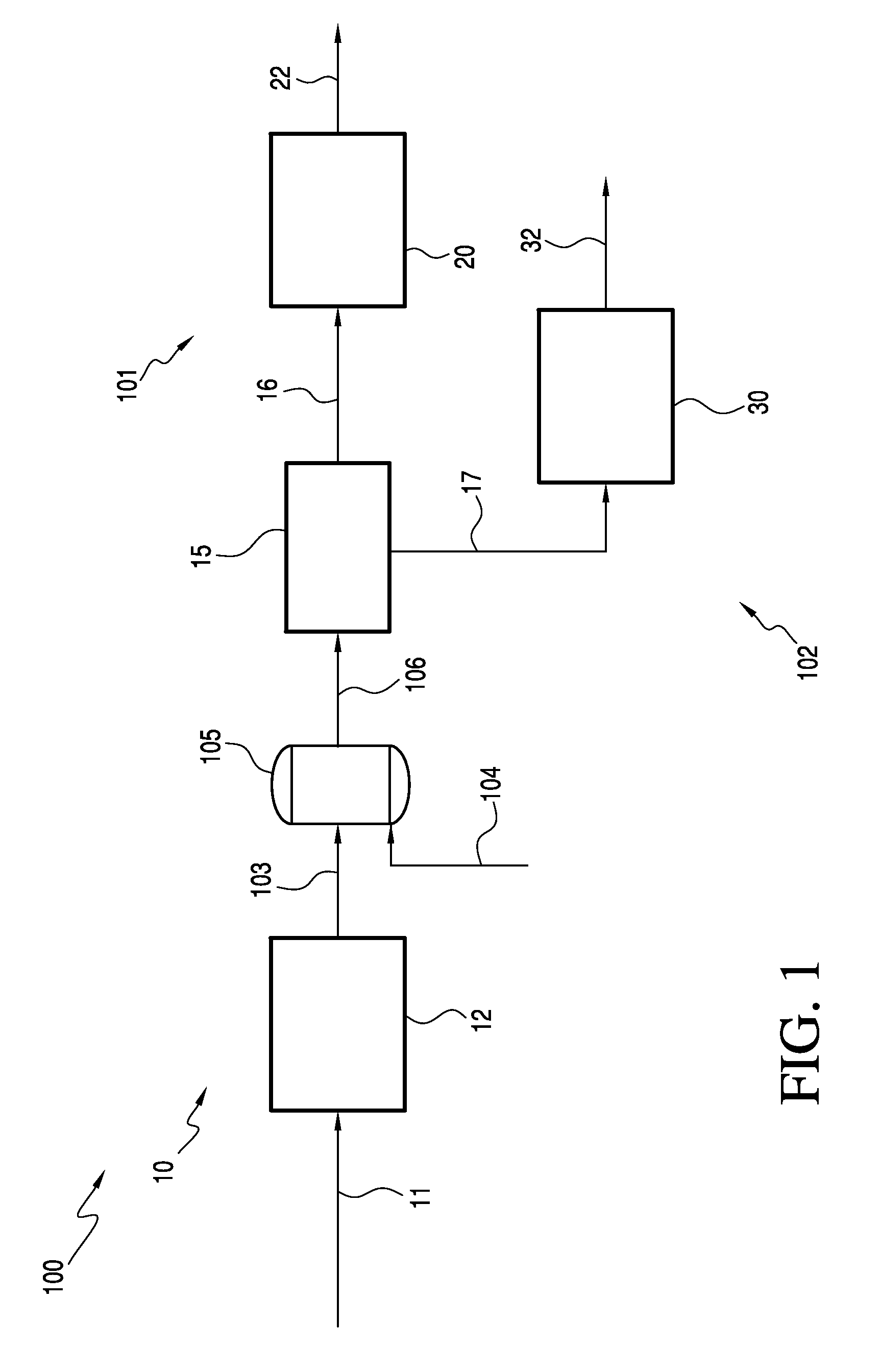
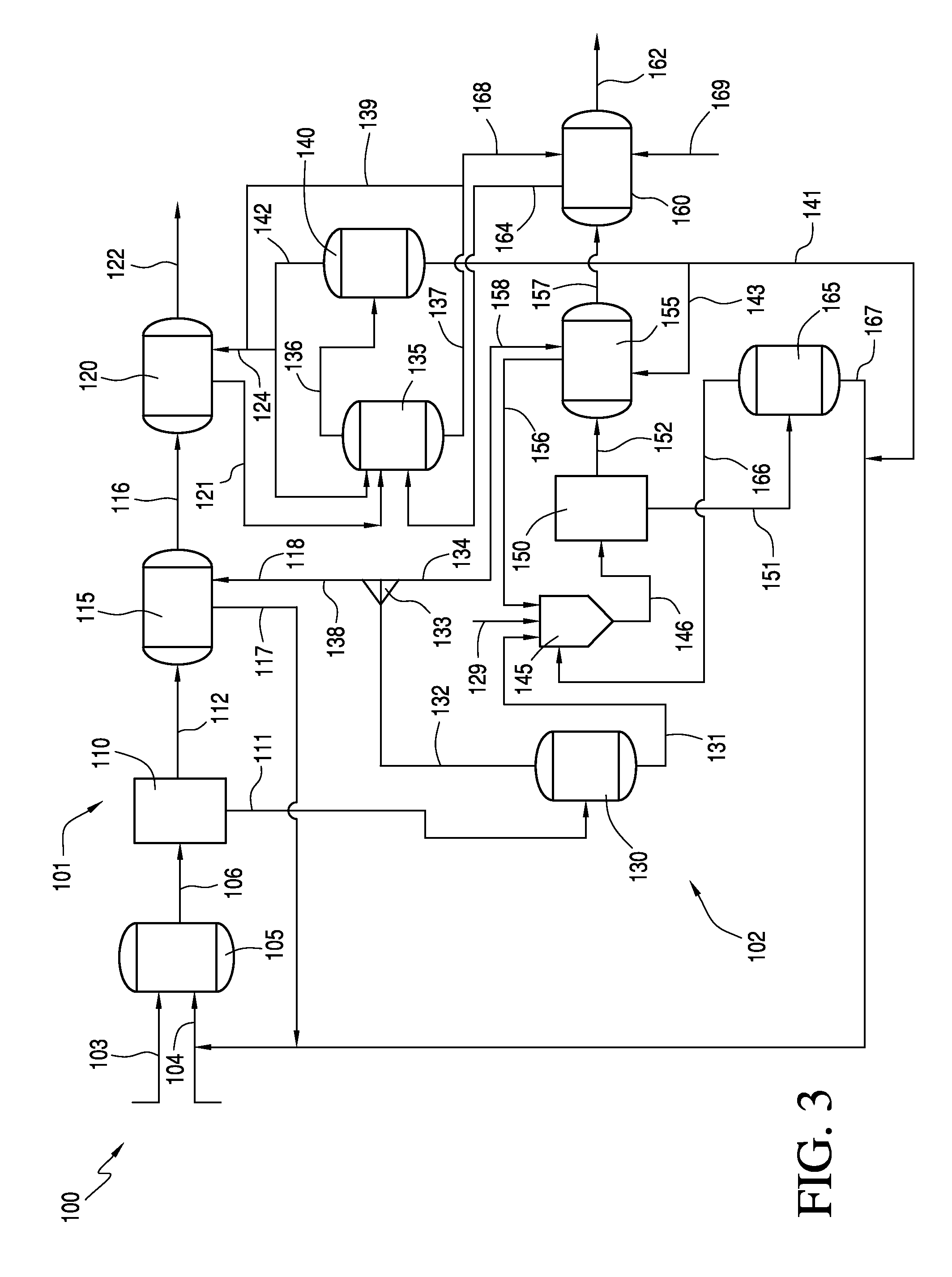
Processes for pretreating and purifying a cellulosic material
a cellulosic material and purification technology, applied in the field of purification of cellulosic products from raw cellulosic materials, can solve the problems of incompatible with certain industrial uses, high cost of such pulps, and inability to meet the requirements of certain industrial uses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example a
Water Pretreatment with Single Extraction (Samples 1 Through 11)
[0153]A commercially available hardwood paper grade pulp from a species indigenous to the southeastern United States comprising 74.2% glucan, 19% xylan, and 0.9% mannan as determined by sugar analysis was mixed with water in a pulp to water ratio of 1:10 and then heated to the temperature shown in Table 7 below for 30 to 60 minutes. The pulp was then collected by filtration, washed with water, and dried in a hood.
[0154]After the pulp had been dried, it was then uniformly mixed with an extractant comprising 21 wt. % EMIMAc / ACN at the solid / liquid ratio as shown in Table 7 below. The mixture was sealed in a vial and heated to 95° C. for 1 hour. The mixture was then centrifuged at 51 g force (8000 rpm) for 5 minutes to remove the liquid from the pulp by using a centrifuge tube with a metal filter in the middle. The pulp was then washed with 20 mL water four times, with centrifuging at 51 g force (8000 rpm) for 5 minutes be...
example b
Dilute Acetic Acid Pretreatment with Single Extraction (Samples 33 Through 40)
