Sesamol Derivatives as Novel Inhibitors of Arachidonic Acid Formation
a technology of arachidonic acid and derivatives, which is applied in the direction of drug compositions, metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disorders, etc., can solve the problems of difficult synthesizing, potential toxicity of sesamol, and toxicity of sesame lignans, so as to reduce or completely eliminate the toxicity of sesamol
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Acylated Sesamol Derivatives
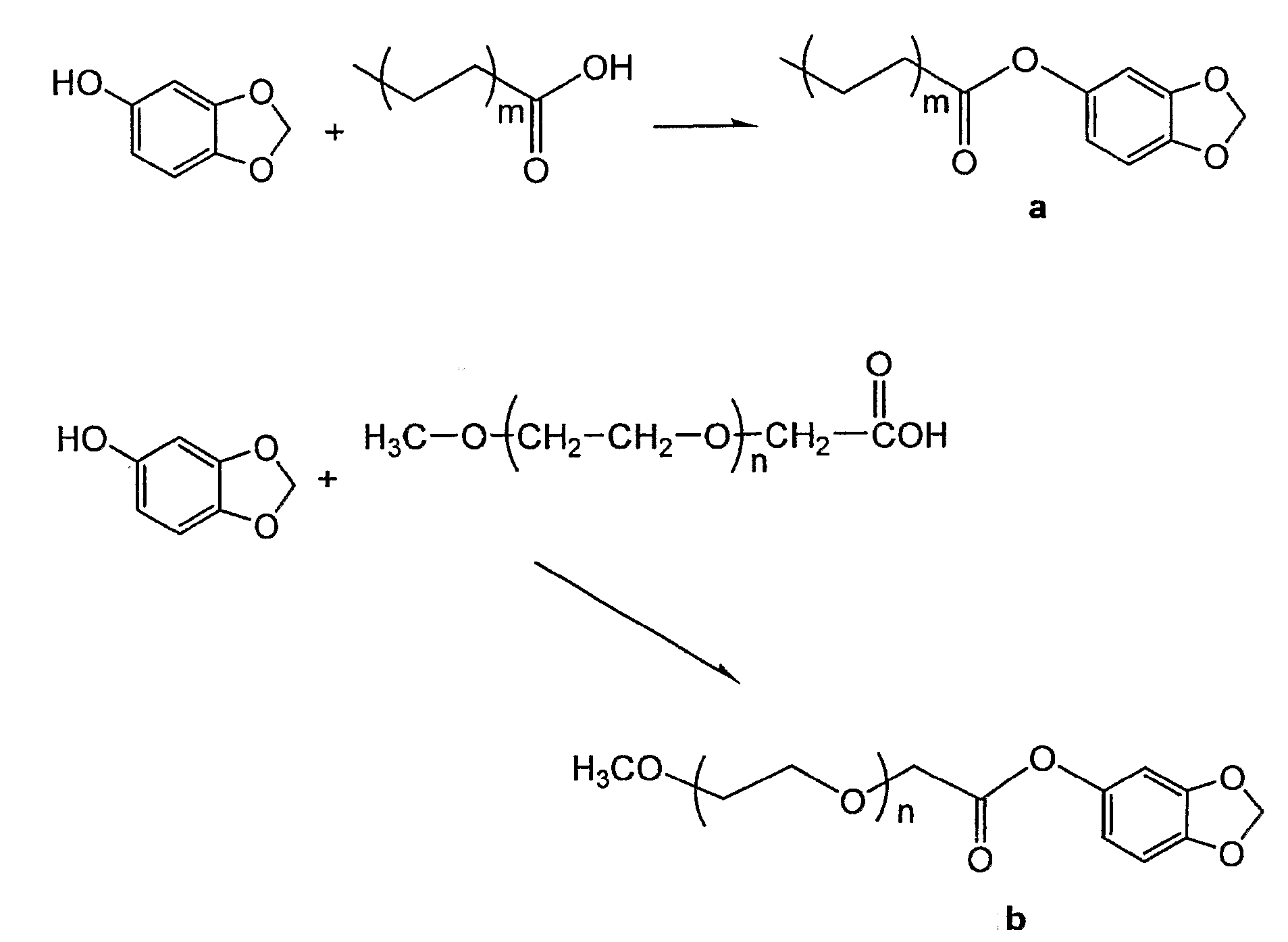
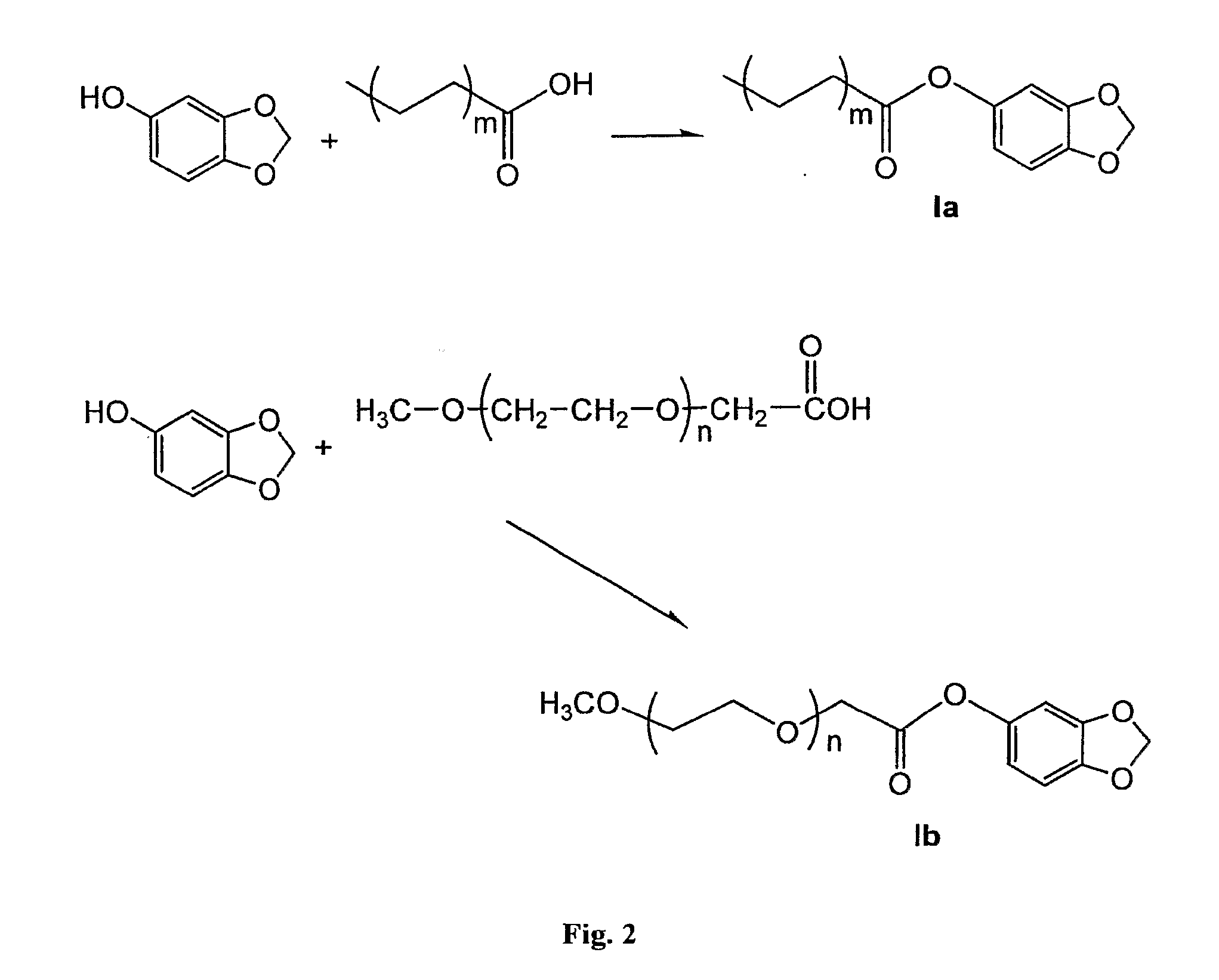
[0019]Fatty acid is activated using a 1:1 molar amount of 1,1 carbonyl diimidazole in a dry benzene solution. The solution is taken to dryness at the completion of the activation. To the dried compound is added an equimolar amount of sesamol. The combined reactants are heated under vacuum at a low temperature for 1-2 hours. The completeness of the reaction is determined by thin layer chromatography. The acylated sesamol is then isolated by column chromatography to yield the isolated invention. The physical state of the invention depends on the chain length of the fatty acid and its degree of unsaturation.
example 2
Preparation of Sesamol Oleate
[0020]17.7 mmoles of oleic acid was dissolved in 40 ml of dry benzene. To the mixture was added 17.7 mmoles of 1,1 carbonyldiimidazole. The reaction to activate the oleic acid was continued at room temperature until vigorous evolution of carbon monoxide has ceased. The reaction was then driven to completion by driving off the excess benzene under vacuum at 60° C. To the neat activated oleic