Fuel Cell, Method and Apparatus for Manufacturing Fuel Cell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first example embodiment
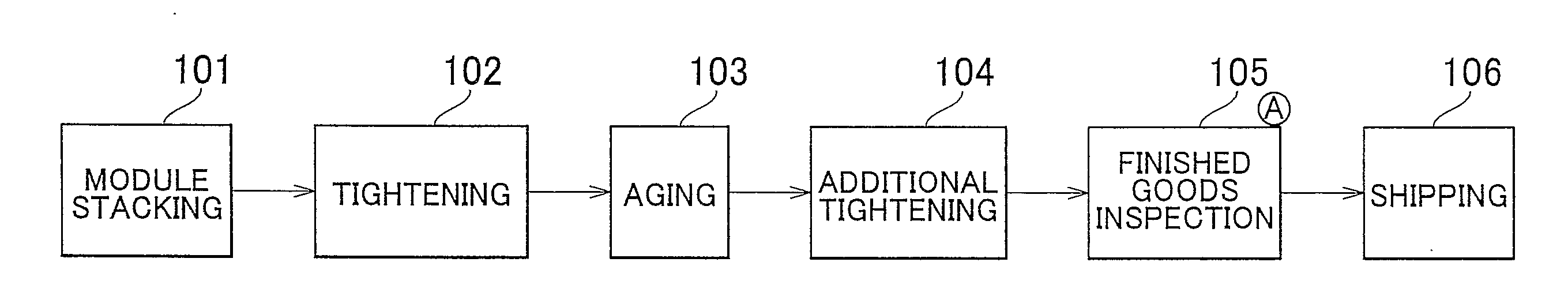
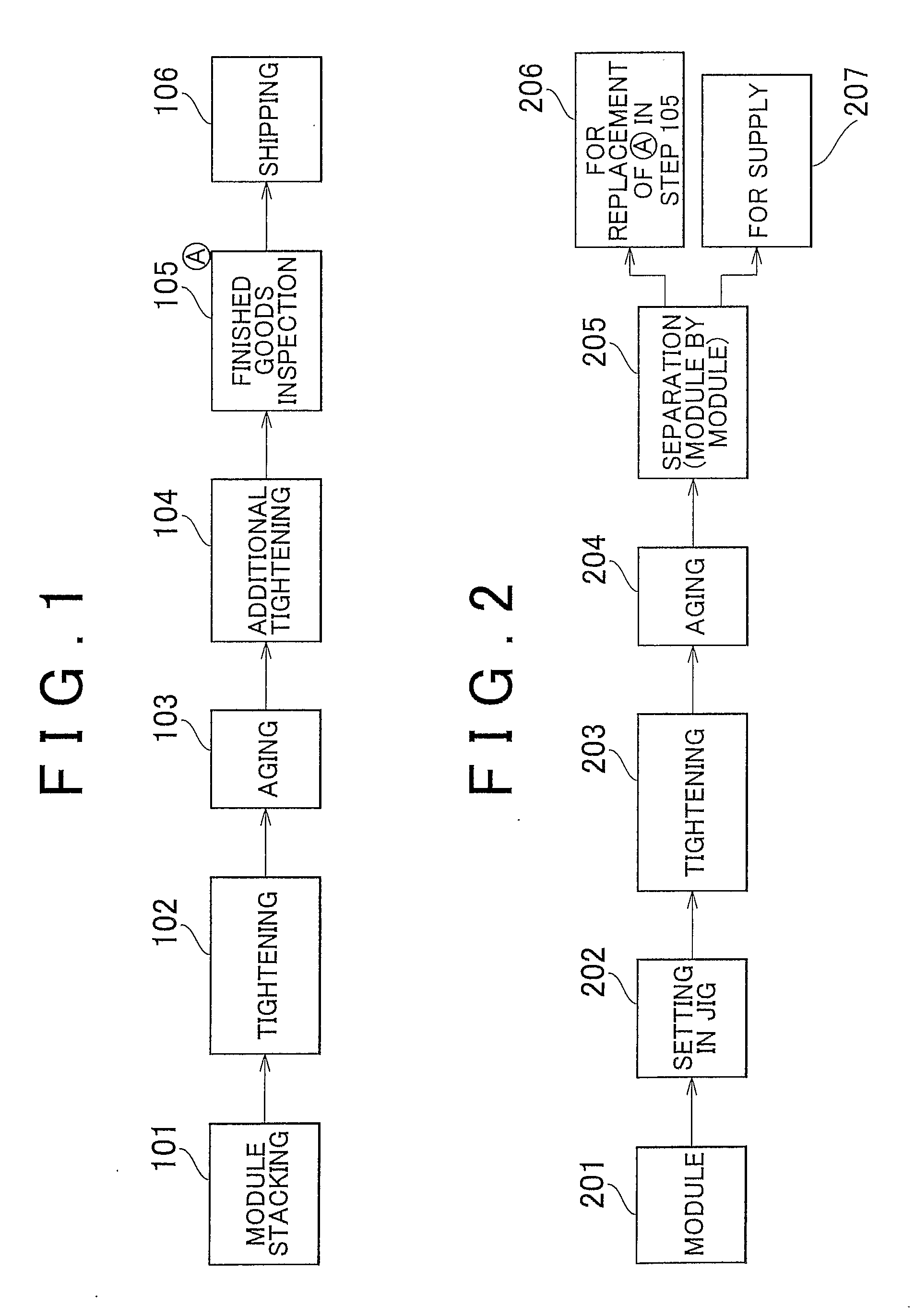
FIG. 1
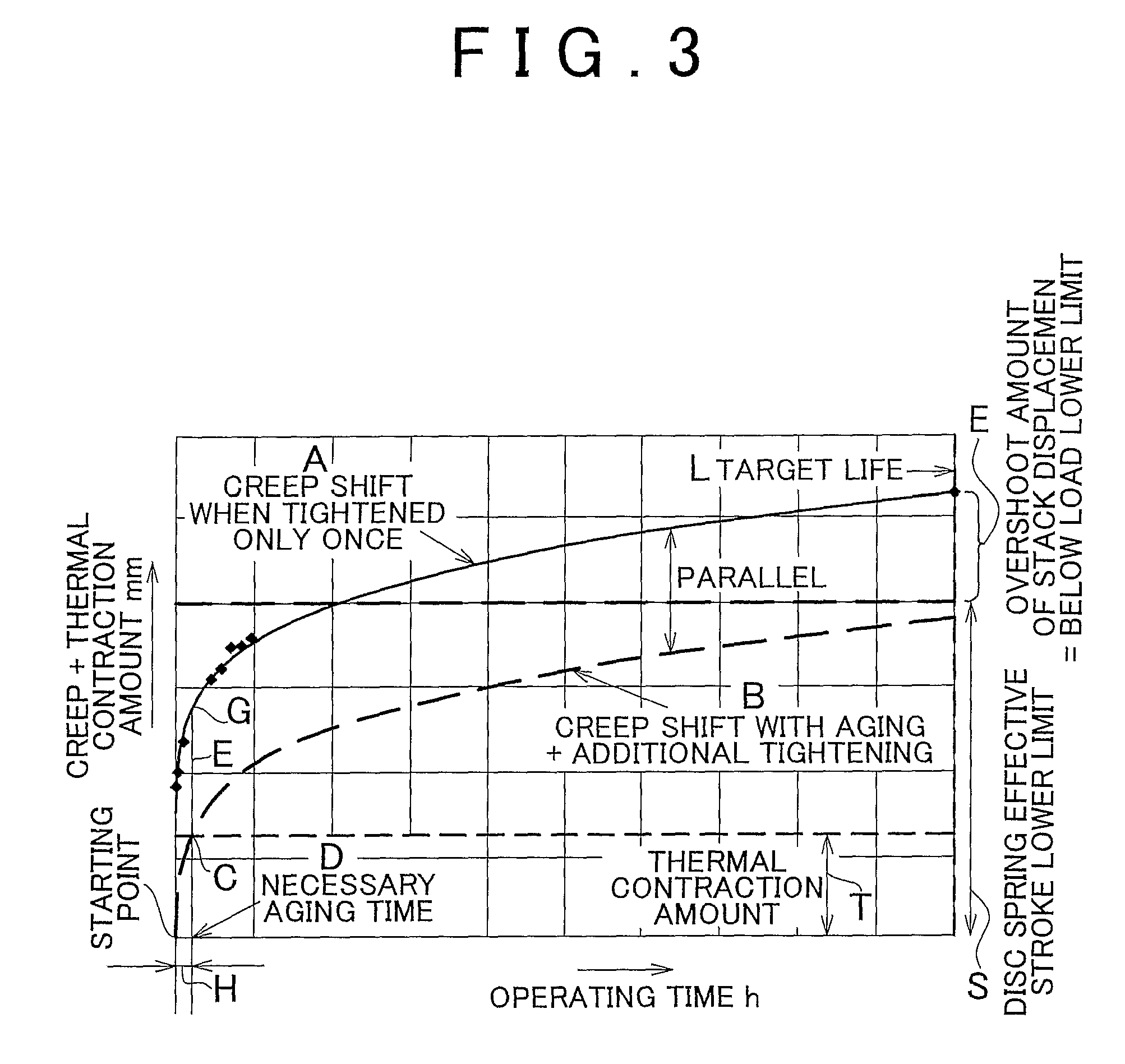
[0066]The fuel cell (the stack 23 or the single cell 10) according to the first example embodiment of the invention is manufactured according to FIG. 1. Also, the manufacturing method of the fuel cell (the stack 23 or the single cell 10) according to the first example embodiment of the invention is a manufacturing method according to the steps shown in FIG. 1. The manufacturing method of a fuel cell (the stack 23 or the single cell 10) according to the first example embodiment of the invention is a manufacturing method of a fuel cell, which includes an aging step 103 for progressing through initial creep by applying at least a compression load to a cell module after stacking, and an additional tightening step 104 for additionally tightening the fuel cell stack 23 after the aging step 103.
[0067]In the fuel cell (the stack 23 or the single cell 10) and the manufacturing method thereof according to the first example embodiment of the invention, as shown in FIG. 1, the cell module...
second example embodiment
FIG. 2
[0071]The fuel cell (the stack 23 or the single cell 10) according to the second example embodiment of the invention is manufactured according to FIG. 2. Also, the manufacturing method of the fuel cell (the stack 23 or the single cell 10) according to the second example embodiment of the invention is a manufacturing method according to the steps shown in FIG. 2. The manufacturing method of a fuel cell (the stack 23 or the single cell 10) according to the second example embodiment of the invention includes an aging step for progressing through initial creep by applying at least a compression load to a cell module before stacking, and an incorporating step for incorporating the cell module into the stack after the initial creep has been progressed.
[0072]With the fuel cell (the stack 23 or the single cell 10) and the manufacturing method thereof according to the second example embodiment, as shown in FIG. 2, cell modules are supplied in step 201. The cell module is set, either in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com