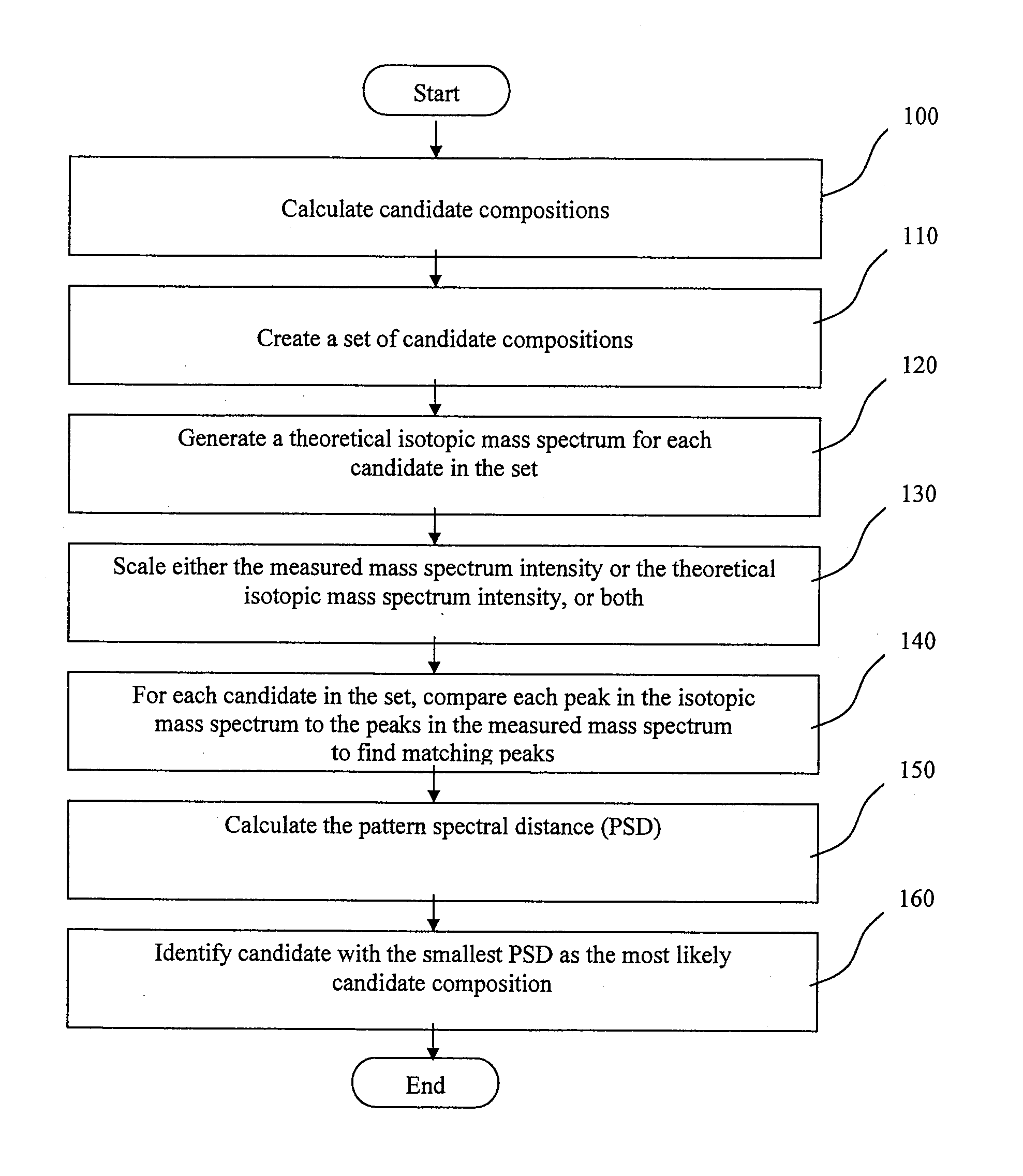
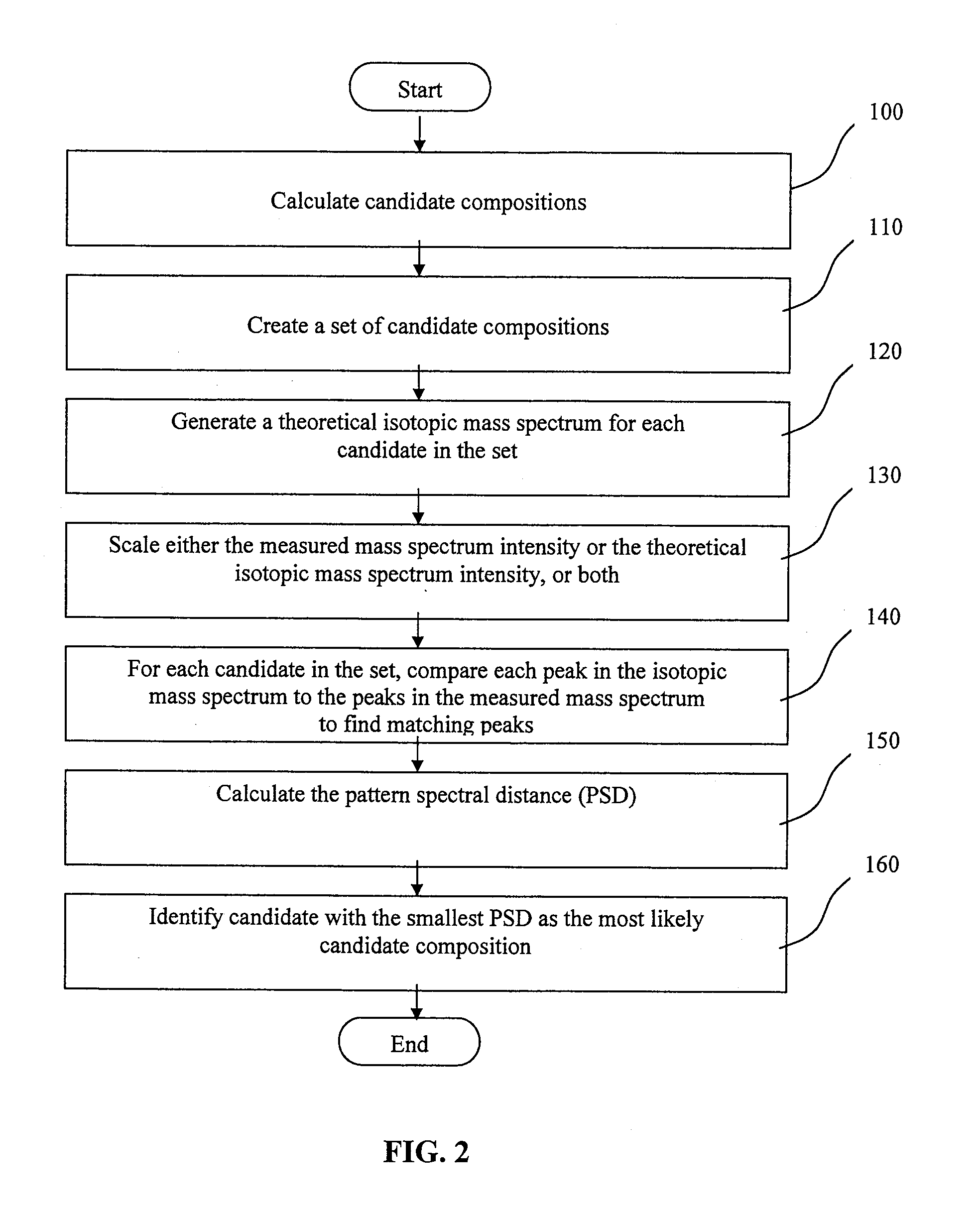
Method of Processing Spectrometric Data
a spectrometry and data processing technology, applied in chemical methods analysis, particle separator tube details, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient unequivocal identification, critical and time-consuming molecular formula assignment of mass data, and insufficient mass accuracy alone, so as to improve the correct assignment of elemental compositions, improve the accuracy of sample characterization, and reduce the time taken to characterize a given sample.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
