Ophthalmic composition
a technology of ophthalmic composition and composition, applied in the field of ophthalmic composition, can solve the problems of eye strain, eye dryness for contact lens users, inhomogeneity, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing eye stress, suppressing eye dryness, and effectively reducing eye strain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
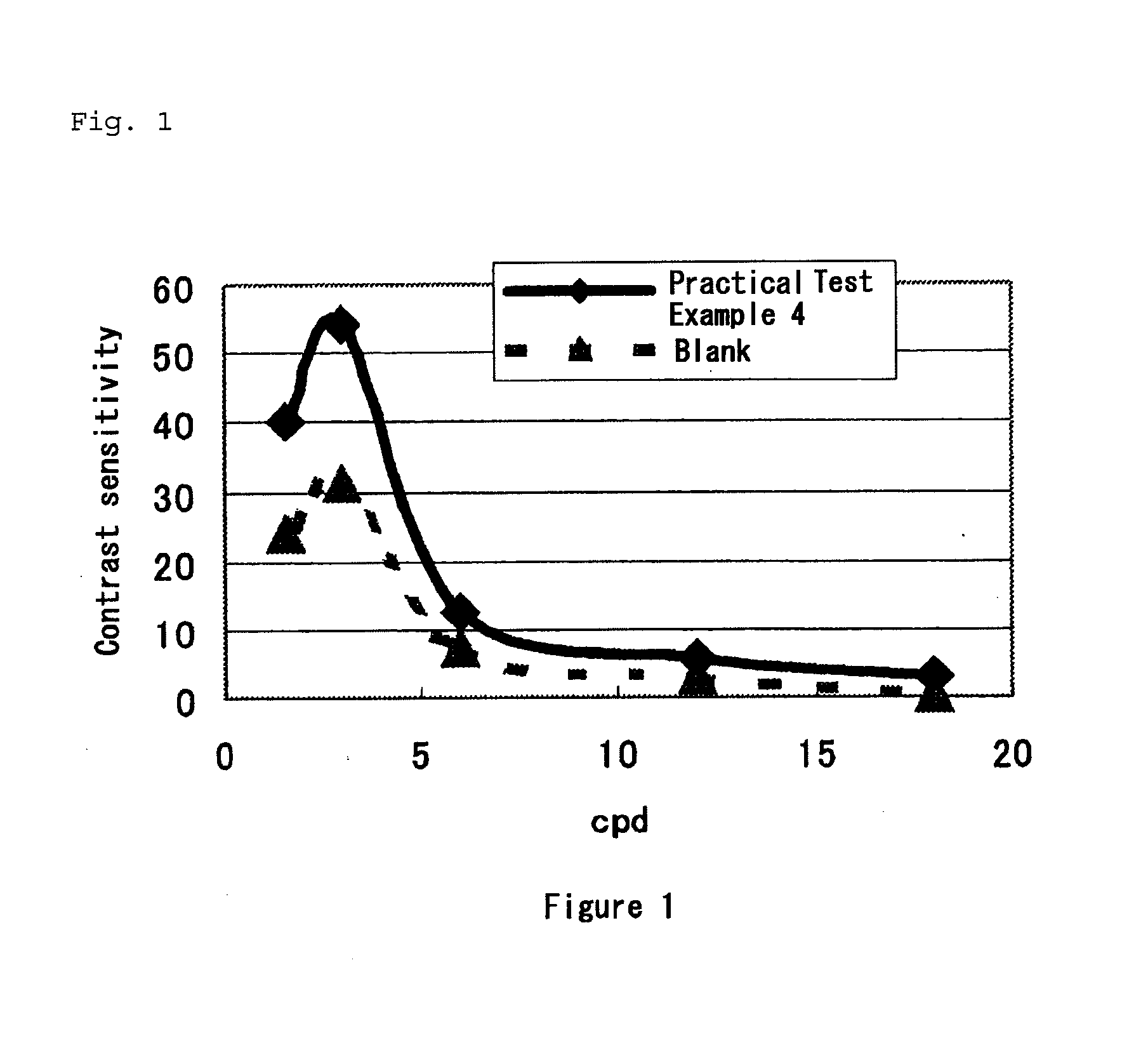
Image
Examples
examples
[0091]The present invention is illustrated in more detail by Test Examples and Examples, but should not be construed to be limited thereto.
