Wireless power transmission system
a power transmission system and wireless technology, applied in the direction of transformers/inductance circuits, basic electric elements, inductances, etc., can solve the problems of long charging time, inefficient power transmission, and difficulty in reducing the size of devices, so as to suppress the generation of eddy current, reduce the size of power transmission devices, and reduce the size of power reception devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
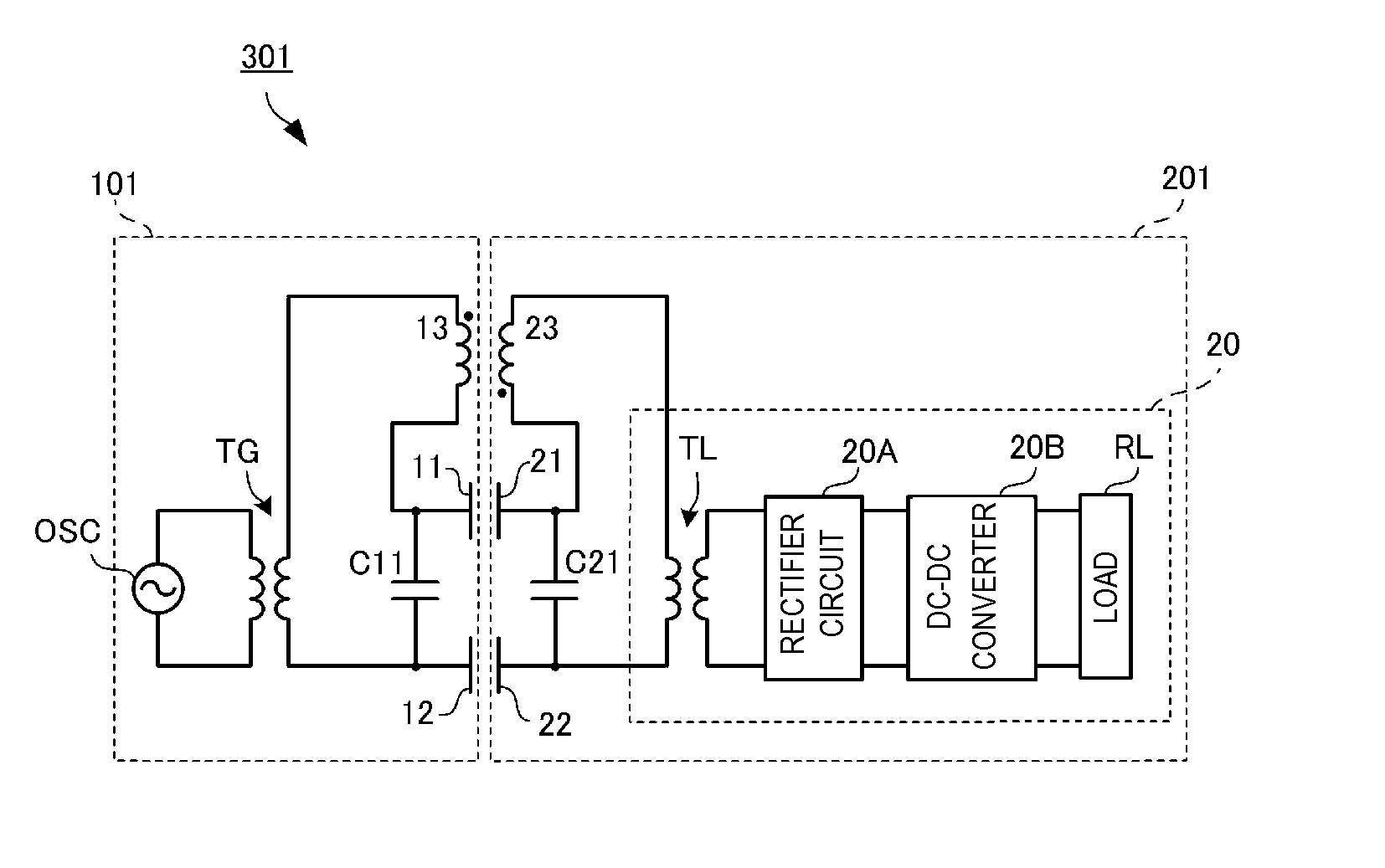
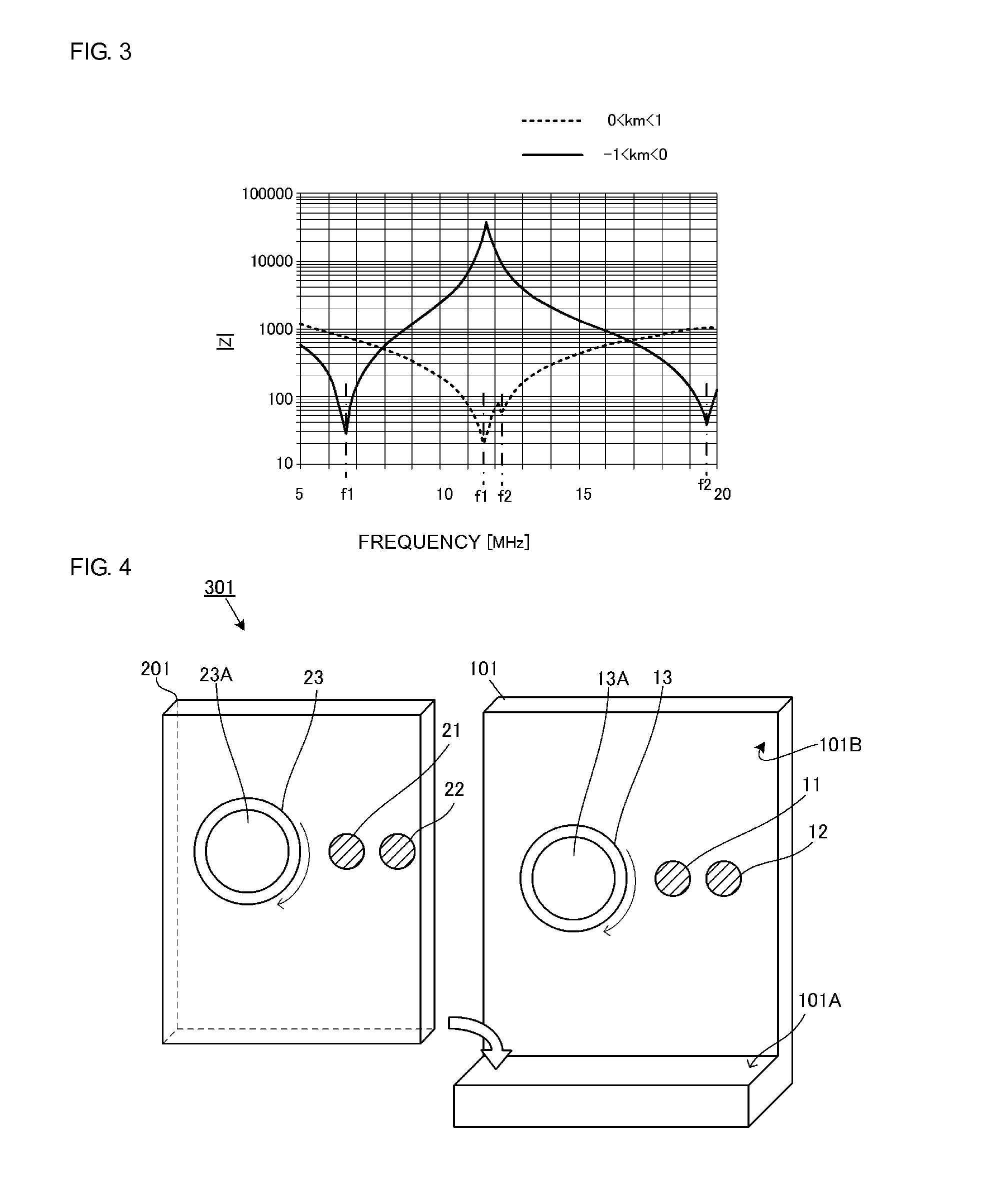
[0060]FIG. 4 is a perspective view illustrating a power transmission device and a power reception device of a wireless power transmission system 301 according to Embodiment 1. Active electrodes 11 and 21, passive electrodes 12 and 22 and planar coils 13 and 23 are provided inside casings of a power transmission device 101 and a power reception device 201 and these casings are illustrated in a see-through manner in FIG. 4.
[0061]The power reception device 201 of the wireless power transmission system 301 is a mobile electronic appliance equipped with a battery module including a secondary battery, a charging circuit and so forth. Examples of such a mobile electronic appliance include cellular phones, portable music players, laptop PCs, digital cameras and so forth. The power reception device 201 is mounted on the power transmission device 101 and the power transmission device 101 charges the secondary battery of the power reception device 201.
[0062]The power transmission device 101 ha...
embodiment 2
[0082]Hereafter, Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. In this embodiment, the shapes of the active electrodes and the passive electrodes of the power transmission device and power reception device are different to those in Embodiment 1. This difference will be described hereafter.
[0083]FIG. 7 is a perspective view illustrating a power transmission device 102 and a power reception device 202 of a wireless power transmission system 302 according to Embodiment 2. FIG. 8 is a sectional view illustrating the positional relationship between active electrodes 14 and 24, passive electrodes 15 and 25 and planar coils 13 and 23 when the power reception device 202 is mounted on the power transmission device 102.