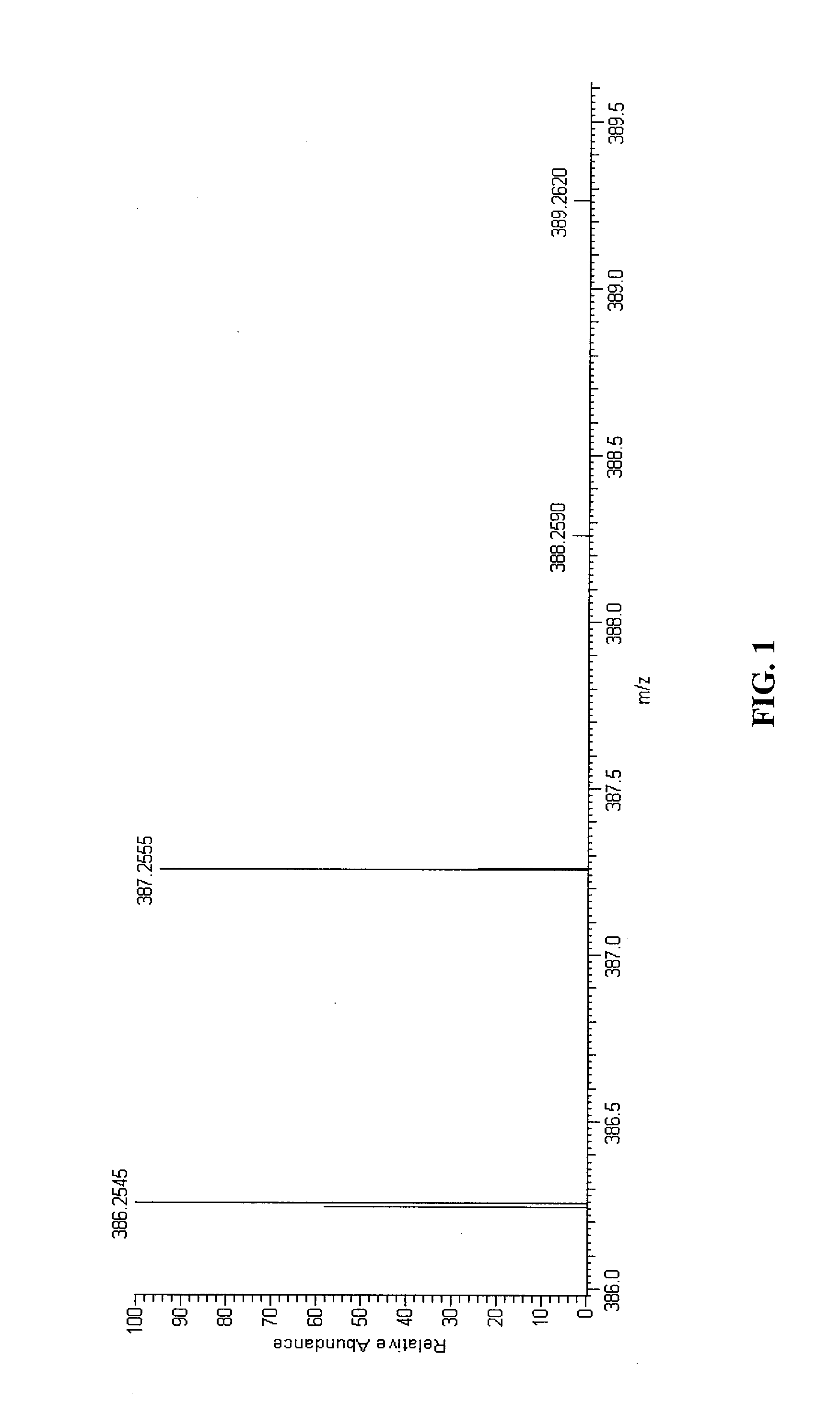
[0051]The invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the mass spectrum of a known compound, Buspirone. However, it will be appreciated that the individual features of the invention described are of general applicability. FIG. 1 shows a mass spectrum of Buspirone, obtained by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS). The mass analysis was carried out using an FT-ICR mass spectrometer operated at high resolution. Specific details of the experimental arrangement (i.e. the specific components employed in the mass spectrometer arrangement) are not critical to an understanding of the present invention and, in any event, various embodiments would be familiar to the skilled reader. Such arrangements are shown, just as examples, in U.S. Pat. No. 6,987,261 and U.S. Pat. No. 7,211,794 and in Parts per Million Mass Accuracy on an Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer via Lock Mass Injection into a C-trap”, Mol. Cell. Proteomics, December 2005; 4: 2010-2021; Jesper V. Olsen, Ly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com