Back-end matching method supporting front-end knowledge-based probabilistic authentication systems for enhanced credential security
a probabilistic authentication and back-end matching technology, applied in the field of computer security, can solve the problems of difficult brute force, if not impossible, of sharing secrets, and achieve the effect of being harder to brute for
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
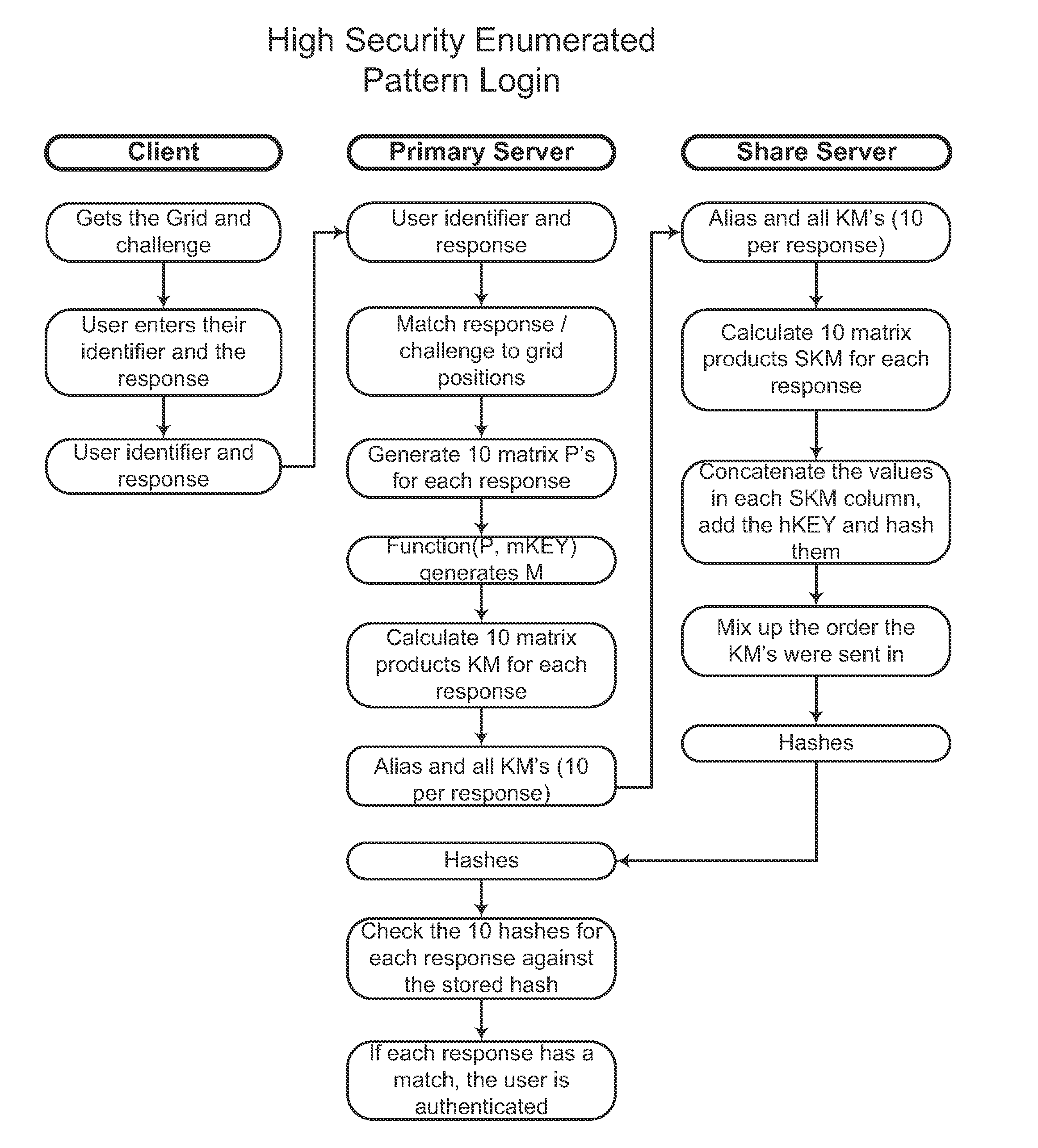
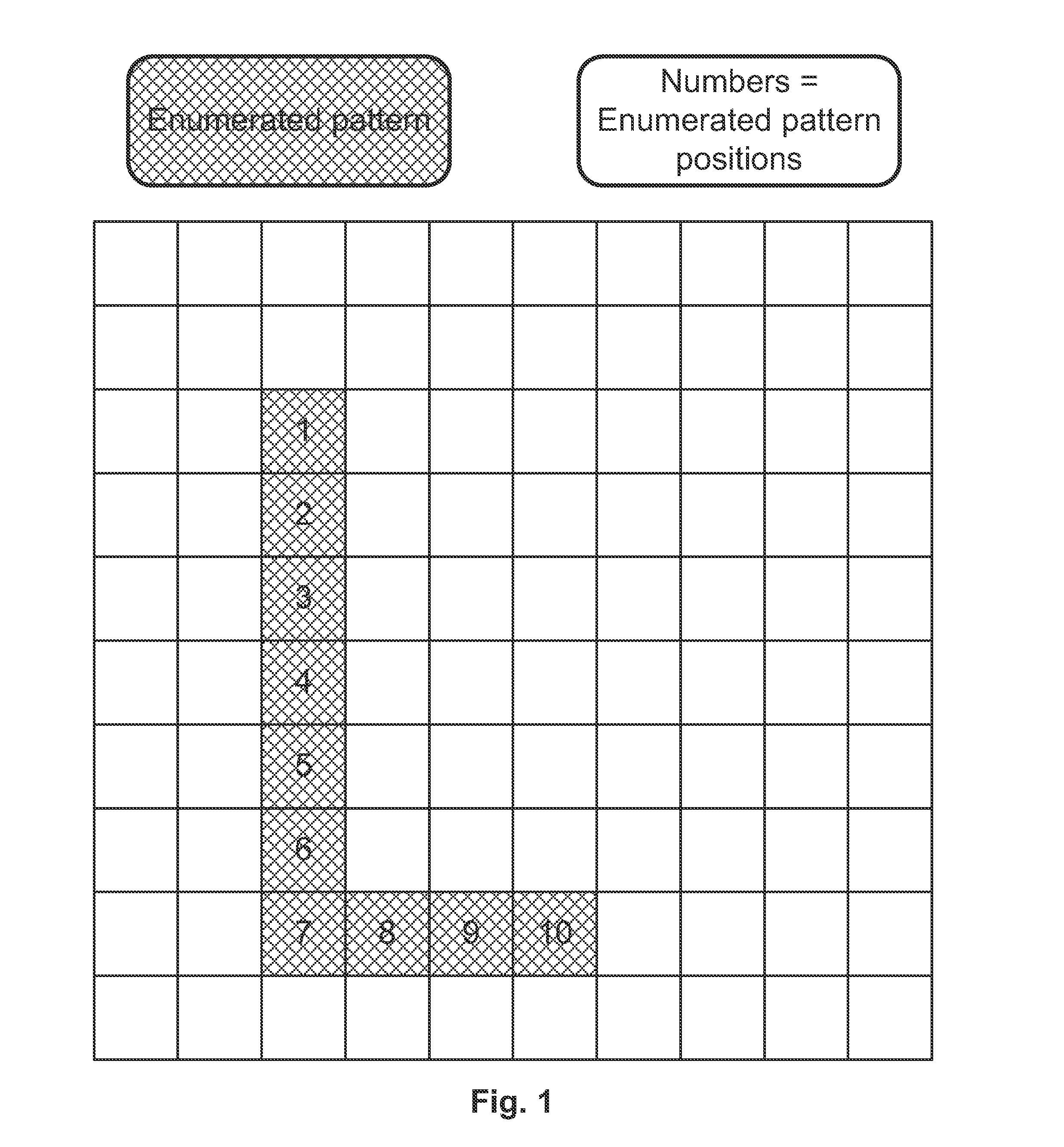
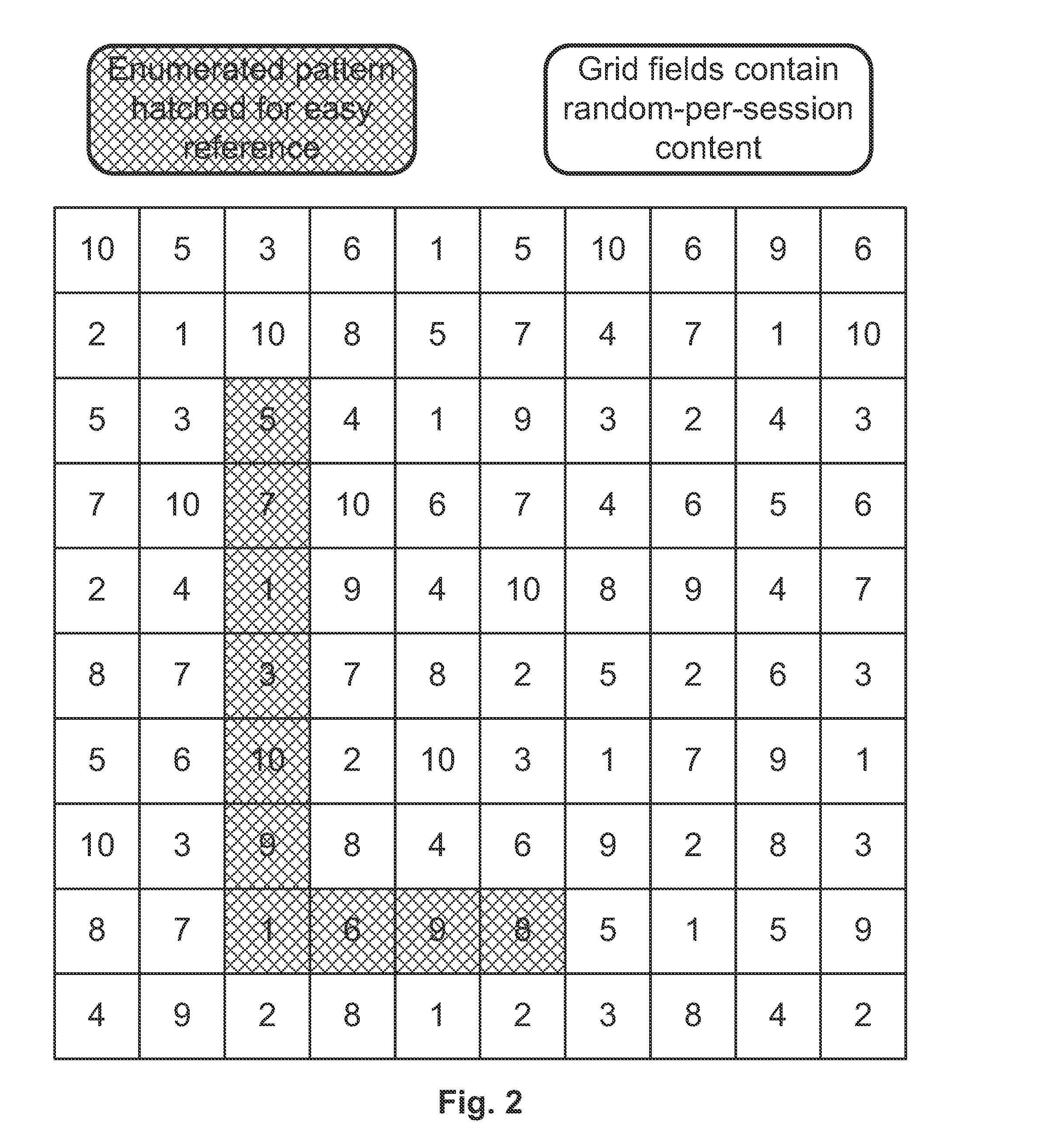
[0077]The first embodiment wherein the algorithm chosen is less complex will be detailed. The high level steps for a credential creation operation are as follows (also see FIG. 4):[0078]1. A user enters an identifier and the credential in the client.[0079]2. The client splits the credential into credential elements.