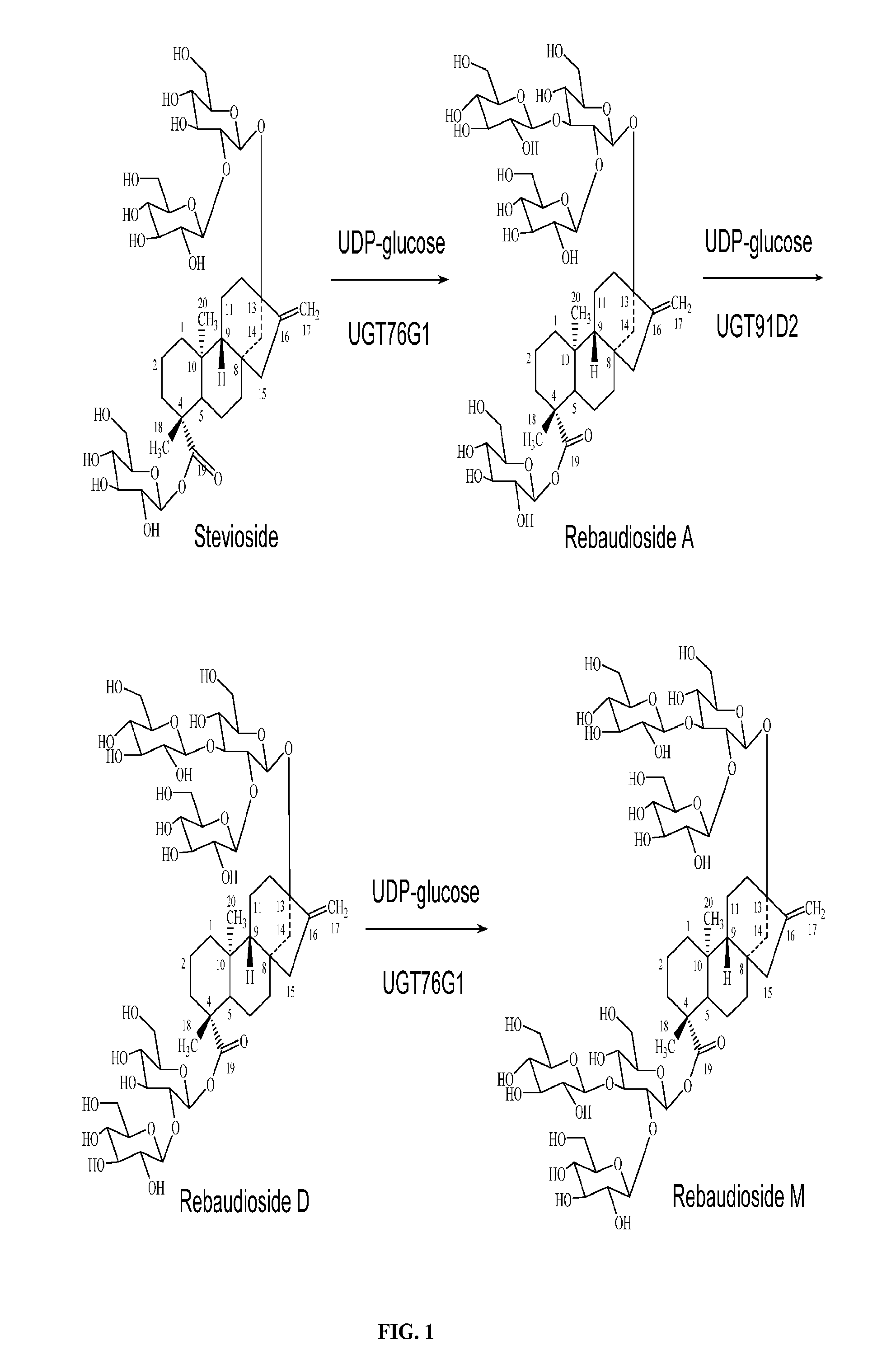
High-Purity Steviol Glycosides
a technology of steviol glycosides and steviol, which is applied in the direction of transferases, tobacco, tobacco treatment, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable commercial use methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
In-Vivo Production of UGT76G1
[0285]NcoI and NdeI restriction sides were added to the original nucleic sequence as described in Genbank accession no. AAR06912.1. After codon optimization the following nucleic sequence was obtained:
(SEQ ID NO: 1)CCATGGCCCATATGGAAAACAAAACCGAAACCACCGTTCGTCGTCGTCGCCGTATTATTCTGTTTCCGGTTCCGTTTCAGGGTCATATTAATCCGATTCTGCAGCTGGCAAATGTGCTGTATAGCAAAGGTTTTAGCATTACCATTTTTCATACCAATTTTAACAAACCGAAAACCAGCAATTATCCGCATTTTACCTTTCGCTTTATTCTGGATAATGATCCGCAGGATGAACGCATTAGCAATCTGCCGACACATGGTCCGCTGGCAGGTATGCGTATTCCGATTATTAACGAACATGGTGCAGATGAACTGCGTCGTGAACTGGAACTGCTGATGCTGGCAAGCGAAGAAGATGAAGAAGTTAGCTGTCTGATTACCGATGCACTGTGGTATTTTGCACAGAGCGTTGCAGATAGCCTGAATCTGCGTCGTCTGGTTCTGATGACCAGCAGCCTGTTTAACTTTCATGCACATGTTAGCCTGCCGCAGTTTGATGAACTGGGTTATCTGGATCCGGATGATAAAACCCGTCTGGAAGAACAGGCAAGCGGTTTTCCGATGCTGAAAGTGAAAGATATCAAAAGCGCCTATAGCAATTGGCAGATTCTGAAAGAAATTCTGGGCAAAATGATTAAACAGACCAAAGCAAGCAGCGGTGTTATTTGGAATAGCTTTAAAGAACTGGAAGAAAGCGAACTGGAAACCGTGATTCGTGAAATTCCGGCACCGAGCTTTCTGATTCCGCTGCCGA...
example 2
In-Vitro Production of UGT76G1
