Alkylation process comprising monitoring ionic liquid catalyst acidity
a technology acidity, which is applied in the direction of organic chemistry, physical/chemical process catalysts, organic compounds/hydrides/coordination complex catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of deactivation, loss of activity, and need to be replaced, so as to achieve sufficient reaction, efficiently regenerated and recycled, and the effect of monitoring the deactivation level of ionic liquid catalys
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of N-Butylpyridinium Chloroaluminate Catalyst
N-butylpyridinium chloroaluminate (C5H5C4H9Al2Cl7) ionic liquid catalyst was purchased. The catalyst had the following composition.
Wt % Al12.4Wt % Cl56.5Wt % C24.6Wt % H3.2Wt % N3.3
example 2
C4 Olefin and Isobutane Alkylation
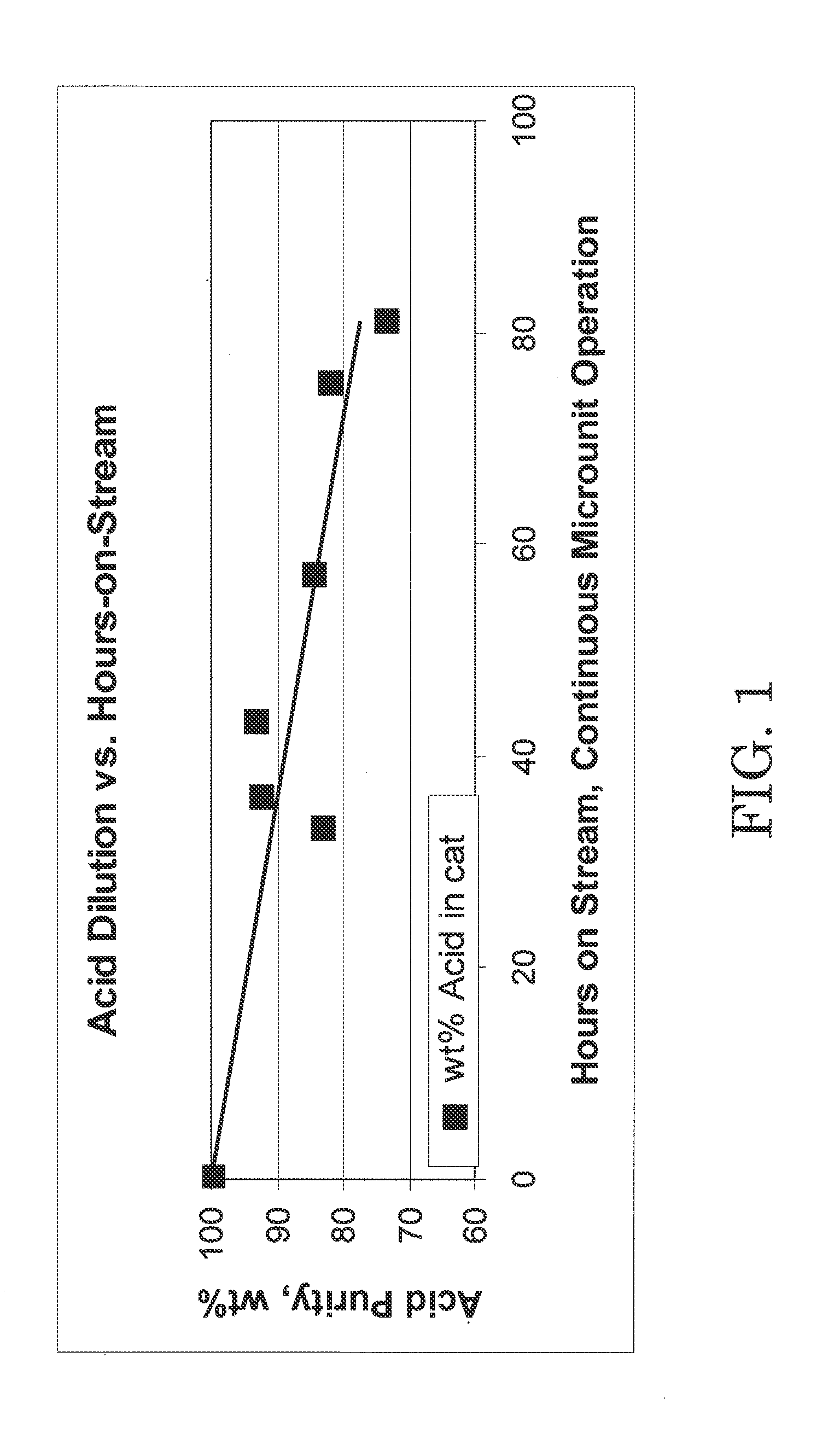
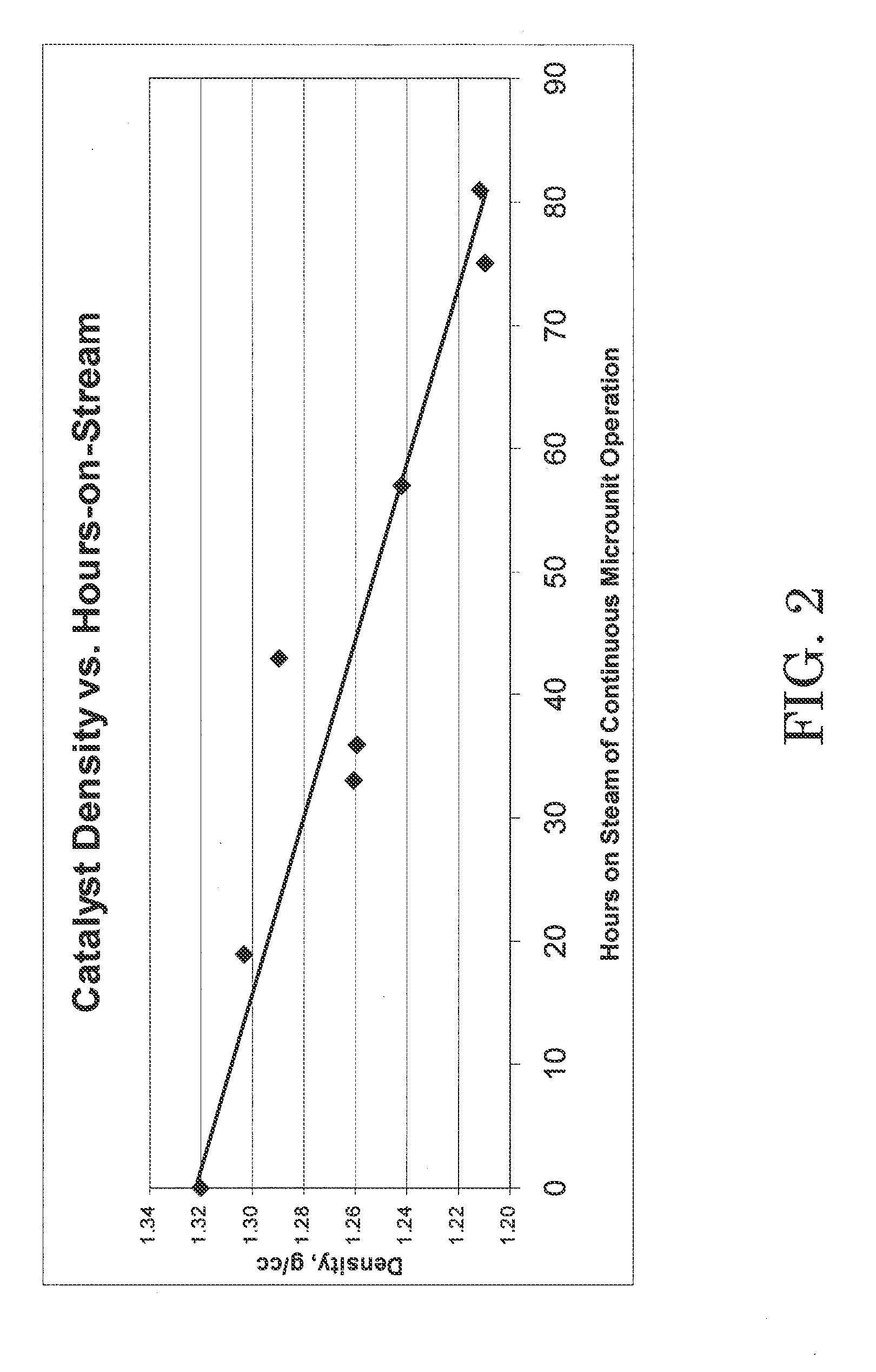
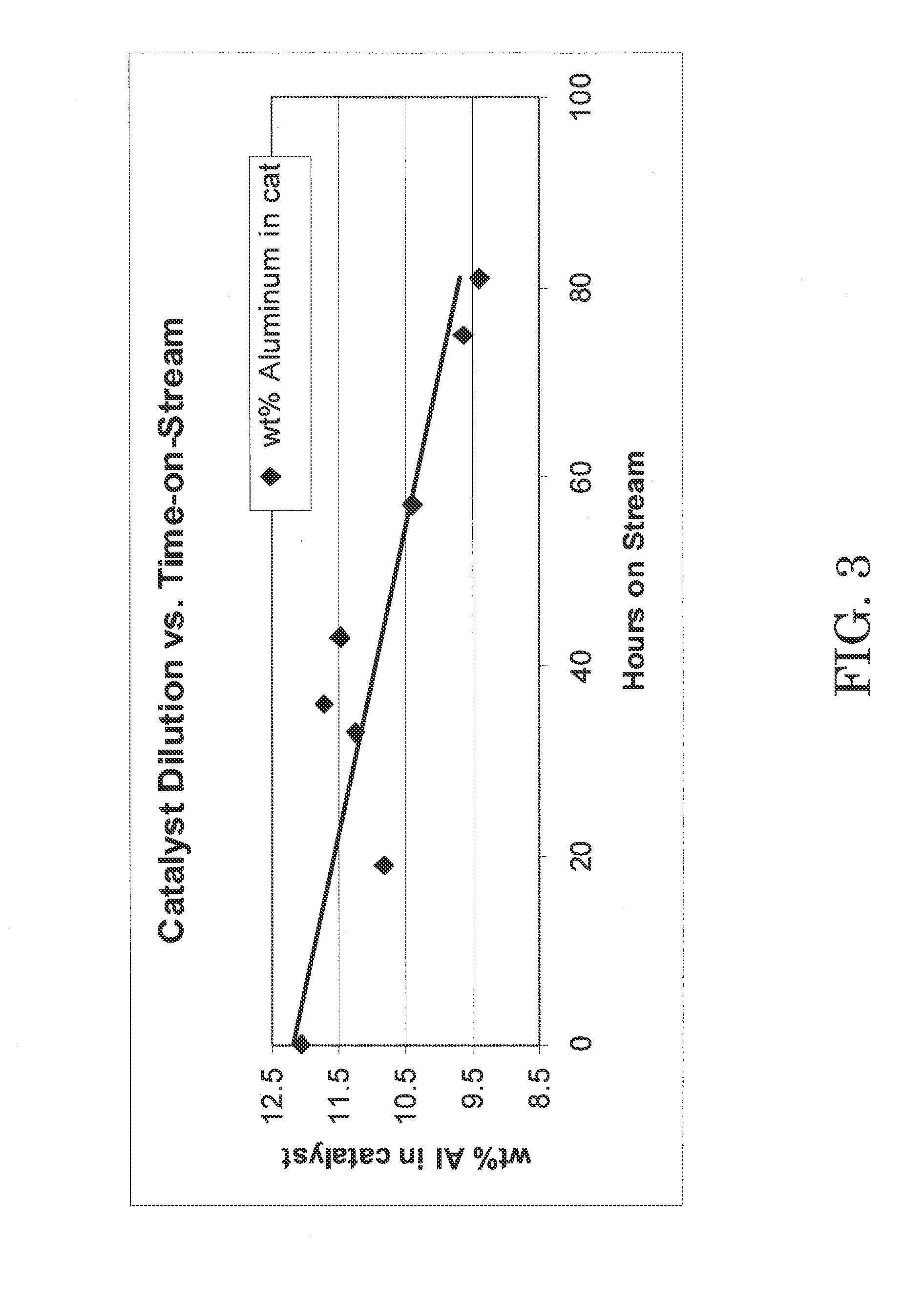
