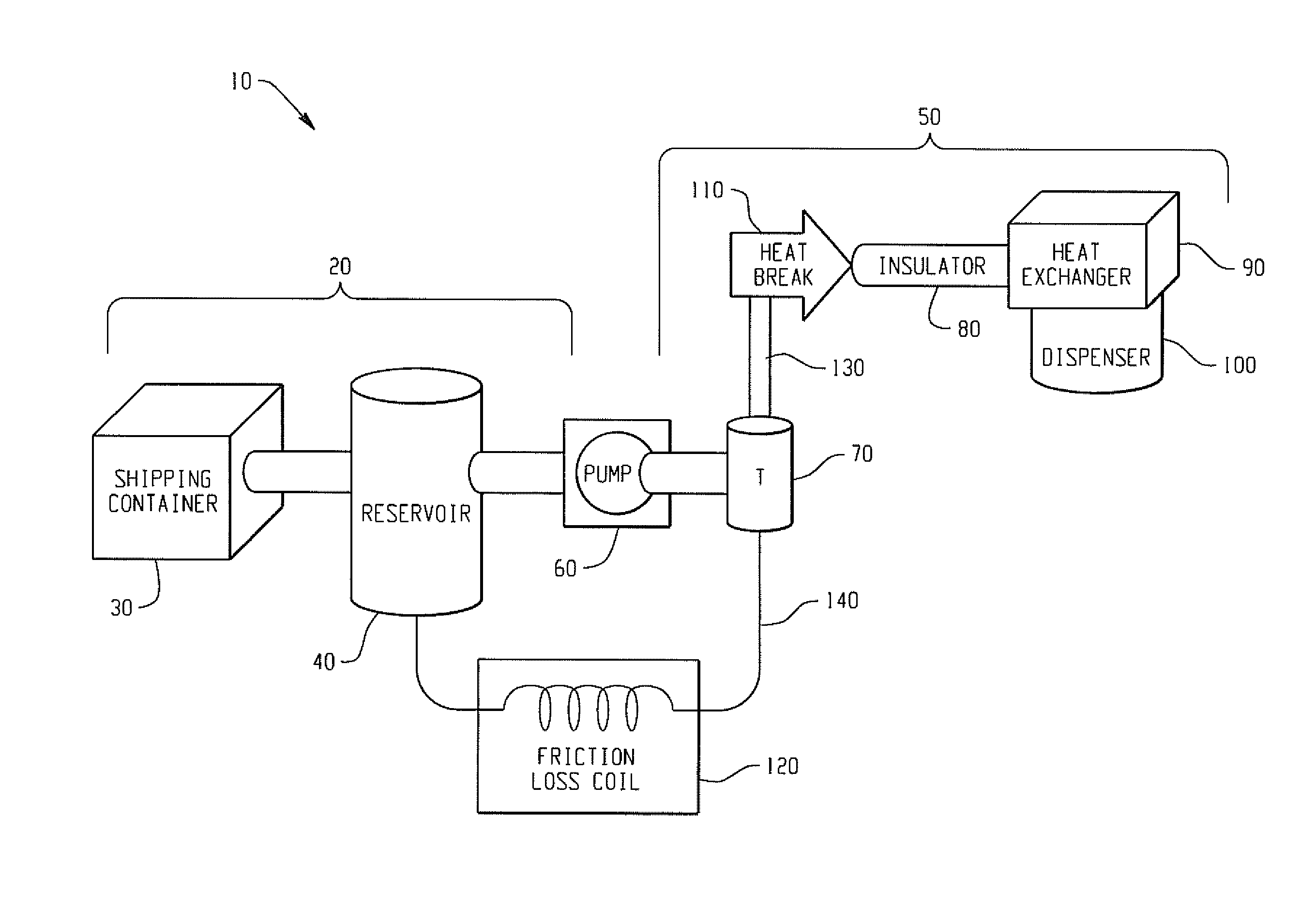
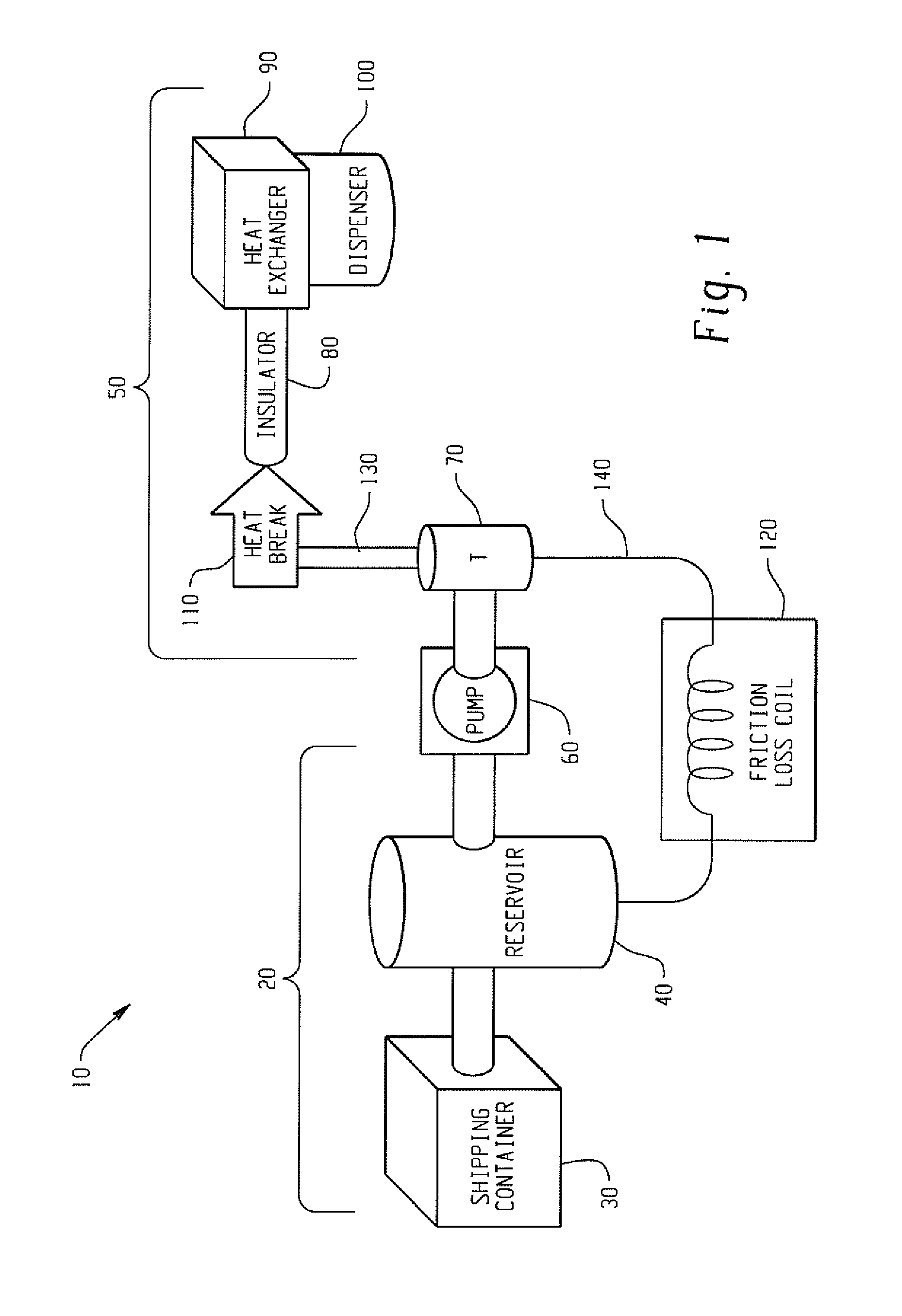
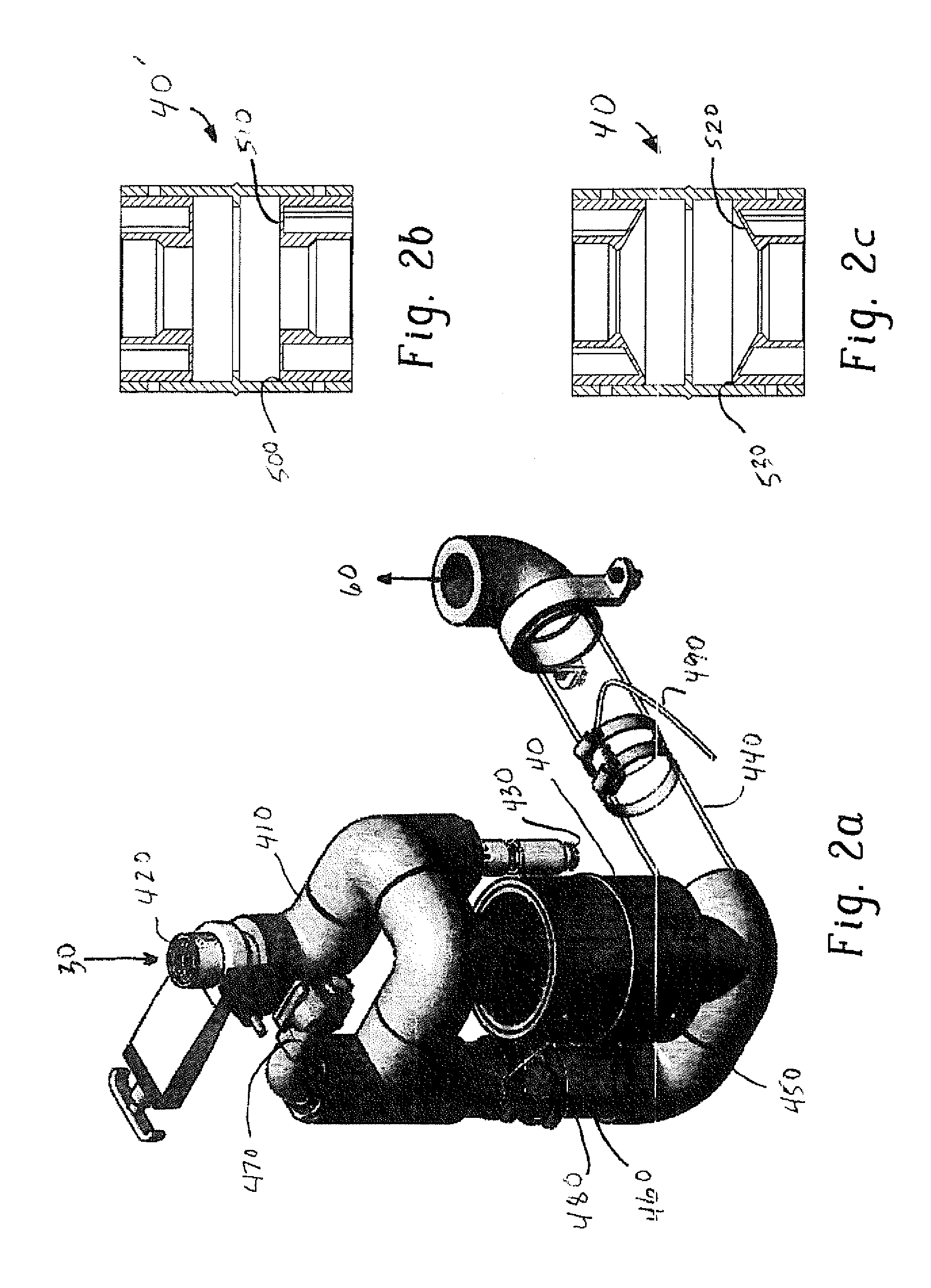
Improved, low viscosity, shelf stable, energy-actiivated compositions, equipment, sytems and methods for producing same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 2a-2b
Exemplary Intermediate Examples 2A-2B
[0177]In preparing the exemplary examples for intermediates, the polypropylene, polyethylene and silica were heated to approximately 260° F. to create a molten homogeneous liquid. The molten material was dispensed using a standard hot melt unit with a module fitted with a spray pattern nozzle to dispense the molten liquid into the room temperature soybean oil to create the first set of exemplary Intermediate Examples 2A-2B. In this example, the intermediate was dispersed in oil that created domains where the oil was well below the melting or solubility temperatures but above the room temperature in the regions where the molten homogeneous liquid enters the carrier.