[0084]The power transmission device 102 includes the planar coil 13, the circular active electrode 14 and the annular passive electrode 15 provided along a backrest surface 101B. The planar coil 13, the active electrode 14 and the passive electrode 15 are provided su...
embodiment 3
[0089]Hereafter, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. In this embodiment, the configurations of the magnetic-field-coupled coils and the active electrodes and passive electrodes of the power transmission device and power reception device are different to those in Embodiment 1. This difference will be described hereafter.
[0090]FIG. 9 is a circuit diagram of a wireless power transmission system 303 according to Embodiment 3.
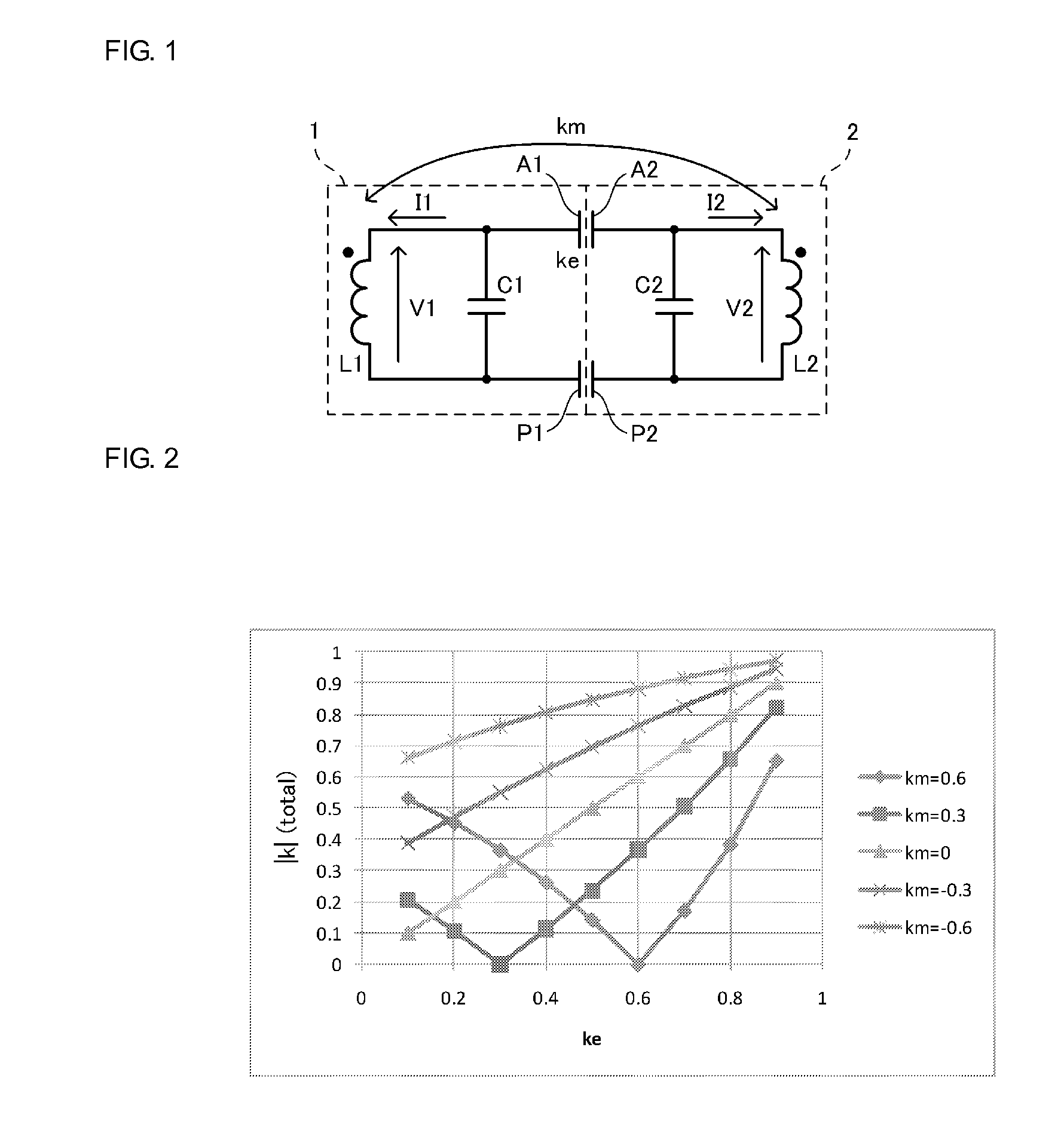
[0091]In this embodiment, a first coil 18A and a second coil 18B are connected to an active electrode 16 and a passive electrode 17 in a power transmission device 103. The first coil 18A and the second coil 18B form an LC resonance circuit with a capacitor C11 and so forth. The first coil 18A and the second coil 18B are connected to a secondary coil L12 of a step-up transformer TG and the first coil 18A, the second coil 18B and the secondary coil L12 form a single coil (hereafter, referred to as power-transmission-side coil). The active electrod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com