[0290]The S30 T7 High Yield Protein expression system kit from Promega was used. 4 μg of UGT76G1_pET30a+ plasmid from E. coli EC100 was mixed with 80 μL of S30 premix plus and 72 μL of S30 T7 extract was added. Nuclease-free water was added in order to obtain a total volume of 200 μL and the resulting solution was incubated for 2 h at 30° C. 180 μL was used in the catalytic test reaction.
example 3
In-Vitro Production of UGT91D2
[0291]NcoI and NdeI restriction sides were added to the original nucleic sequence as described in Genbank accession no. ACE87855.1. After codon optimization the following nucleic sequence was obtained:
(SEQ ID NO: 2)CCATGGCACATATGGCAACCAGCGATAGCATTGTTGATGATCGTAAACAGCTGCATGTTGCAACCTTTCCGTGGCTGGCATTTGGTCATATTCTGCCGTATCTGCAGCTGAGCAAACTGATTGCAGAAAAAGGTCATAAAGTGAGCTTTCTGAGCACCACCCGTAATATTCAGCGTCTGAGCAGCCATATTAGTCCGCTGATTAATGTTGTTCAGCTGACCCTGCCTCGTGTTCAAGAACTGCCGGAAGATGCCGAAGCAACCACCGATGTTCATCCGGAAGATATTCCGTATCTGAAAAAAGCAAGTGATGGTCTGCAGCCGGAAGTTACCCGTTTTCTGGAACAGCATAGTCCGGATTGGATCATCTATGATTATACCCATTATTGGCTGCCGAGCATTGCAGCAAGCCTGGGTATTAGCCGTGCACATTTTAGCGTTACCACCCCGTGGGCAATTGCATATATGGGTCCGAGCGCAGATGCAATGATTAATGGTAGTGATGGTCGTACCACCGTTGAAGATCTGACCACCCCTCCGAAATGGTTTCCGTTTCCGACCAAAGTTTGTTGGCGTAAACATGATCTGGCACGTCTGGTTCCGTATAAAGCACCGGGTATTAGTGATGGTTATCGTATGGGTCTGGTTCTGAAAGGTAGCGATTGTCTGCTGAGCAAATGCTATCATGAATTTGGCACCCAGTGGCTGCCGCTGCTGGAAACCCTGCATCAGGTTCCGGTTGTTCCGGTGGGT...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wet weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com