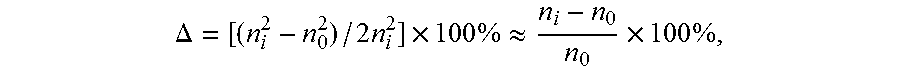Bending insensitive single-mode optical fiber
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
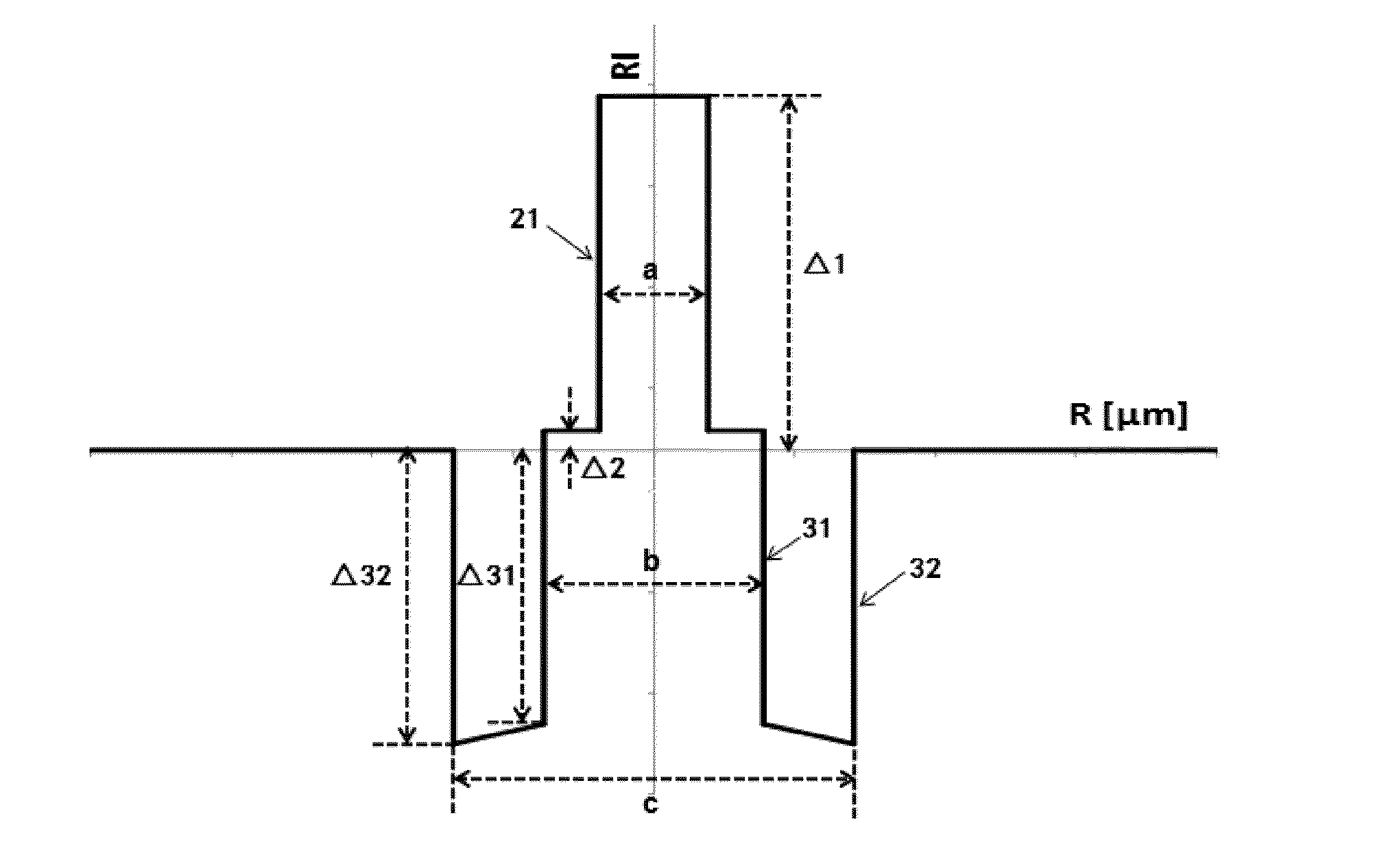
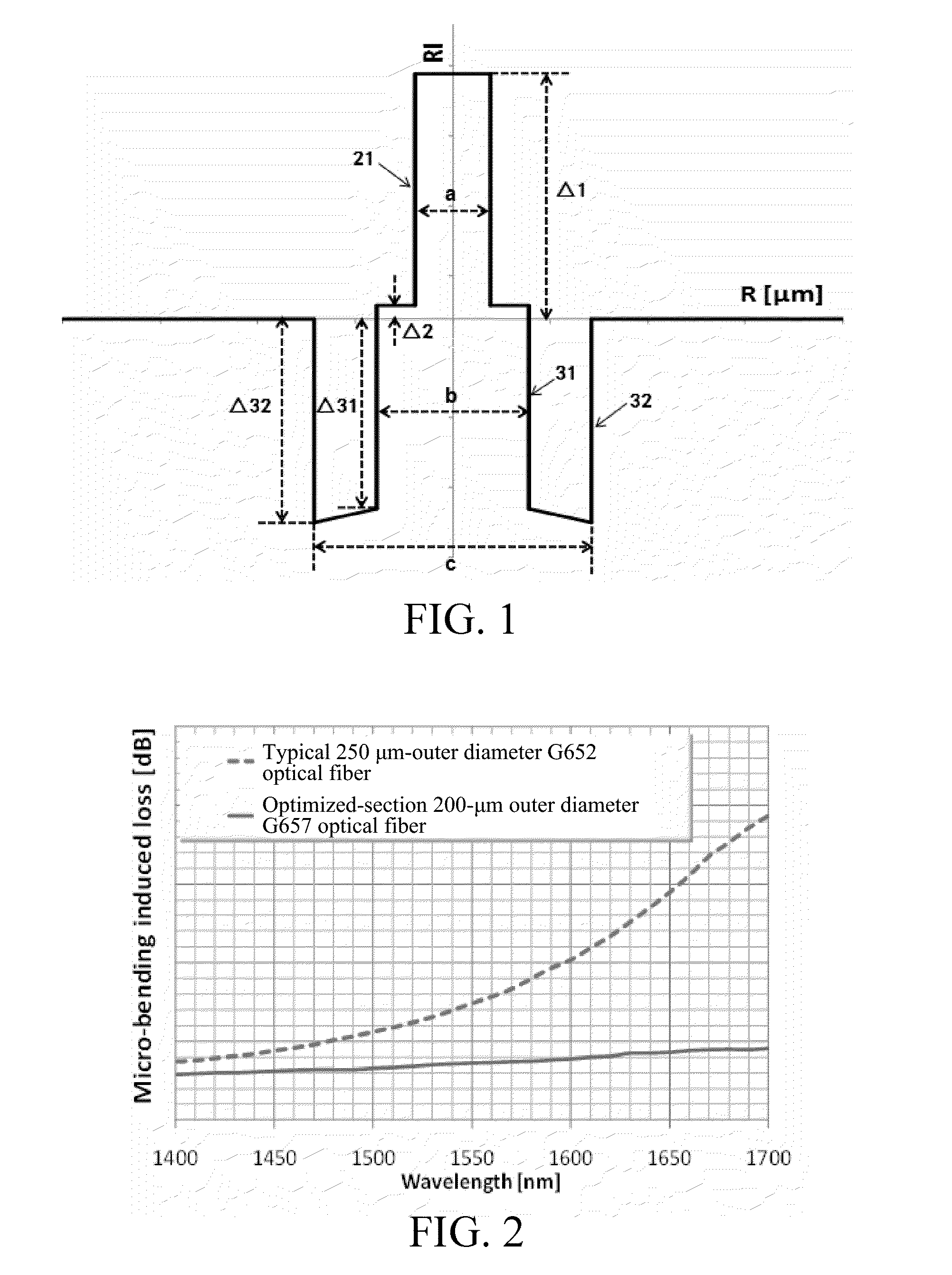
[0053]Referring to FIG. 1, the bend insensitive single-mode optical fiber in this embodiment includes a core layer and cladding layers surrounding the core layer. The cladding layers have an inner cladding layer, a trench cladding layer, and an outer cladding layer sequentially formed to cover the core layer from inside to outside. The relative refractive index difference Δ3 of the trench cladding layer changes in a gradient manner, and increases gradually from outside to inside. The relative refractive index difference Δ32 at the outermost interface 32 is smaller than the relative refractive index difference Δ31 at the innermost interface 31. The outer cladding layer surrounds the trench cladding layer. The diameter d of the outer cladding layer is about 125 μm. The refractive index of the outer cladding layer is the refractive index of pure silicon dioxide glass.
[0054]The core layer and the inner cladding layer are a germanium (Ge) and fluorine (F) doped quartz glass layer compris...
embodiment 2
[0059]In this embodiment, the PCVD+OVD processes are adopted to prepare the G.657 optical fiber preform rod. The RIC process is adopted to perform direct drawing on the preform rod, where the drawing speed is 1500 m / min, and the fiber diameter of the naked optical fiber is 125±0.7 μm. A double-layer ultraviolet-cured optical fiber coating is adopted to apply inner and outer ultraviolet-cured polyacrylic acid