Multiplexed analysis of polymorphic loci by concurrent interrogation and enzyme-mediated detection
a polymorphic locus and multi-layered technology, applied in the field of molecular diagnostics and genetic typing or profiling, can solve the problems of high labor intensity, low sample throughput, and high complexity, and achieve the effect of reducing the degree of degeneracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
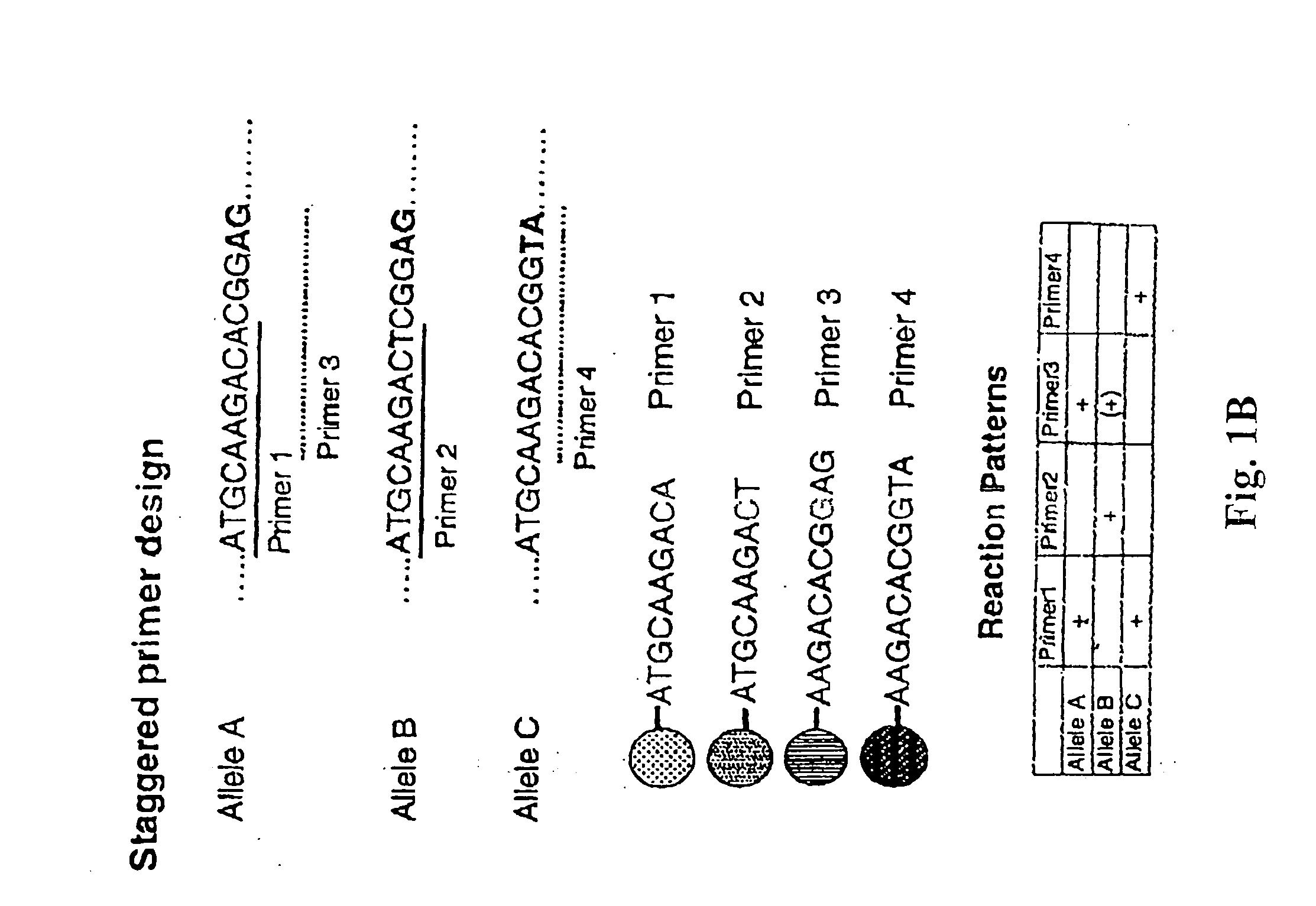
Staggered Probe Design for Multiplexed SSP Analysis
[0140]Probes for each polymorphism are immobilized on a solid phase carrier to provide a format in which multiple concurrent annealing and extension reactions can proceed with minimal mutual interference. Specifically, this method provides a design which accommodates overlapping probes, as illustrated in FIG. 1. In this example, we consider three alleles: allele A, allele B and allele C. Probes 1 and 2 detect SNPs that are aligned with their respective. 3′ termini while probes 3 and 4 detect two-nucleotide polymorphisms that are aligned with their respective 3′ termini. The polymorphic sites targeted by probes 1 and 2 are located five nucleotides upstream of those