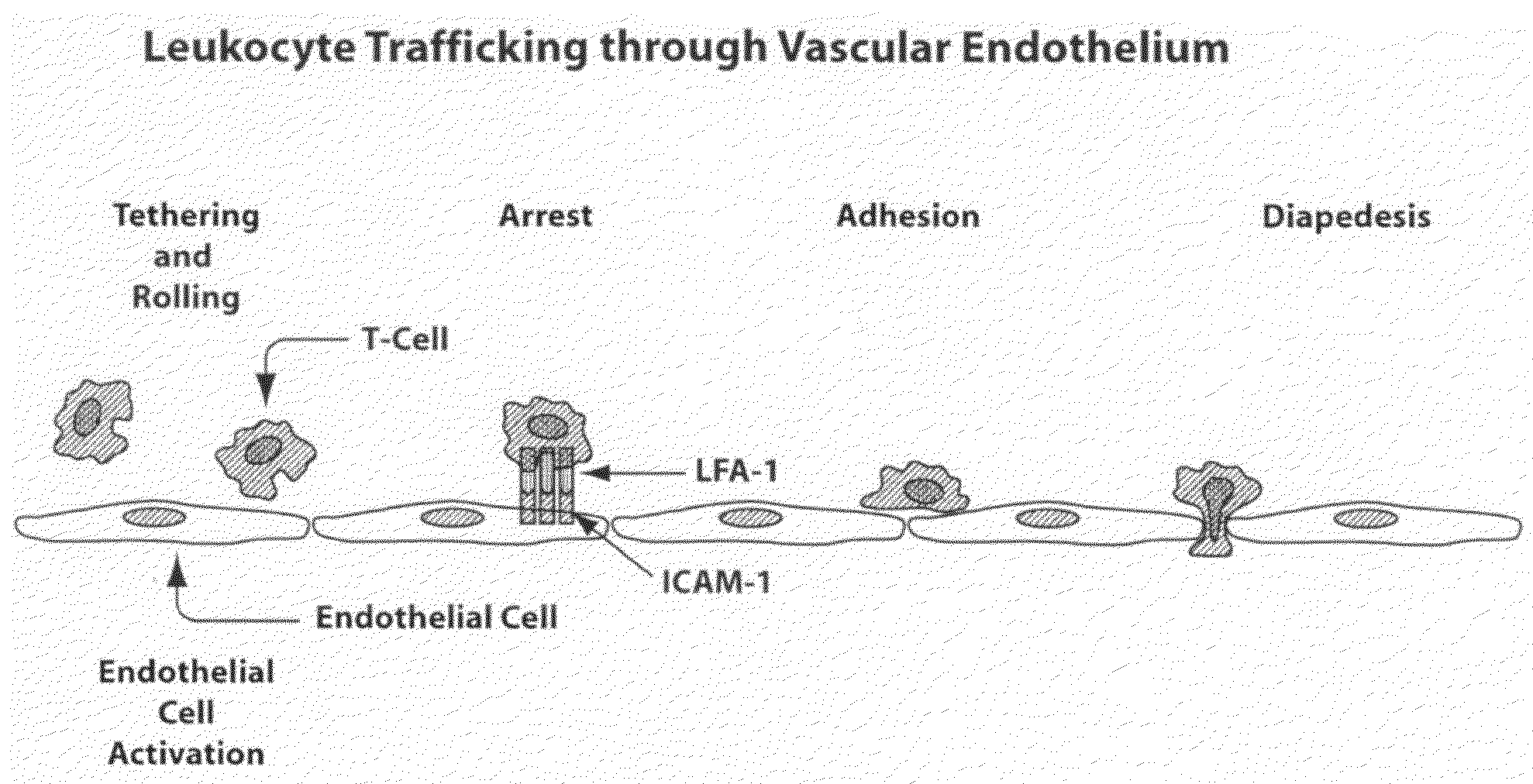
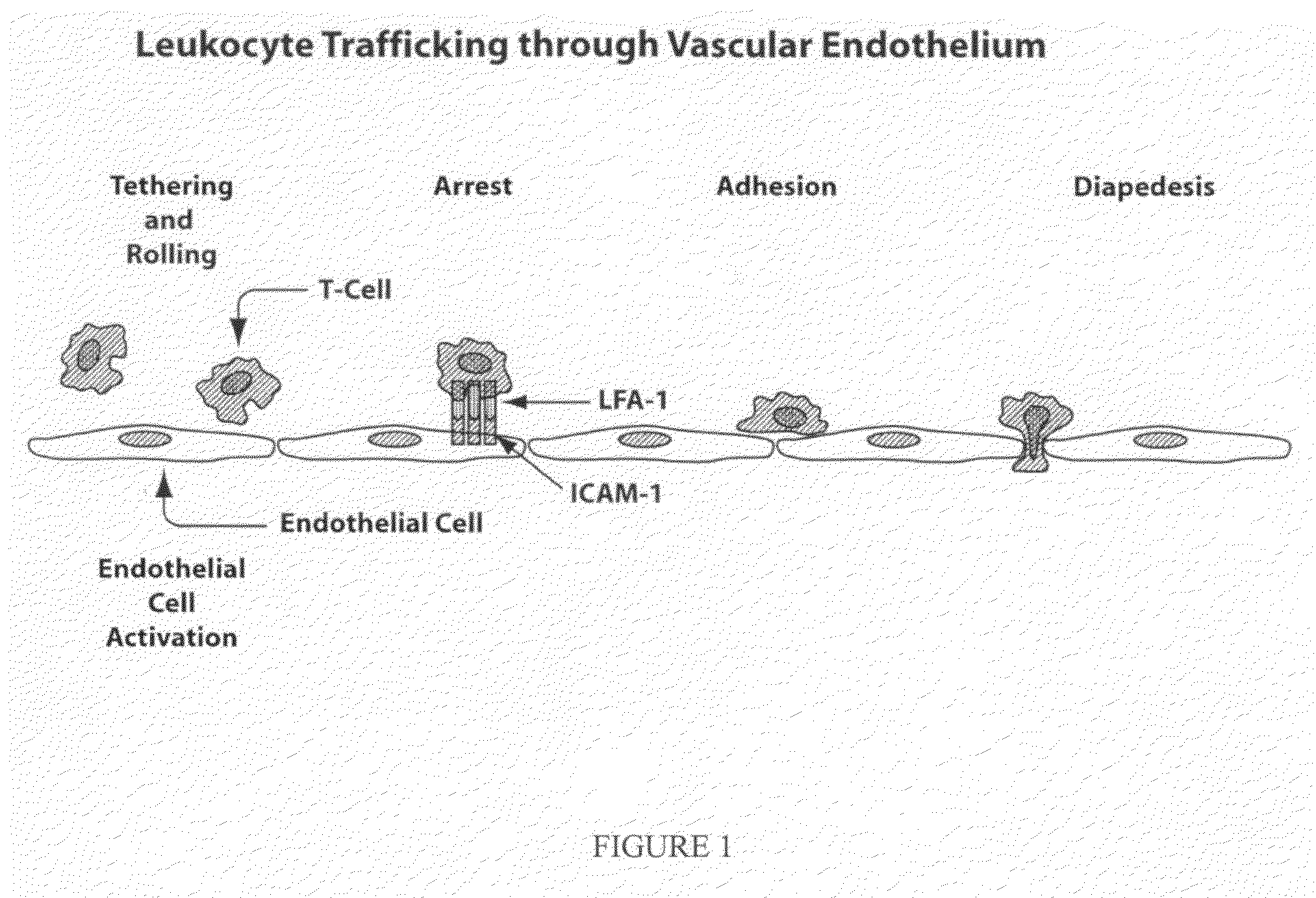
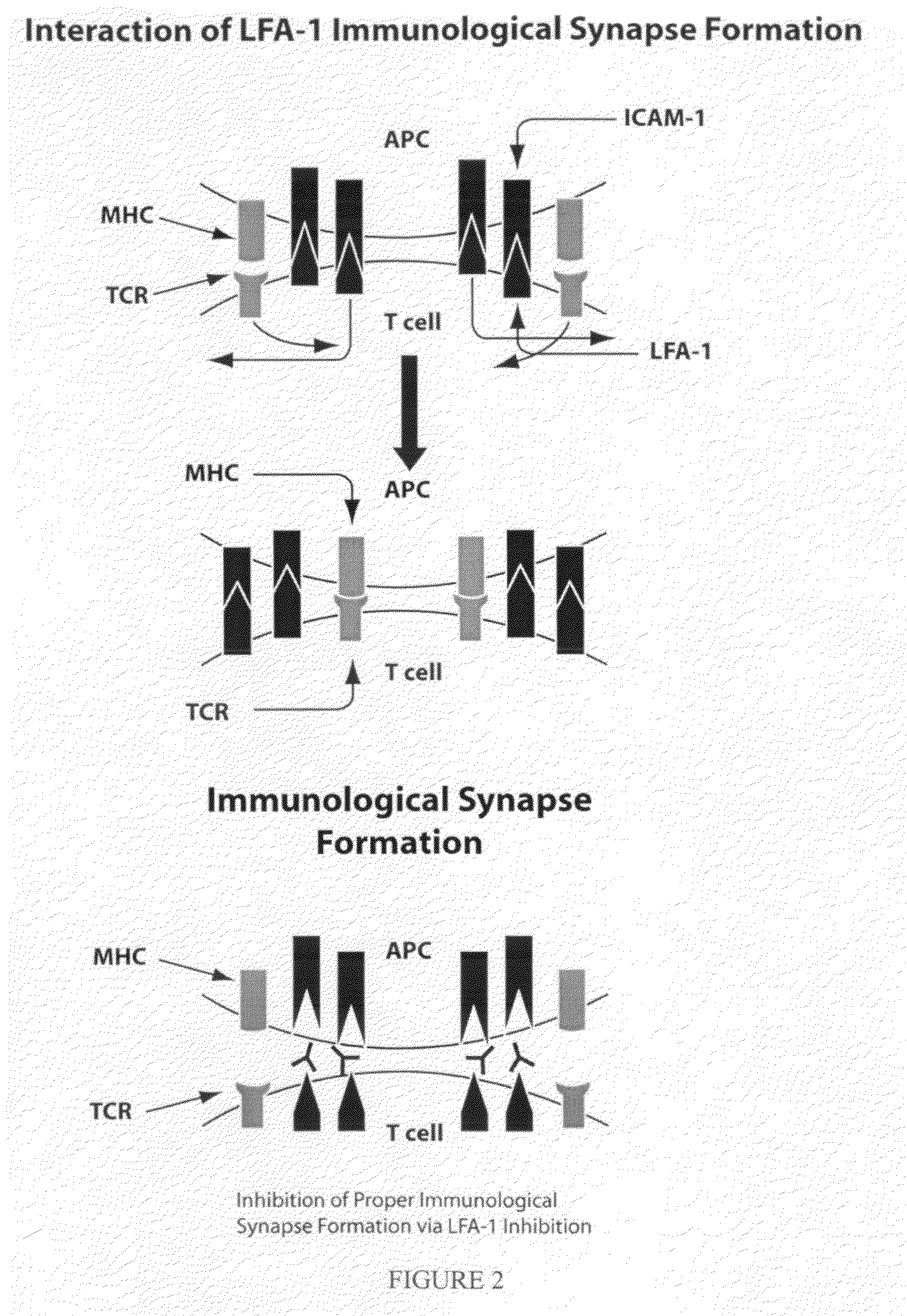
Compositions and methods for treatment of diabetic retinopathy
a technology for diabetic retinopathy and compositions, applied in the field of compositions and methods for treating diabetic retinopathy, can solve the problems of loss of workplace and personal functions following such loss of visual function, and achieve the effect of reducing and/or preventing macular edema
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Affinity Measurements
[0353]The affinities of the small molecules for LFA-1 were measured using fluorescence polarization (FP) in a competitive format with a small molecule antagonist, compound 1 (FIG. 2), as previously described. All measurements were performed in buffer containing 50 mM Hepes, pH 7.2, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% n-octyglucoside and 0.05% bovine gamma globulins (BGG) and either 1 mM MnCl2, or 1 mM CaCl2 and 1 mM MgCl2. The affinity of compound 1 for LFA-1 was first measured by addition of 2 nM compound 1 to serial dilutions of LFA-1 starting from 1 μM in buffer containing either MnCl2 or CaCl2 and MgCl2. Competition experiments were performed by addition of serial