Cereal-based infant nutrition with fibre
a cereal-based, infant-based technology, applied in the field of cereal-based infant nutrition, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory products, achieve the effects of reducing undesirable texturising effects, and reducing product-technological properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cereal Milk for Infants
[0076]A dry composition comprising skimmed milk powder, demineralised whey powder, vegetable fat, rice flour and ground corn, glucose, fructose, maltodextrin, fibre mixture, others (minerals, trace elements, vitamins flavours).
[0077]The composition comprises 67.9 g digestible carbohydrates per 100 g:[0078]13.5 g glucose[0079]4.7 g fructose[0080]21.4 g lactose[0081]0.5 g digestible polysaccharides (maltodextrin)[0082]27.6 g starch
[0083]The composition comprises 2.2 g of the dietary fibre mixture per 100 g:[0084]2.1 wt. % medium chain pectin (from Ultra low viscosity pectin, Obipektin AG)[0085]47.9 wt. % inulin (from Raftiline ST, Orafti)[0086]8.1 wt. % resistant starch (from HI Maize 1043, National Starch)[0087]41.9 wt. % Oat Fibre (Vitacel Haferfaser HF 600-30, JRS)
[0088]Additionally the composition comprises 1.1 g fibre present in the cereal component. 26 g of the powder is reconstituted with 75 ml water, yielding about 100 ml. The viscosity at 20° C. and at ...
example 2
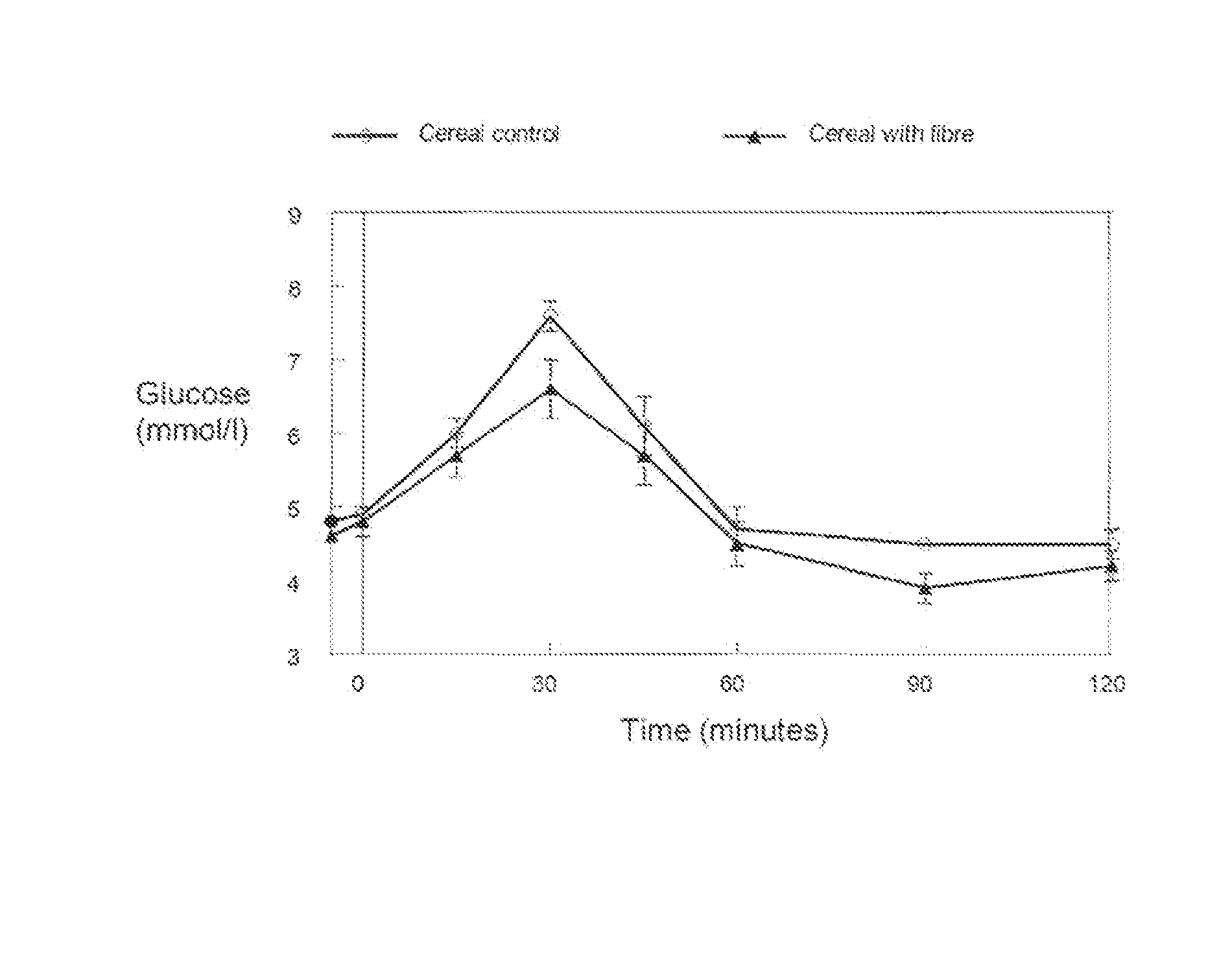
[0089]10 healthy adult volunteers consumed, in a cross over design, the cereal composition of example 1, reconstituted with water, comprising 25 g available, digestible carbohydrate and 1.2 g fibre (0.87 g deriving from the fibre mixture, 0.435 g fibre deriving from the cereal component) or a similar cereal composition but without the fibre mixture, reconstituted with water, comprising 25 g available, digestible carbohydrate and 0.435 g fibre deriving from the cereal. As a control 25 g glucose was consumed by the volunteers on a different day. Consumption of cereals or glucose occurred in the morning after overnight fasting. Blood glucose levels were determined at 5 minutes before consumption, at t=0, t=15, t=30, t=45, t=60, t=90 and t=120 min. Results are shown in FIG. 1 and table 1.
TABLE 1Average Incremental Area under the curve (IAUC) of BloodGlucose after Consumption of Glucose, Cereals with a FibreMixture or Cereals without Fibre Mixture.IAUC TestIAUC 25 gproductGlucoseGlucosem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com