Functionalizing implantable devices with a poly (diol co-citrate) polymer
a technology of diol cocitrate and implantable devices, which is applied in the direction of non-embryonic pluripotent stem cells, prosthesis, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of blood vessel walls in which the stent is placed to become disrupted or injured, potential trauma or injury to the expanded passage or vessel, etc., to reduce the thrombogenicity of the graft and the effect of less thrombogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Biodegradable Elastomeric Polymers
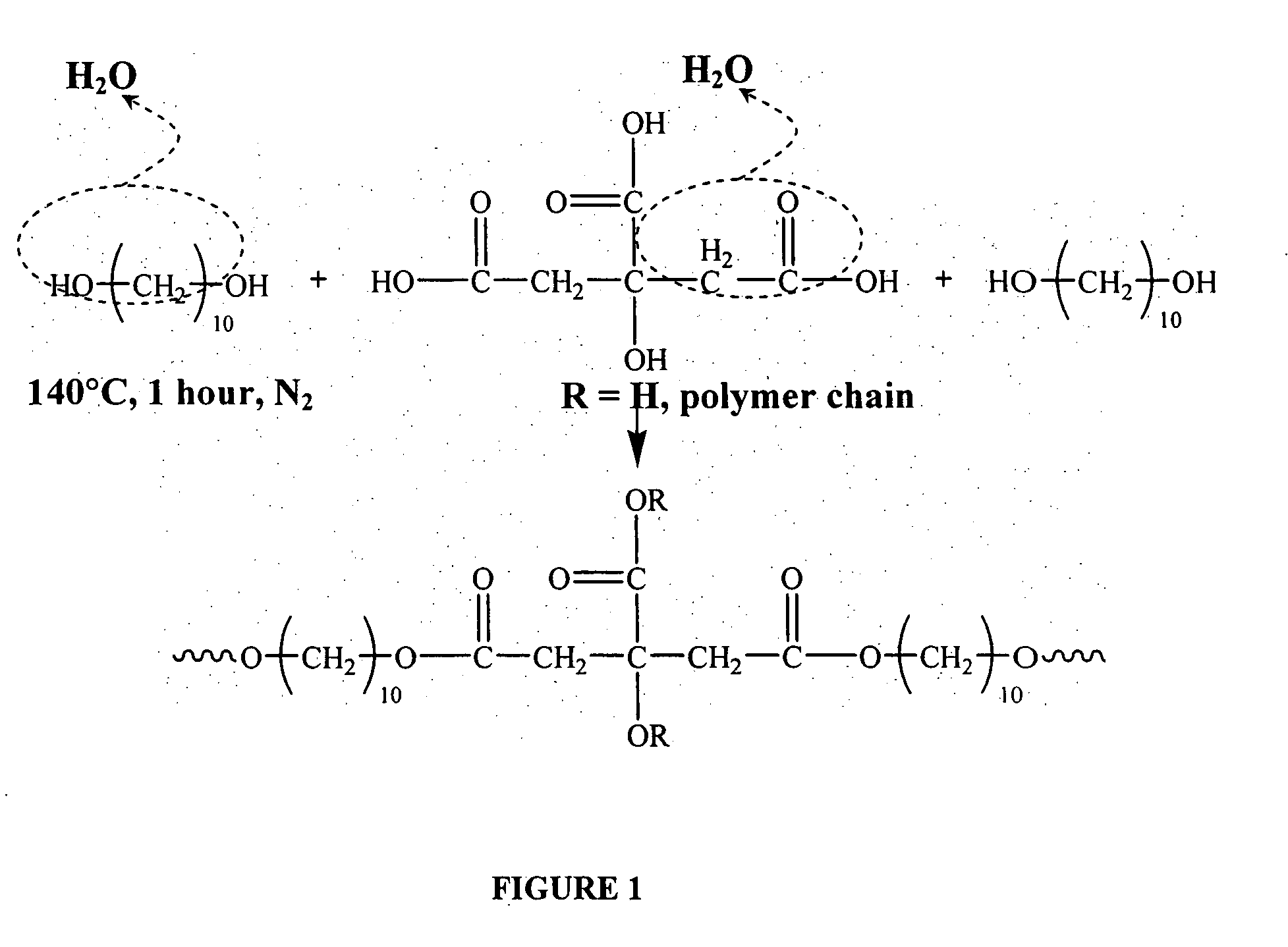
[0072] The coating compositions of the invention are based on biodegradable elastomeric polymers of poly(diol) citrate molecules. Such molecules typically comprising a polyester network of citric acid copolymerized with a linear aliphatic di-OH monomer in which the number of carbon atoms ranges from 2 to 20. Polymer synthesis conditions for the preparation of these molecules vary from mild conditions, even at low temperature (less than 100° C.) and no vacuum, to tough conditions (high temperature and high vacuum) according the requirements for the materials properties. By changing the synthesis conditions (including, but not limited to, post-polymerization temperature, time, vacuum, the initial monomer molar ratio, and the di-OH monomer chain length) the mechanical properties of the polymer can be modulated over a wide range. This series of polymers exhibit a soft, tough, biodegradable, hydrophilic properties and excellent biocompatibility in vitro...
