Methods and Systems for Preventing Iron Oxide Formulation and Decarburization During Steel Tempering
a technology of iron oxide and steel tempering, which is applied in the field of metal heat treatment processes, can solve the problems of hcl, sulfuric acid, concentrated hydrochloric acid, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing iron oxide formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032]Before describing the disclosed embodiments of this technology in detail, it is to be understood that the technology is not limited in its application to the details of the particular arrangement shown here since the technology described is capable of other embodiments. Also, the terminology used herein is for the purpose of description and not of limitation.
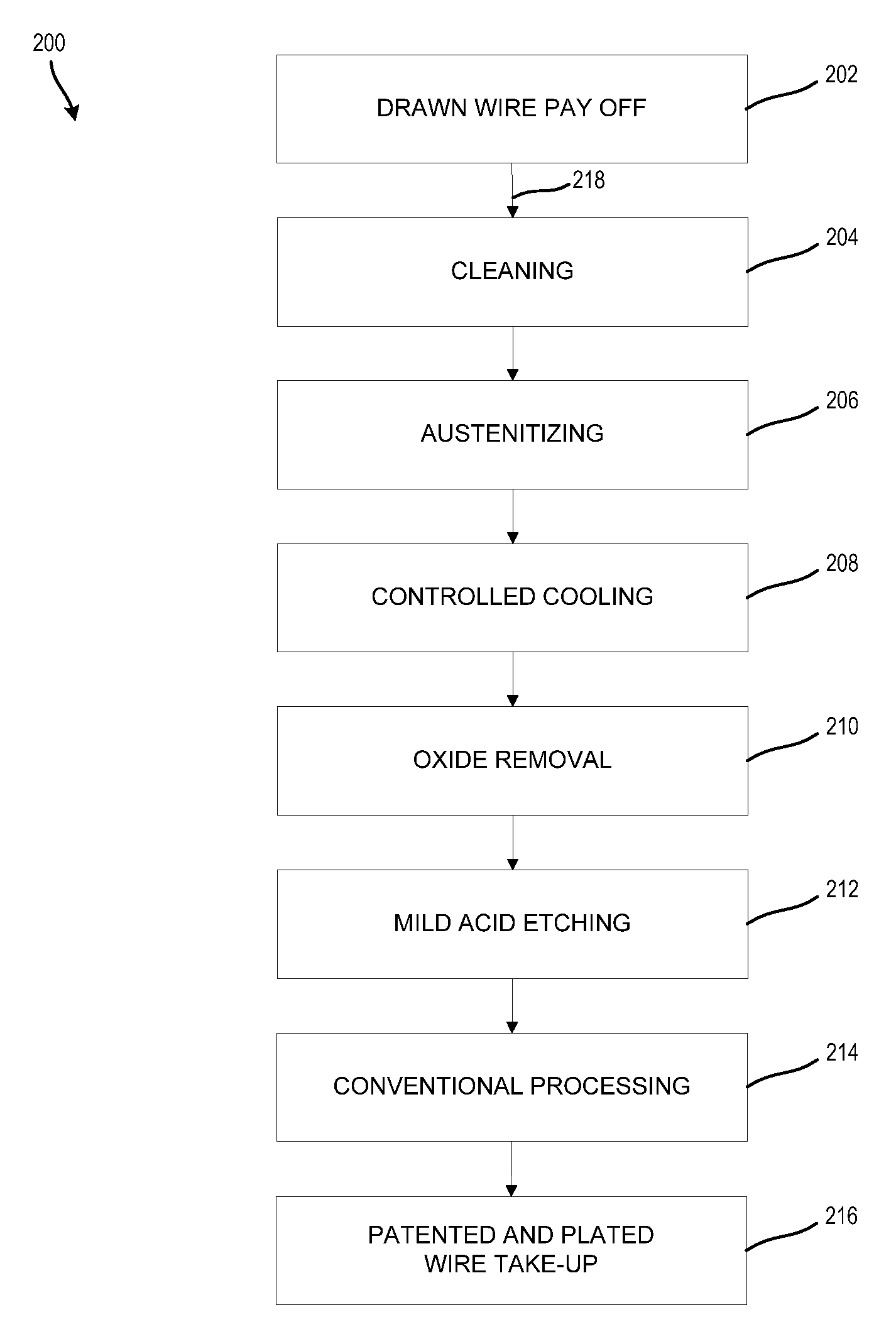
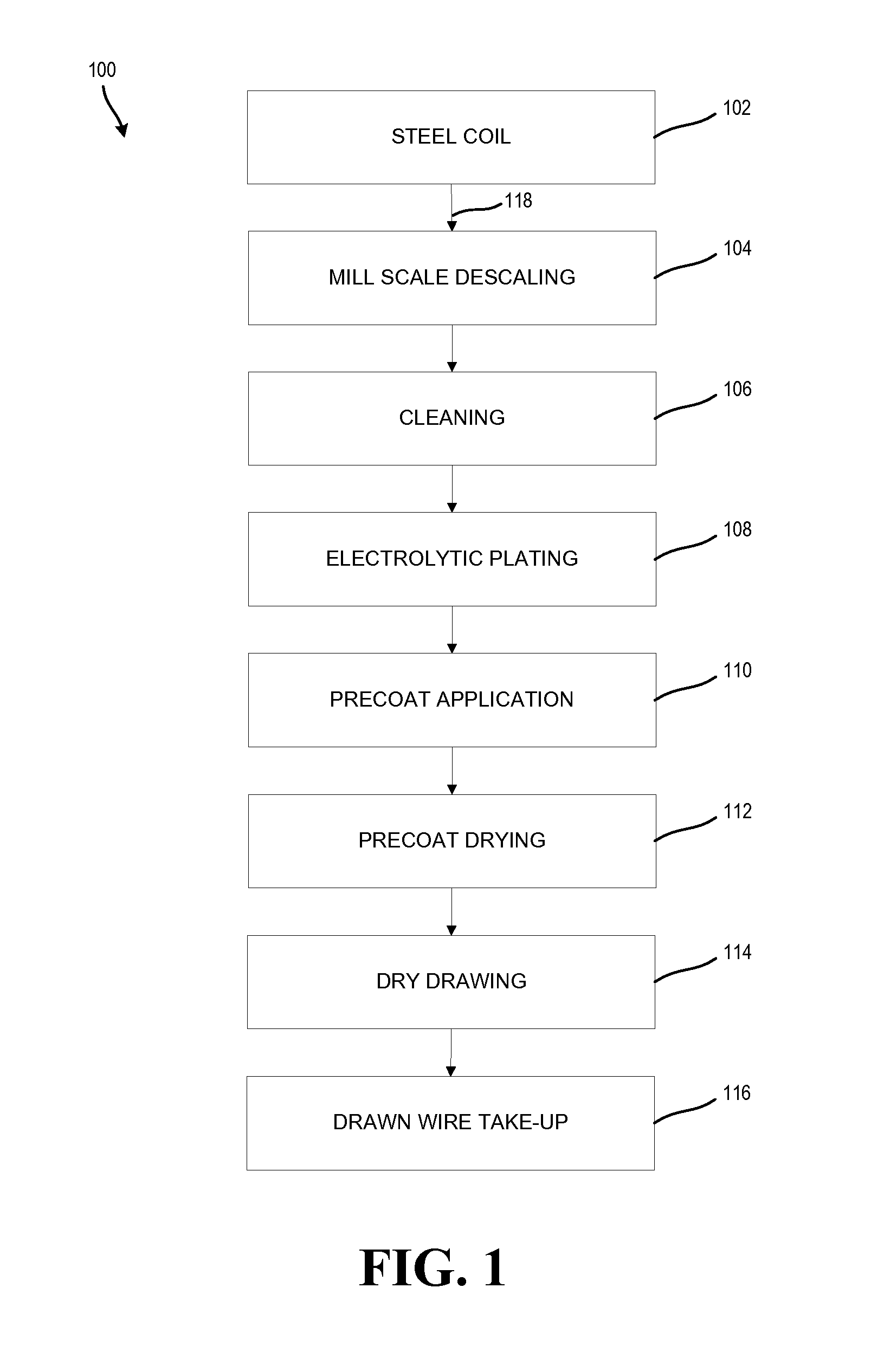
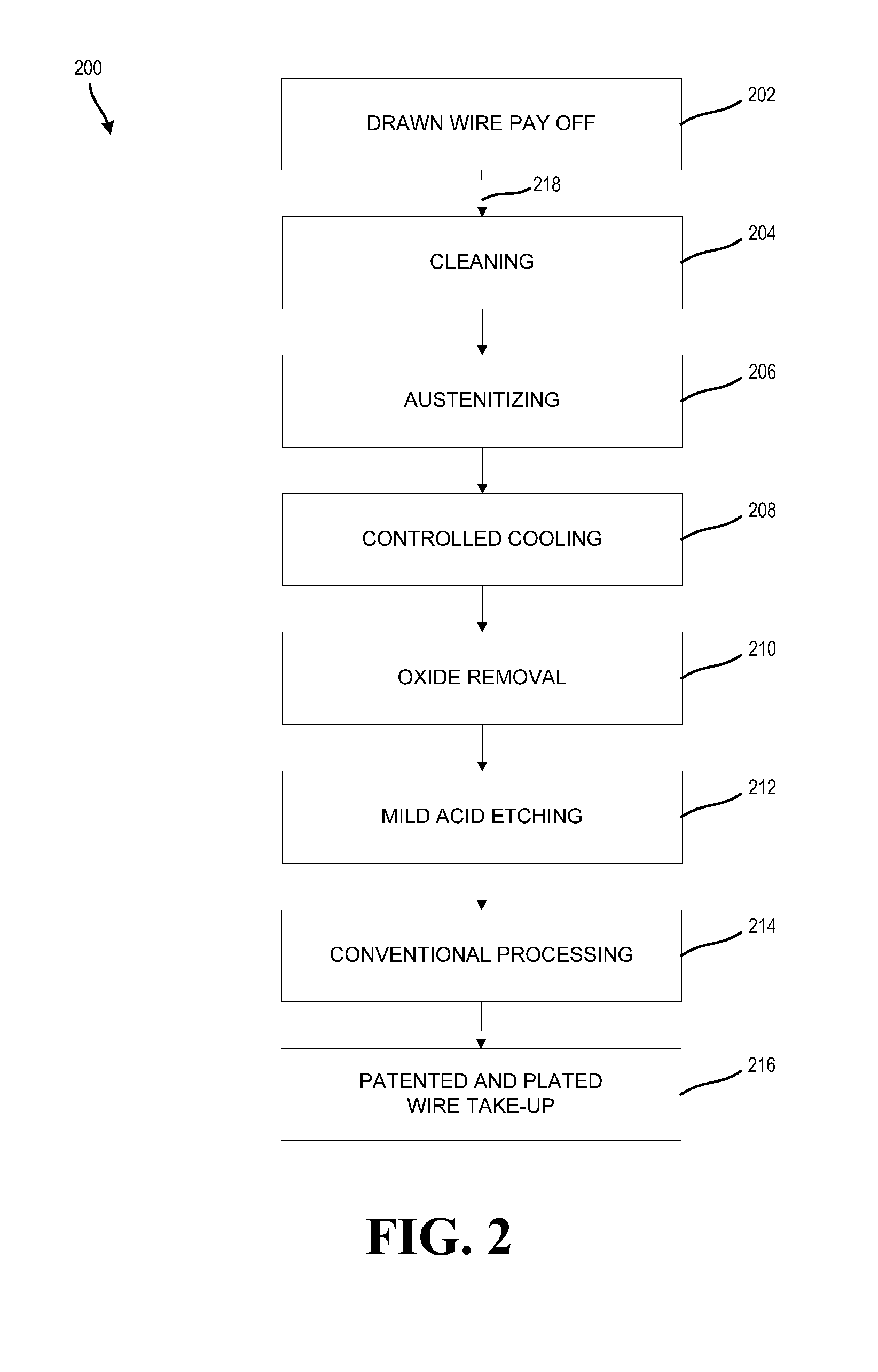
[0033]In various exemplary embodiments, the technology described herein provides systems and methods to prevent iron oxide formation and decarburization during strand heat treating of a steel product without the required use of acid pickling. Additionally, this technology provides placing a coating, such as copper pyrophosphate electrolytic plating, to the surface of a steel wire prior to strand heat treating to avoid both the iron oxide formation and decarburization through the surface of the steel wire by preventing interactions between the steel wire and the furnace atmosphere. Furthermore, the technology prevents iron ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com