acid was added 21 mmoles of sesamol. The mixture was heated at 60° C. for 2 hours under vacuum with constant rotation. The crude reaction mixture was purified using 50 grams of silica gel 60 in 2×44 cm column eluting with hexane and increasing percentages of acetone. The fractions containing the active compound were collected and evaporated to dryness giving 10 mmoles of the sesamol oleate for a 56% yield. HPLC chromatography using a 98:2 cyclohexanone / isopropyl eluting solvent give a single component with greater than 90% purity.
example 3
Polyethylene Oxide Sesamol Derivatives
[0021]Methoxy polyethylene oxide molecules of various chain lengths are oxidized by KMnO4 to yield a carboxylic acid derivative. The carboxylic acid derivative of methoxy polyethylene oxide is activated using a 1:1 molar amount of 1,1 carbonyl diimidazole in a dry benzene solution. The solution is taken to dryness at the completion of the activation. To the dried compound is added an equimolar amount of sesamol. The combined reactants are heated under vacuum at a low temperature for 1-2 hours. The completeness of the reaction is determined by thin layer chromatography. The acylated sesamol is then isolated by column chromatography to yield the isolated invention. The physical state of the invention depends on the chain length of the methoxy polyethylene oxide molecule.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| carboxylic acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compositions | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| chemical structures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com