TABLE 5Exemplary IntermediateExemplary IntermediateIngredient ID2A2BSoybean Oil41.541.5Polypropylene-116.516.5Polyethylene-100.25Silica0.50.5
examples 3a-3c
Exemplary Intermediate Examples 3A-3C
[0178]In another embodiment of the invention the oil and silica were heated to approximately 200 to 230° F. and the highest melting polymers which had melting points of about 300° F., polypropylene and maleated polypropylene, were added, stirred and allowed to bring the temperature down to less than 190° F. where the polymer having lower melting points of about 200° F., polyethylene, was added stirred and allowed to cool.
TABLE 6ComparativeComparativeComparativeIntermediateIntermediateIntermediateIngredient ID3A3B3CSoybean Oil41.541.540.5Polypropylene-116.516.516.5Maleated PP-1004Polyethylene-1033Silica0.50.50.5% Premix Total58.561.564.5
examples 4a-4e
Exemplary Intermediate Examples 4A-4E
[0179]In another embodiment of the invention the oil and silica was heated to approximately 130° F. and the highest melting polymers which had melting points of about 300° F., polypropylene and maleated polypropylene, were added, at which time the polymer having lower melting points of about 200° F., polyethylene, was added stirred and then the entire mixture was heat to 145° F. and the temperature is maintained for 20 minutes and then allowed to cool. Examples 4A and 4C.
[0180]Example 4B follows the same process as described for example 4A except for that at 100° F., the EVA is added to the formulation and mixed for 5 minutes. The mixture is then allowed to cool.
[0181]Example 4D follows the same process as described for example 4A except that instead of Silica, Pluronic F-127 surfactant is added to the oil at the start of the process.
[0182]Example 4E follows the same process as described for example 4A except that Irganox B225 is added to the oil...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com