C4 olefin alkylation with isobutane was performed in a 100 cc continuously stirred tank reactor. A mixture of isobutane and 2-butene having a 8:1 molar ratio was fed to the reactor while vigorously stirring at 1600 RPM. The chloroaluminate ionic liquid catalyst of Example 1 was fed to the reactor via a second inlet port targeting to occupy 8 vol % in the reactor. A small amount of anhydrous HCl gas was added to the process. The average residence time (combined volume of feeds and catalyst) was about 8 minutes. The outlet pressure was maintained at 100 psig using a backpressure regulator. The reactor temperature was maintained at 0° C. using external cooling. The reactor effluent was separated in a 3-phase separator into C4-gas, an alkylate hydrocarbon phase, and the ionic liquid catalyst. The ionic liquid catalyst was recycled back to the reactor continuously. The amount of catalyst in the system was about 220 g, and the catalyst circulation was 100...
example 3
Measurement of Properties of Fresh and Used Catalyst
The total acidity of the fresh catalyst used in Example 2 and the used catalyst drained in Example 2 was determined using an acid / base titration method as follows. An automatic potentiometric titrator was set up using 100 mL of nitrogen purged, de-aerated water and isopropyl alcohol mixture in a beaker. The solution in the beaker was blanketed with dry nitrogen gas and stirred. Using an airtight syringe, a catalyst sample was drawn to transfer approximately 0.05 g into the beaker. The weight charged to the beaker was determined by difference to the nearest 0.0001 g. The catalyst sample charged to the beaker dissolved in the water / isopropyl mixture rapidly, and the pH value of the solution decreased. The resulting solution was titrated with standardized 0.1 N KOH solution to the same potential as the blank. A well-defined inflection point was shown in the resulting titration curve around pH 7. From the amount of KOH solution consume...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com