resin coatings (i.e., the first and second coating layers of ultraviolet-cured polyacrylic acid resin) on the surface of the optical fiber, and after applying, the outer diameter of the optical fiber is 200±10 μm. In this embodiment, the design of the naked optical fiber section is still as shown in Embodiment 1. By optimizing the process of optical fiber application layer, a bend insensitive optical fiber with a small outer diameter is prepared. In this embodiment, the optical fiber application adopts a double-layer ultraviolet-cured acrylic ester coating, in which the first la...
embodiment 3
[0060]In the design of FTTh, as optical fibers need to pass through special bending environments such as indoor and inlet conduits and corners in the configuration process, it becomes necessary to design and fabricate a bend insensitive optical fiber having have high macro-bending performance. Based on the specifications in the ITU-T standard, the G.657.B3 optical fiber requires that on the condition of the minimum bend radius of 5 mm, at 1550 nm and 1625 nm wavelengths, the attenuation loss is smaller than 0.15 dB and 0.45 dB, respectively, so as to guarantee that the macro-bending performance of the optical fiber can meet relevant requirements of FTTh with the current FTTh optical fiber configuration conditions. As discussed above, the G.657 optical fiber can enhance the bend insensitive characteristic by adopting the method of reducing the MAC value and adopting a deep and wide depressed cladding layer, and the mode field diameter can be effectively lowered by appropriately reduc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com