dilutions of antagonists to 2 nM compound 1 (using either 3 nM LFA-1 (in MnCl2) or 40 nM LFA-1 (in CaCl2 and MgCl2)). In the ICAM-1-Ig competition experiments, the LFA-1 concentrations were reduced to 2 and 20 nM LFA-1 in the two divalent cation buffer conditions to maximize inhibition by ICAM-1-Ig. The different L...
example 2
LFA-1 / ICAM-1 and LFA-1 / Small Molecule Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISAs)
[0354](A) Antagonist Competition: Small molecules and sICAM-1 were assayed for the ability to disrupt binding of ICAM-1-Ig or a fluorescein-labeled small molecule antagonist, compound 2B, to LFA-1 in a competitive format. Compound 2B is similar to compound 1, but with a longer linker between the small molecule and fluorescein to maximize the binding of the anti-fluorescein detection antibody. 96-well plates were coated with 5 μg / ml (33.3 nM) mouse anti-human β2 integrin (a non-function blocking antibody) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) overnight at 4° C. The plates were blocked with assay buffer (20 mM Hepes, pH 7.2, 140 mM NaCl, 1 mM MnCl2, 0.5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 0.05% Tween-20) for 1 hour at room temperature. After washing in buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MnCl2, and 0.05% Tween-20), 8 nM LFA-1 (LFA-1 / ICAM-1 ELISA) or 2 nM LFA-1 (LFA-1 / small molecule ELISA) were adde...
example 3
Crosslinking of a Radiolabeled, Photoactivatable Analogue of Compound 3 to LFA-1
[0356]Full length human membrane-associated LFA-1 or BSA (0.35 mg / mL [1.4 and 5.3 μM, respectively] in 20 mM Hepes, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM CaCl2, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM MnCl2, and 1% n-octylglucoside, pH 7.2) was incubated overnight at 37° C. with 4.1 μM compound 5, a tritium-labeled photoactivatable analogue of compound 3, in either the presence or absence of 290 μM compound 3. The molar ratio of compound 5 to LFA-1 was 3:1. A 96-well plate precoated with 1% BSA was used for the incubation. Just prior to crosslinking, excess compound 5 was rapidly removed by gel filtration with a G-25 microspin column in a 96-well format equilibrated with the same buffer. The LFA-1 / compound 5 complex was crosslinked by exposure to a high-pressure mercury-vapor lamp (450 watts, Ace glass, Vineland, N.J.). During irradiation, samples were cooled on ice and protected by a 5-mm thick plate of borosilicate glass to minimize protein deg...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com