[0080]3. The client encodes each credential element into a value M (M1, M2, . . . , Mn).[0081]4. The client randomly generates a value K.[0082]5. The client uses a one-way function to calculate KM for each value M (KM1, KM2, . . . , KMn).[0083]6. If not done so already (depends on the one-way function), the KM's should be hashed.[0084]7. The client encrypts K with the share server's public key, so that K becomes protected data.[0085]8. The client sends the user identifier, K and KM's to the primary server.[0086]9. The primary stores the user identifier and the KM's. The hashed KM's together constitute a representation of the credential characterized by the condition that ...
second embodiment
[0107]The second embodiment wherein the algorithm is more security conscious will be detailed. The high level steps for credential creation are as follows (also see FIG. 6):[0108]1. A user enters an identifier and the credential in the client.[0109]2. The client splits the credential into elements and encodes each one into a value M (M1, M2, . . . , Mn).[0110]3. The client randomly generates a value K.[0111]4. The client uses a one-way function to calculate KM for each value M (KM1, KM2, . . . , KMn) in the authentication credential.[0112]5. The client encrypts all the KM's with the share server's public key.[0113]6. The client sends the user identifier, K and encrypted KM's to the primary server, so that the KM's become protected data.[0114]7. The primary stores the user identifier and K.[0115]8. The primary server sends the encrypted KM's to the share server.[0116]9. The share server decrypts the KM's with its private key.[0117]10. The share server generates a random value S.[0118...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com