Combined therapy of alpha-1-antitrypsin and temporal t-cell depletion for preventing graft rejection
a technology of temporal t cell depletion and graft rejection, which is applied in the direction of antibody medical ingredients, immunological disorders, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of delayed onset acute rejection or acute rejection of grafts, and achieve the effect of prolonging the survival of xenografts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
hAAT Monotherapy During Rat-to-Mouse Islet Transplantation
[0086]The initial dose for hAAT monotherapy (60 mg / kg from 1 day prior to transplantation) was selected from previous reports. In order to explore a higher impact monotherapy protocol, both a higher dose was examined (240 mg / kg) and an extended 10-day pretreatment protocol was tested. hAAT injections were repeated every 3 days in all experiments. A total of n (number in group)=6 mice were grafted under these conditions, including two recipients per modified protocol. In addition, n=6 mice were grafted with no added therapy, as control. As shown in FIG. 1A, neither of the three modified hAAT monotherapy protocols delayed islet xenograft rejection day (CT 10,11,12,13,15, 22 and hAAT 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 24). The extended hAAT protocol is thereby used throughout the following studies.
[0087]Intragraft changes were examined (FIG. 1B-D). According to histology on day 7 post-transplantation (n=3 per group, representative images), inf...
example 2
DLN Molecular Profile During hAAT Monotherapy
[0089]In order to achieve a robust immune response, improve detection of changes in DLN, and achieve responses with low variability, skin xenotransplantation was performed. Treatment groups included control mice and mice receiving hAAT. Day-14 inguinal DLN were collected for FACS analysis. As shown in FIG. 2A, the number of B cells in the lymph nodes rose by 22.4% on average in transplanted mice, compared to control non-grafted mice. However, hAAT-treated mice displayed a 54.2% decrease on average of B cells from skin transplanted untreated mice. Surface levels of CD40 significantly increased compared to non-grafted mice, and then reduced with hAAT treatment (FIG. 2A).
[0090]DLN RT-PCR analysis was performed 3 days after transplantation. FIG. 2B depicts relative changes in specific transcript numbers. While DLN CD40, IL-6 and IL-10 transcript levels did not increase after xenotransplantation at this time point, CD86 displayed a significant...
example 3
Islet Xenotransplant Survival is Extended under hAAT and Temporary T Cell Depletion Combination
[0091]Since monotherapy with hAAT appears to have allowed an uninterrupted xeno-response, we sought to examine the combination of hAAT treatment with a technique for modifying xenoimmunity, namely, temporary T cell depletion.
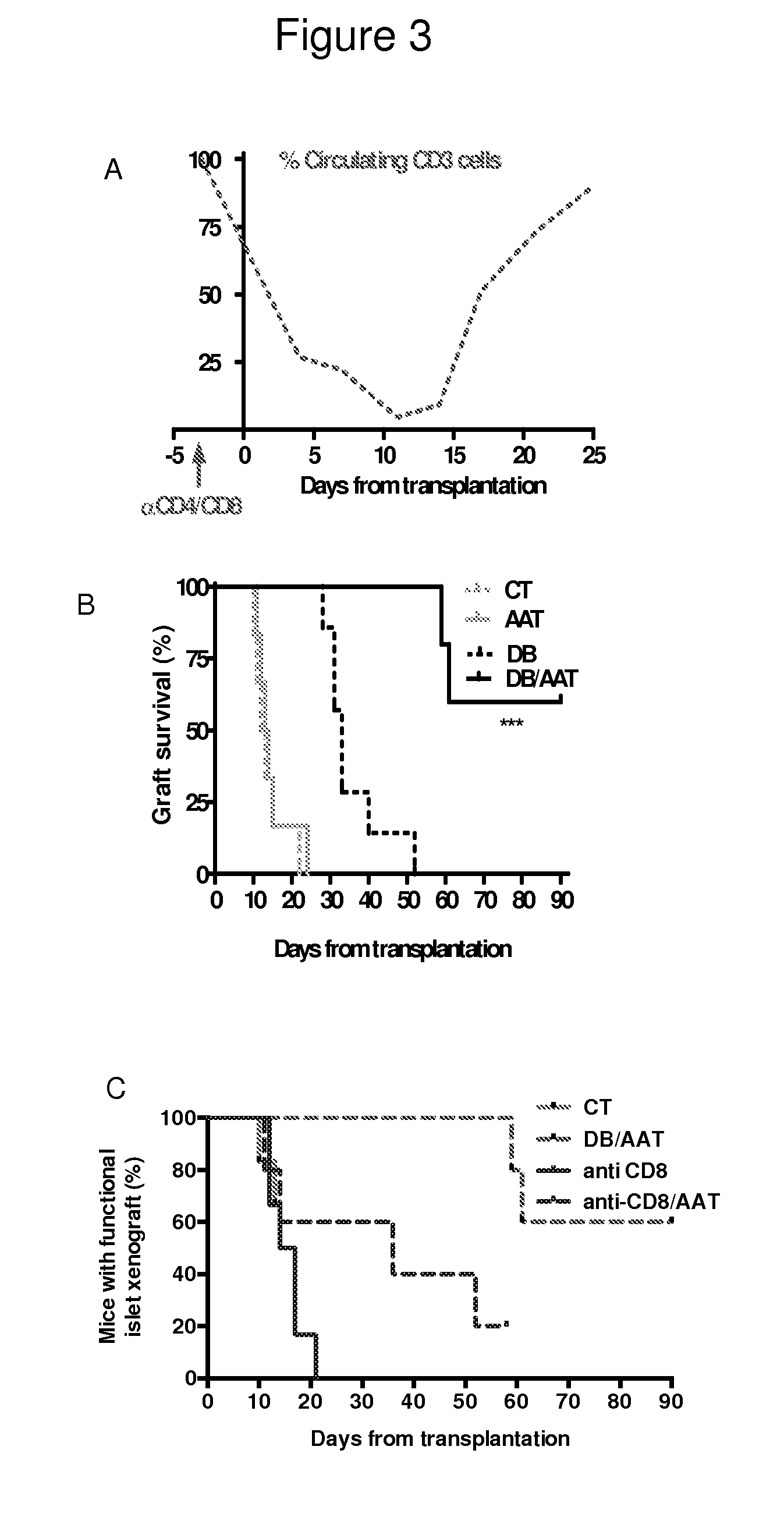
[0092]Debulking therapy was examined alone and in combination with hAAT (FIG. 3A-E and FIG. 4). Recipient mice were treated with single-dose anti-CD8 / CD4 depleting antibodies, with or without hAAT (n=5-7 per group). According to circulating mouse CD45+CD3+ follow-up (FIG. 3A, representative result), mice injected with depleting antibodies exhibited a decrease in the relative number of circulating T cells and a spontaneous return to normal lymphocyte levels after a period of approximately two weeks.
[0093]As shown in FIG. 3B, animals treated by debulking therapy (DB) displayed a delay in xenograft rejection (days 28, 31, 31, 33, 33, 40, 52). In contrast, combined debulki...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pathological immune reactivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com