targeted by probes 3 and 4. This design permits each probe to bind its corresponding target and permits elongation to proceed when there is a perfect match at the designated polymorphic site. Thus, probes 1 and 3 match allele A, probe 2 and possibly probe 3 match allele B,...
example 2
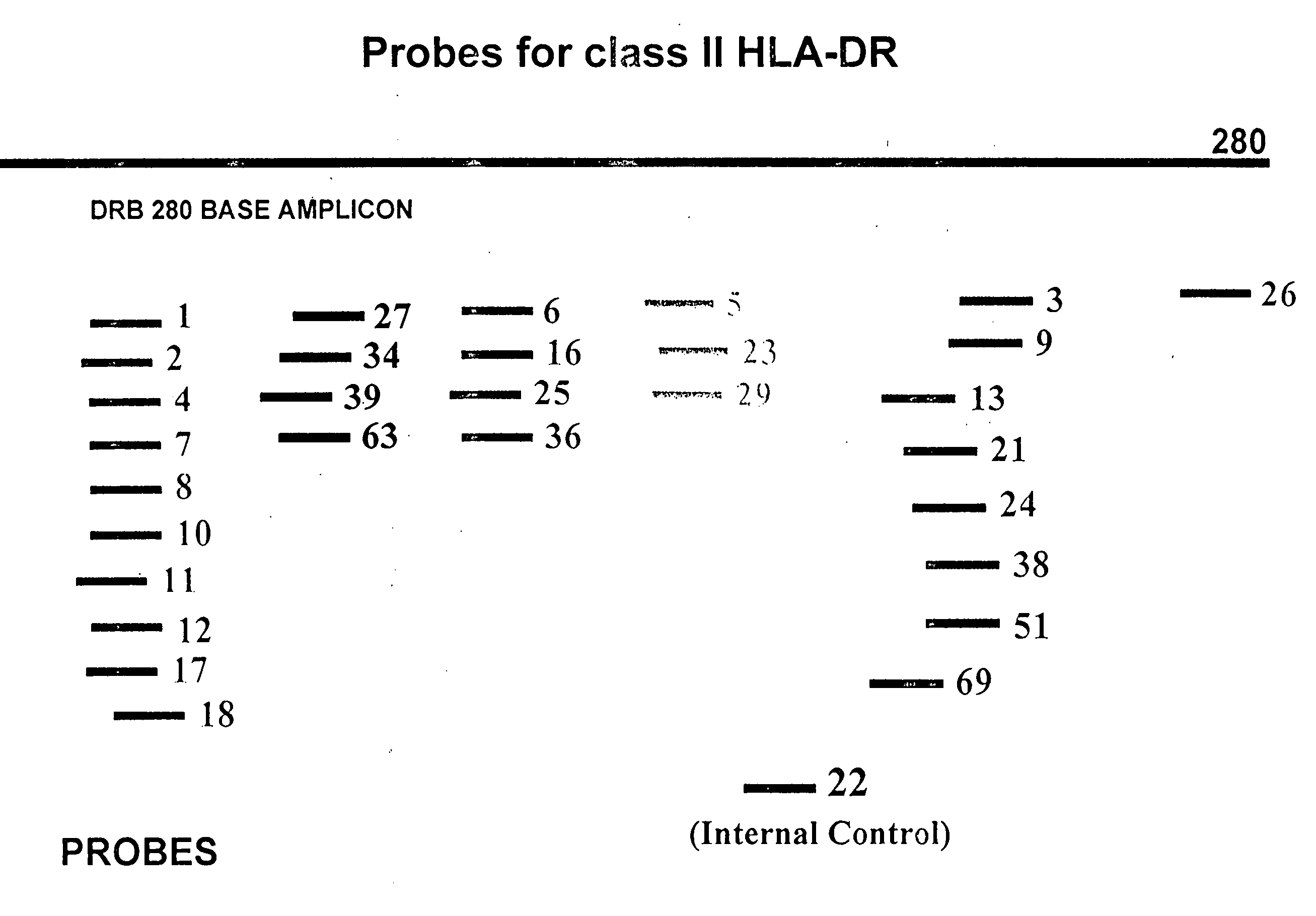
Probe Design for HLA Typing
[0141]To design probes for the analysis of the polymorphic region ranging from base 106 to base 125 of the DRB gene, twenty-two different types of sequences for the 20 base long fragment were located in the DRB database. These are listed in the table below:
7DRB1*0101TTCTTGTGGCAGCTTAAGTT104DRB1*03011TTCTTGGAGTACTCTACGTC26DRB1*04011TTCTTGGAGCAGGTTAAACA1DRB1*0434TTCTTGGAGCAGGTTAAACC3DRB1*07011TTCCTGTGGCAGGGTAAGTA1DRB1*07012TTCCTGTGGCAGGGTAAATA28DRB1*0801TTCTTGGAGTACTCTACGGG1DRB1*0814TTCTTGGAGTACTCTAGGGG1DRB1*0820TTCTTGGAGTACTCTACGGC1DRB1*0821TTCTTGGAGTACTCTATGGG1DRB1*09012TTCTTGAAGCAGGATAAGTT2DRB1*10011TTCTTGGAGGAGGTTAAGTT1DRB1*1122TTCTTGGAGCAGGCTACACA1DRB1*1130TTCTTGGAGTTCCTTAAGTC18DRB1*15011TTCCTGTGGCAGCCTAAGAG9DRB3*01011TTCTTGGAGCTGCGTAAGTC1DRB3*0102TTCTTGGAGCTGTGTAAGTC1DRB3*0104TTCTCGGAGCTGCGTAAGTC16DRB3*0201TTCTTGGAGCTGCTTAAGTC1DRB3*0212TTCTTGCAGCTGCTTAAGTC6DRB4*01011TTCTTGGAGCAGGCTAAGTG14DRB5*01011TTCTTGCAGCAGGATAAGTA
[0142]The first column contains the ...
example 3
Utilizing Mismatch Tolerance to Modify Allele Binding Patterns
[0149]Probe DR-13e, GGACATCCTGGAAGACGA, was used to target the bases 281-299 of the DRB gene. Thirty-four alleles, including allele DRB1*0103, are perfectly matched to this sequence. Thus, in the binding pattern, 13e is positive for theses 34 alleles (that is, 13e will yield elongation products with these 34 alleles). Several additional alleles display the same TEI region but display non-designated polymorphisms in their respective annealing regions. For example, five alleles, such as DRB1*0415, contain T in instead of A in position 4 while four alleles, such as DRB1*1136, contain C in the that position. Due to mismatch tolerance in the annealing region, target sequences complementary to these nine alleles will produce elongation reaction patterns similar to that of the perfectly matched sequence. The result is shown in FIG. 2. TO-3 and TO-4 are completely complementary sequences to allele *0415 and *1136, respectively.
DR...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com