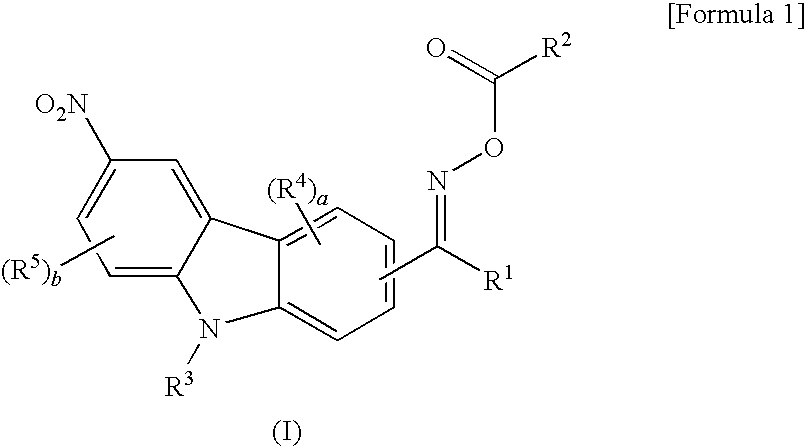
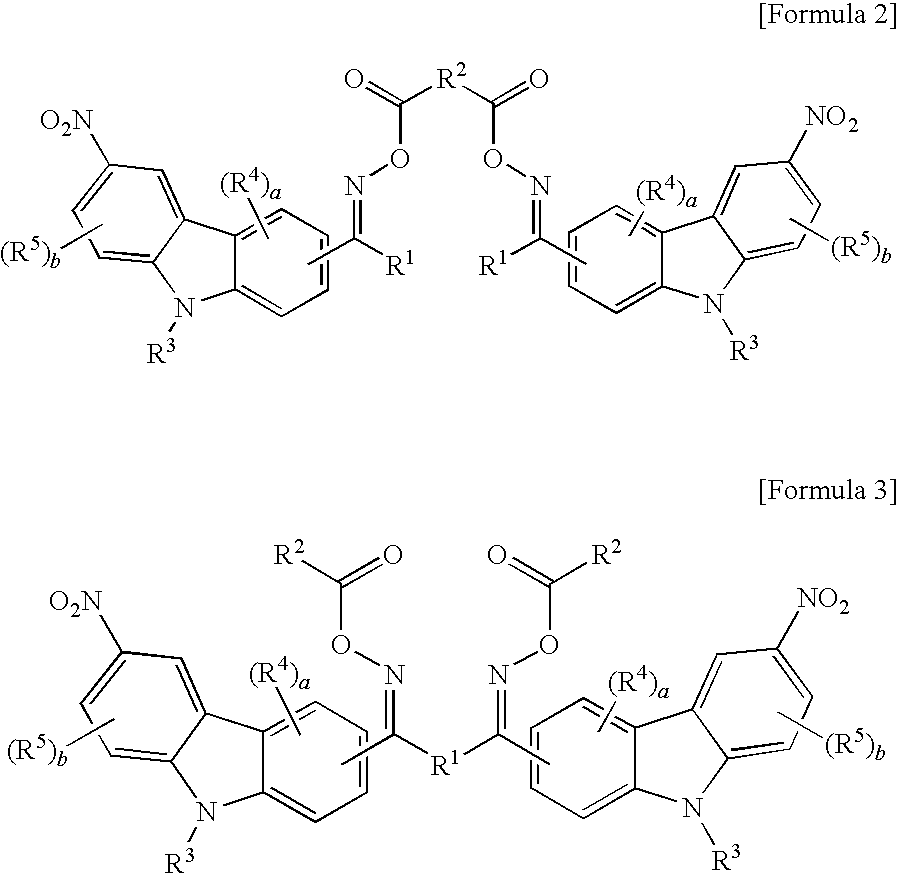
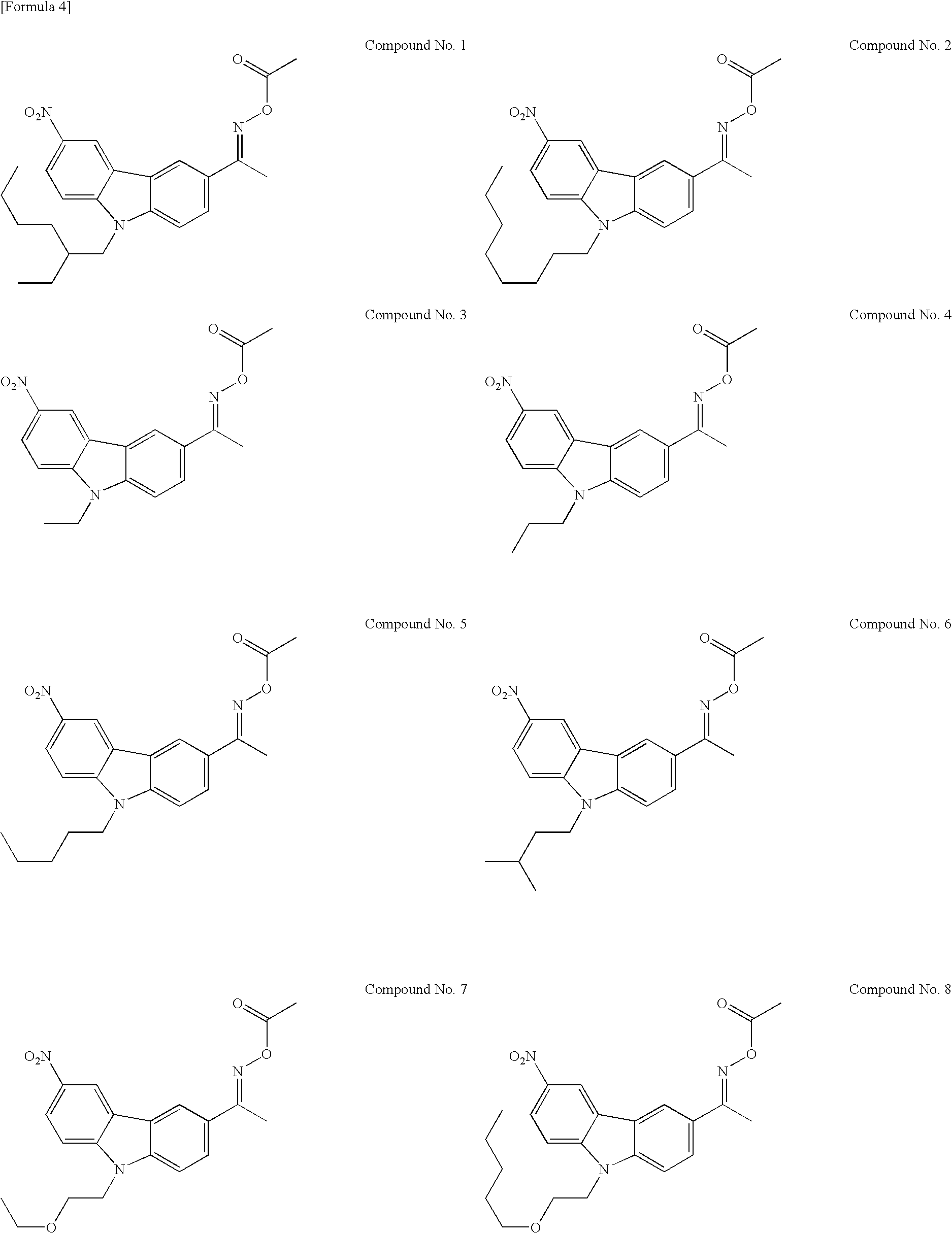
Oxime ester compound and photopolymerization initiator containing the same
a technology of oxime ester and initiator, which is applied in the direction of photomechanical equipment, instruments, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient sensitivity of known o-acyl oxime compounds, and achieve the effect of efficient absorption and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0062]The present invention will now be illustrated in greater detail with reference to Examples, but it should be understood that the invention is not deemed to be limited thereto.
examples 1-1 to 1-22
Preparation of compound Nos. 1 to 3, 7, 10, 12, 20, 33, 45 to 51, and 53 to 58
Step 1—Preparation of Acylated Compound
[0063]In a nitrogen atmosphere, 10.4 g (78 mmol) of aluminum chloride and 33.0 g of dichloroethane were put in a reactor. In the same atmosphere, 36 mmol of an acid chloride and then 30 mmol of a nitrocarbazole compound and 33.0 g of dichloroethane were added slowly while cooling with ice, followed by stirring at 5° C. for 30 minutes. The reaction mixture was poured into ice-water for oil-water separation. The solvent was removed to give a desired acylated compound.
Step 2—Preparation of compound Nos. 1 to 3, 7, 10, 12, 20, 33, 45 to 51, and 53 to 58
[0064]In a reactor were charged 20 mmol of the acylated compound obtained in step (1), 2.1 g (30 mmol) of hydroxylamine hydrochloride, and 16.9 g of dimethylformamide and stirred at 80° C. for 1 hour in a nitrogen stream. The reaction system was cooled to room temperature, followed by oil-water separation. The solvent was r...
example 2
Preparation of Photosensitive Composition No. 1
[0065]To 14.0 g of an acrylic copolymer were added 5.90 g of trimethylolpropane triacrylate, 2.70 g of compound No. 1 obtained in Example 1-1, and 79.0 g of ethyl cellosolve, and the mixture was thoroughly stirred to obtain photosensitive composition No. 1.
[0066]The acrylic copolymer used above was obtained by dissolving 20 parts by mass of methacrylic acid, 15 parts by mass of hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 10 parts by mass of methyl methacrylate, and 55 parts by mass of butyl methacrylate in 300 parts by mass of ethyl cellosolve, adding thereto 0.75 parts by mass of azobisisobutyronitrile, followed by heating at 70° C. for 5 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com