[0092]In Test Examples, the tests were conducted as successively as possible to keep the measuring condition, in particular the subject's condition almost constant. Each Test Example was carried out independently.
[0093]The viscosities in each Example and Comparative Example were determined by using TVE-20L cone-plate type viscometer (manufactured by TOKIMEC Inc. and supplied by TOKI SANGYO, Co., Ltd., Japan), which is a kind of E-type viscometer, under the following measuring condition according to the manufacturer's instructions. Unless stated otherwise, the measurement was carried out according to the viscometric determination described in JP A 2006-348055. The measuring condition used was as follows.
Measuring Condition:
[0094]Rotational frequency: 100 rpm (the viscosity is measured at the highest rotational frequency among the measurable rotati...
examples 7 to 11
[0130]The wetting solution—eye drops for contact lenses (Examples 7 to 11) were prepared according to the formulations described in Table 18. The unit for each ingredient to be compounded in Table 18 is g / 100 mL. All these Examples showed similar effects of the invention as Example 1 in the above Tests 1 to 4.
TABLE 18Ex.Ex.Ex.Ex.Ex.7891011HPMC 1)———0.20.2Hydroxyethyl-0.20.6———cellulose 2)Polyvinyl alcohol————1(partially saponifiedproduct)Dextran 70——0.1——Macrogol 4000———1—l-Menthol0.010.010.005—0.015d-Camphor——0.001—0.01Peppermint oil———0.002—Geraniol——0.005——Mint oil———0.002—Bergamot oil————0.002Polysorbate 800.1———0.3POE hydrogenated—0.050.050.3—castor oil 60Poloxamer 407————0.1Sodium chloride0.440.220.440.440.44Potassium chloride0.080.080.080.080.08Boric acid1111—Borax0.20.20.20.2—Sodium dihydrogen————0.25phosphateDisodium hydrogen————0.05phosphateEdetate sodium0.050.050.050.050.05Polyhexanide————0.0001hydrochloridePurified waterq.s.q.s.q.s.q.s.q.s.Total volume100 mL100 mL100 mL1...
formulation example 1 to 10
[0137]The wetting solution—eye drops for contact lenses (Formulation Example 1 to 10) were prepared according to the prescriptions described in Table 20. The unit for each ingredient to be compounded in Table 20 is g / 100 mL.
TABLE 20-1Form.Form.Form.Form.Form.12345HPMC 1)0.010.2———Hydroxyethyl-——0.050.40.01cellulose 2)Polyvinyl alcohol——2——(partially saponifiedproduct)Polyvinylpyrrolidone2.5——1.5—K90Carboxy vinyl polymer—0.2——0.2l-Menthol0.010.0050.0150.004—d-Camphor0.0080.0050.010——Peppermint oil———0.005—Geraniol————0.005Bergamot oil————0.002Polysorbate 800.05———0.1POE hydrogenated0.050.50.10.2—castor oil 60Potassium magnesium—1———aspartateEpsilon-aminocaproic———2—acidSodium chloride0.440.220.440.440.3Potassium chloride0.080.080.080.080.08Boric acid11—1.81Borax0.20.2—0.20.2Disodium hydrogen——0.3——phosphate•12 hydratesSodium dihydrogen——0.02——phosphate•2hydratesEdetate sodium0.050.050.050.010.2Polyhexanide—0.0001———hydrochloridePotassium sorbate——0.1——Purified waterq.s.q.s.q.s.q.s.q....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com