Method And System For Obtaining Geochemistry Information From Pyrolysis Induced By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
a technology of breakdown spectroscopy and laser induced pyrolysis, which is applied in the direction of optical radiation measurement, instruments, spectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromators, etc., can solve the problems of loss of spatial information regarding inability to program pyrolysis measurements, and inability to accurately determine the distribution of organic matter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
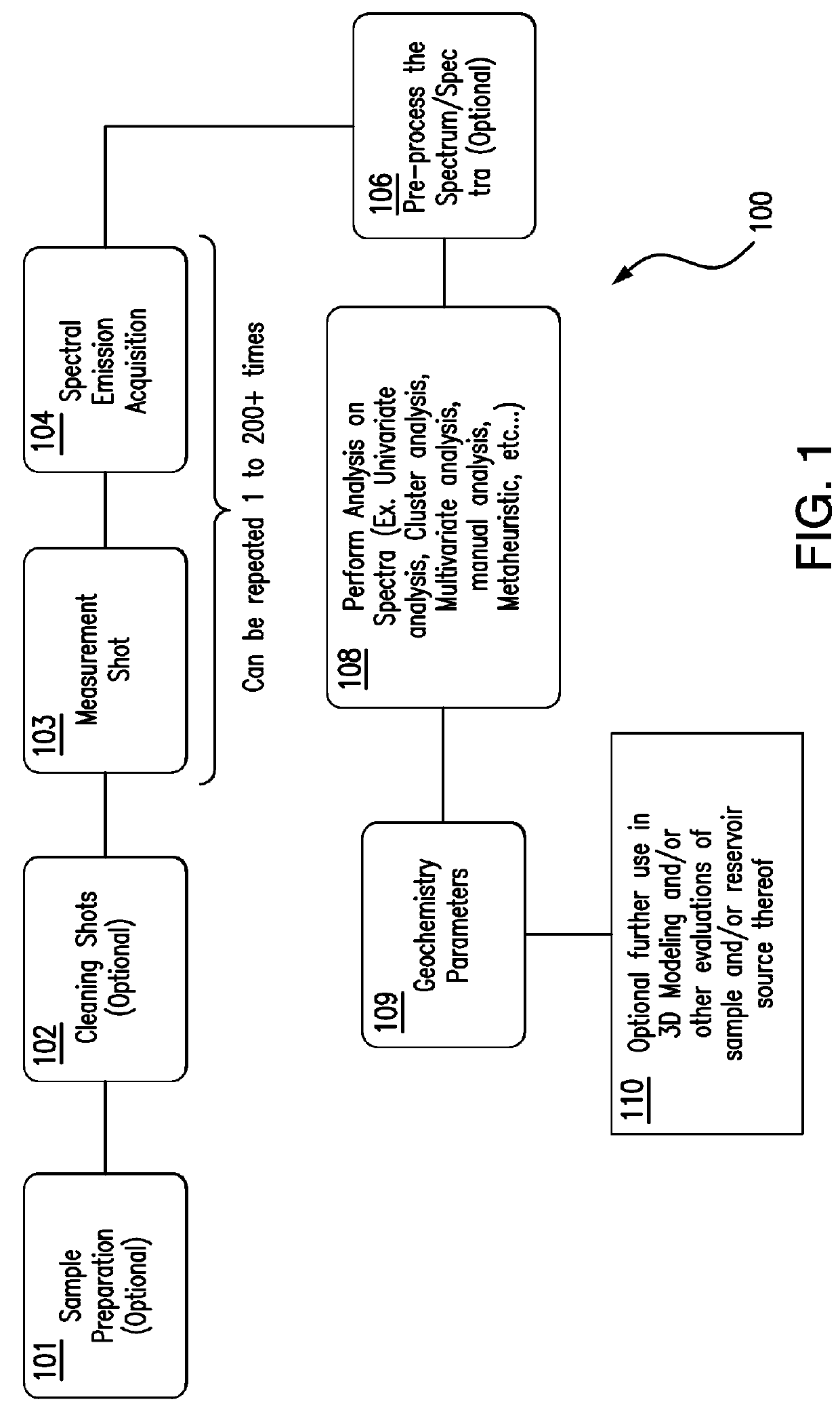
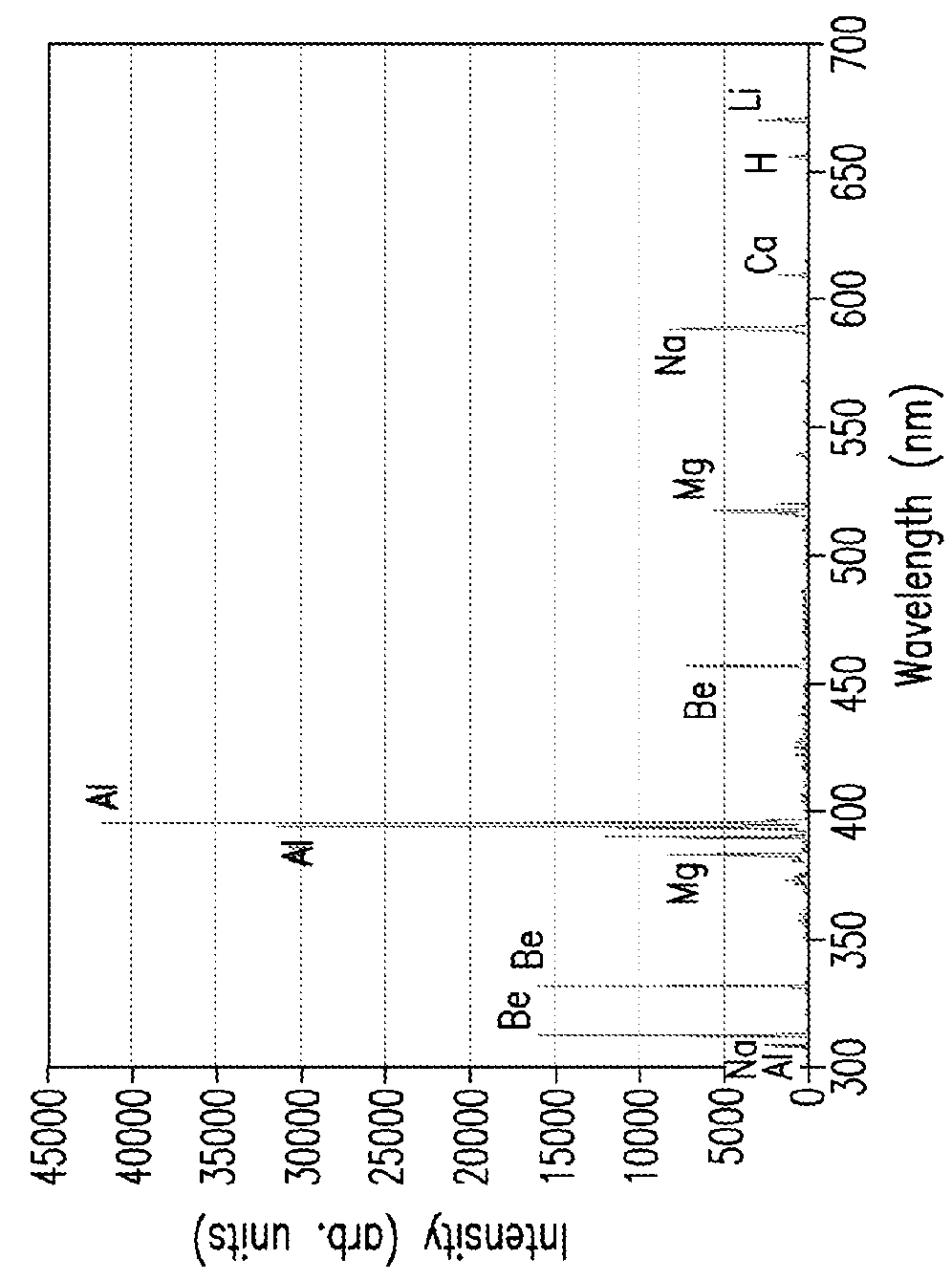
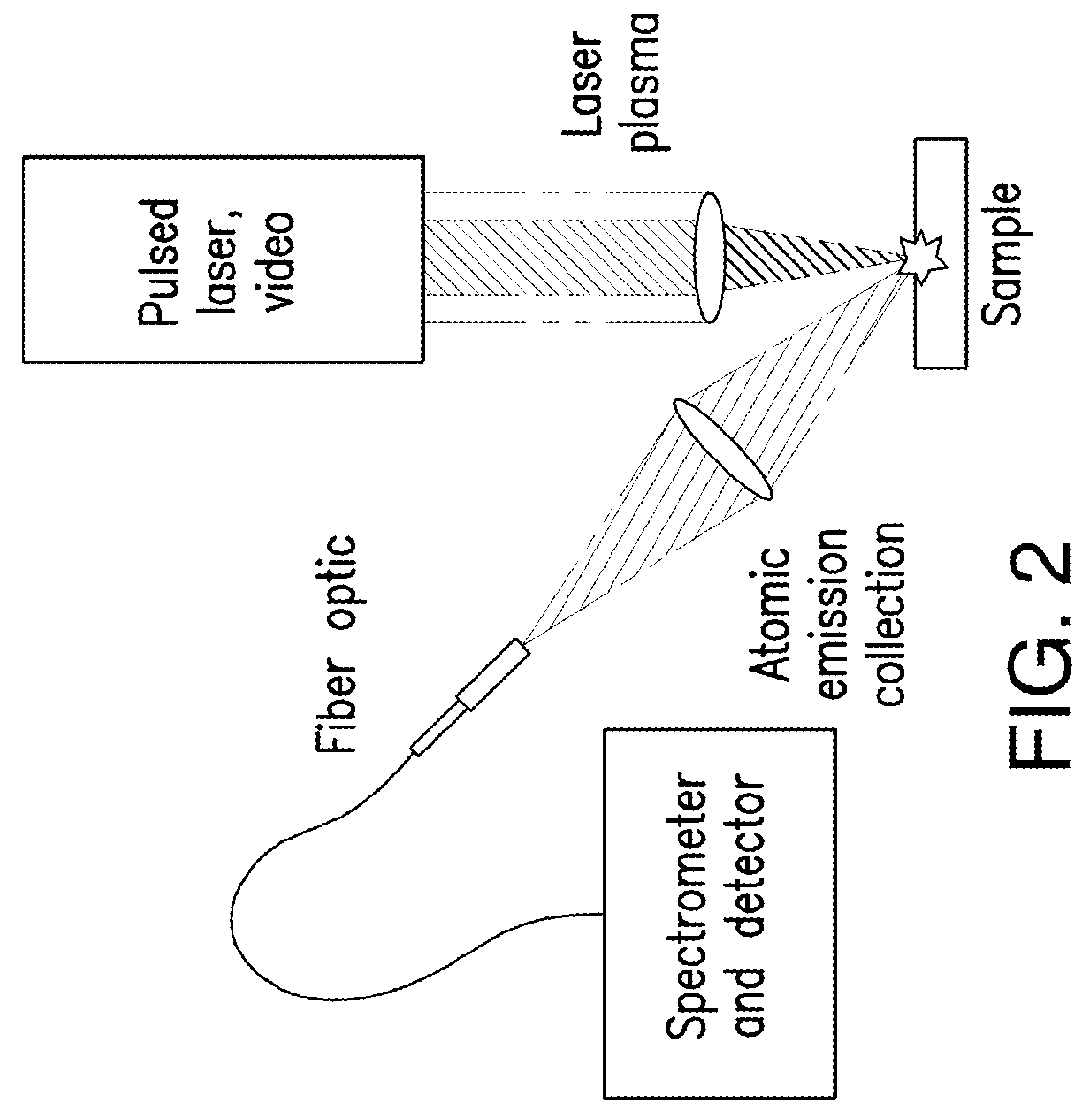
[0057]The present invention relates in part to a method for determining geochemistry of at least one geological sample with laser-induced breakdown spectral measurements performed on the geological sample in a time variant manner with spectral acquisitions made after each of a plurality of measurement shots, and optional or as needed pre-processing is applied to the collected data from the spectral acquisitions and the raw or pre-processed data is analysed to determine at least one geochemistry parameter of the sample. Though the present invention is illustrated herein with regard to analyses of geological samples, it will be appreciated that the invention may have broader application, such as in metallurgy or other uses.
[0058]More specifically, in obtaining spectral data of a sample by LIBS measurements according to a method of the present invention, after cleaning shots, multiple shots of a laser can be performed in rapid succession on the sample to pyrolyse organic matter, wherei...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength range | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com