[0166]A commercially available hardwood paper grade pulp from a species indigenous to the southeastern United States comprising 74.2% glucan, 19% xylan, 0.9% mannan as determined by sugar analysis, was mixed with a dilute glacial acetic acid solution having a strength shown in Table 8 below in a weight ratio of pulp to dilute acid solution of 1 to 40. The mixture was heated to a temperature of 120° C. in an autoclave for 1 hour. The pulp was then collected by filtration, washed with water, and dried in a hood.
[0167]After the pulp had been dried, it was uniformly mixed with an extractant comprising 21 wt. % EMIMAc / ACN at the solid / liquid ratio as shown in Table 8 below. The mixture was sealed in a vial and heated to 95° C. for 1 hour. The mixture was then centrifuged at 51 g force (8000 rpm) for 5 minutes to remove the liquid from the pulp by using a centrifuge tube with a metal filter in the middle. The pu...
example c
Dilute Sulfuric Acid Pretreatment with Single Extraction (Samples 47 Through 57)
[0172]A commercially available hardwood paper grade pulp from species indigenous to the southeastern United States comprising 74.2% glucan, 19% xylan, 0.9% mannan as determined by sugar analysis, was combined with a dilute sulfuric acid solution having a pH shown in Table 9 below in a weight ratio of pulp to dilute acid solution of 1 to 40. The mixture was heated to a temperature of 120° C. in an autoclave for 1 hour. The pulp was then collected by filtration, washed with water, and dried in a hood.
[0173]After the pulp had been dried, it was uniformly mixed with an extractant comprising 21 wt. % EMIMAc / ACN at the solid / liquid ratio as shown in Table 9 below. The mixture was sealed in a vial and heated to 95° C. for 1 hour. The mixture was then centrifuged at 51 g force (8000 rpm) for 5 minutes to remove the liquid from the pulp by using a centrifuge tube with a metal filter in the middle. In Samples 47, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com