example 2
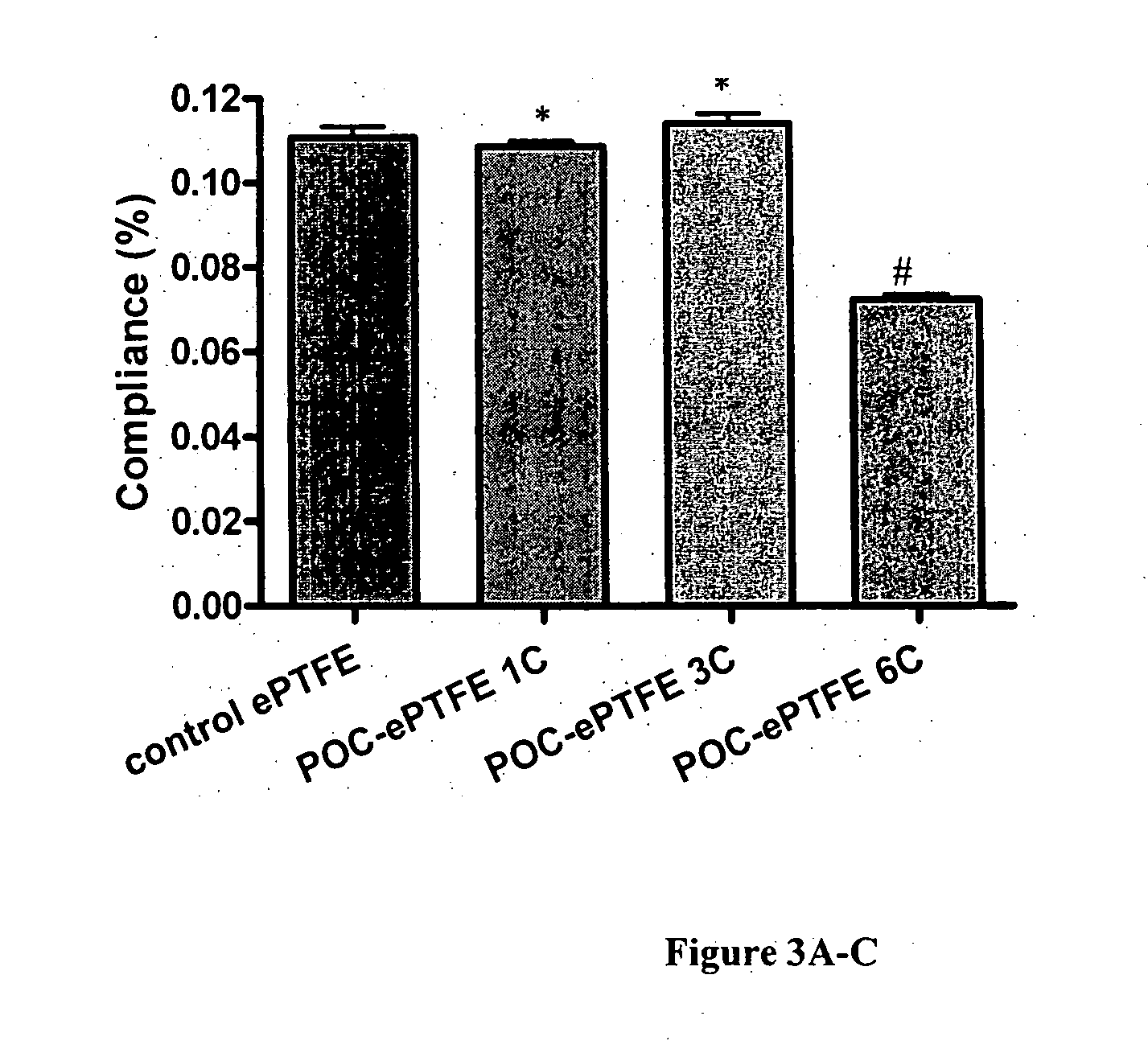
Results and Discussion
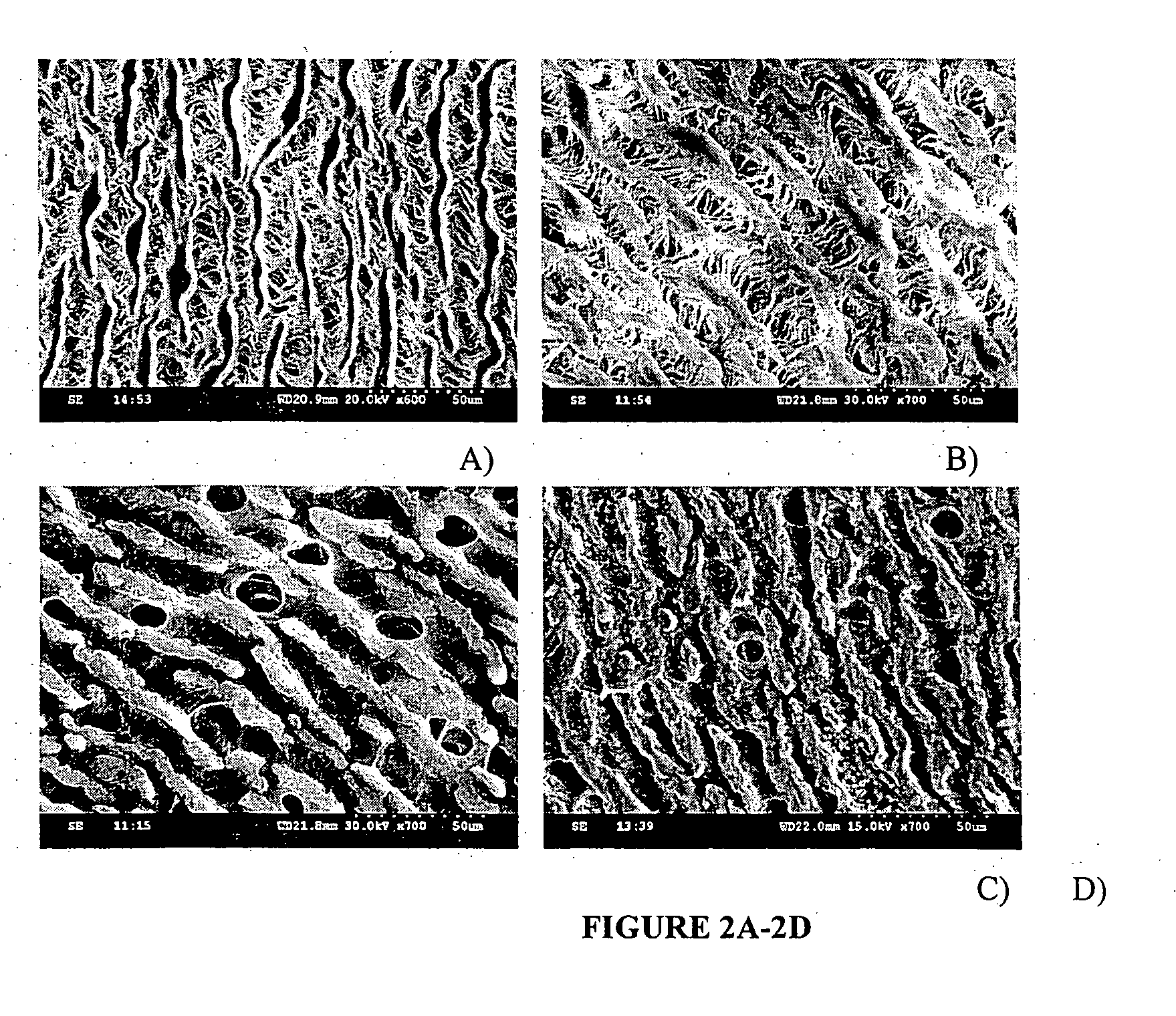
[0100] ePTFE grafts are manufactured by a heating, extruding, and longitudinal stretching at a high strain rate and cracking into a non-woven porous tube. ePTFE grafts are characteristic of a node-fibril structure (FIG. 1A) in which non-continuous nodes connect through fine fibrils. Average internodal distance is about 30 μm for standard ePTFE grafts. ePTFE grafts trigger inflammation, thrombosis and incomplete endothelium formation, the major causes for graft failure together with the compliance mismatch. Many attempts have been tried to modify the lumen of ePTFE grafts to abolish their anti-adhesion properties and improve endothelialization including carbon coating to increase surface electronegativity for reduced thrombus formation31,32, and attaching anticoagulant or antithrombotic agents to the grafts15,33,34 13-17 through chemical or physical modifications. However, there are still no satisfactory grafts with a long term patency available, especially for...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angular velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Speed | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com