Method for the production of antibodies
a technology of antibody production and composition, applied in the field of antibodies, can solve the problems of limited diversity, specificity and specificity of transgenic mouse-derived human antibodies compared to natural human immune repertoires, and the failure of first-generation murine antibodies which were used in humans
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Immunization Procedure of Reconstituted Mice
[0127] Three Rag2− / −γc− / − mice (3 females), were immunized with 100 μg plasmid DNA coding for human HER3 protein. In total up to six immunizations were given intramuscular (i.m.). When serum titers of anti-HER3 were found to be sufficient, mice were additionally boosted three times with 30 μg of purified HER3 proteine in 100 μl PBS intravenously (i.v.) 3,2 and 1 days before fusion.
example 2
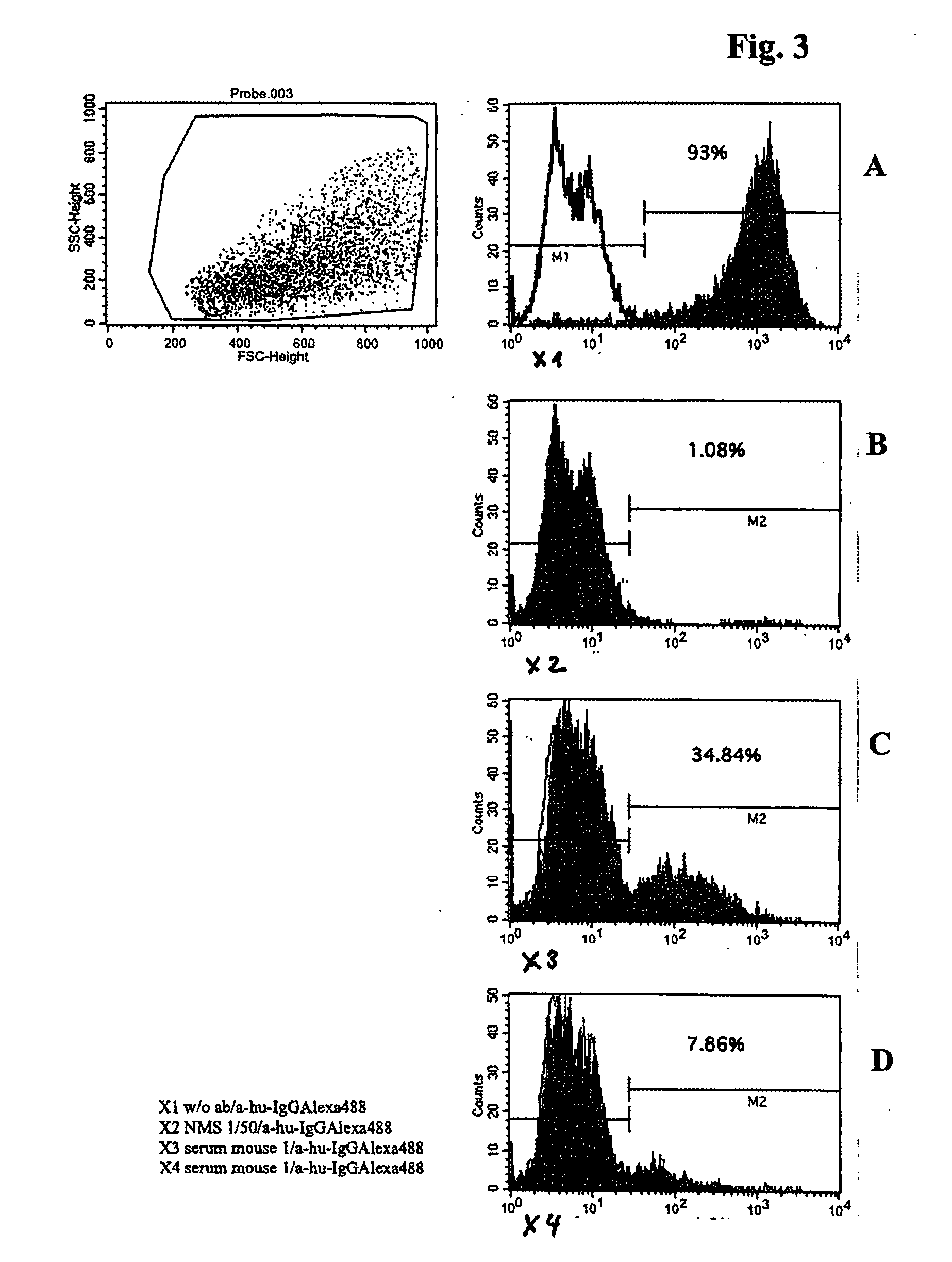
Flowcytometric Analysis of Peripheral Blood of Reconstituted Mice on 15th Week after Engraftment
[0128] The mice were isofluran-anaesthized and then peripheral blood was collected from the orbital vene plexus for measuring the positive ratio of human hemocytes by use of flow cytomenty. The collected blood was instantly blended well with EDTA-2Na and kept at room temperature until analysis. An optimum amount of FITC conjugated anti-human CD45 antibodies was added to and reacted with 50 μl of the whole blood at room temperature for 20 minutes. Thereafter, hemolysis and immobilization were effected using FACS solution and the ratio was measured using FACS Calibur. FIG. 1 shows ratio (%) of human CD45 positive cells in peripheral blood of three tested mice.
example 3
Examination of the Production Ability of Human HER3 Antibodies in the Reconstituted Mice
[0129] The amount of total human IgG in pheripheral blood of reconstituted mice was measured by ELISA. Diluted mice serum was coated on MaxiSorb 96 well plate (NUNC) and incubated for lh at room temperature. After blocking with 2% CroteinC solution for 1 h at room temperature washing was performed and thereafter peroxidase conjugated anti-human IgG monoclonal antibodies were added. After incubation for 45 minutes at room temperature washing was performed and ABTS substrate solution was added for 10 minute reaction at room temperature. Then the absorbance was measured at 405 nm (FIG. 2). The IgG concentration was calculated in accordance with the standard curve.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| binding affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com