Driver for multi-voltage island/core architecture
a multi-voltage island and core architecture technology, applied in logic circuits, logic circuits, logic functions, etc., can solve the problems of static (leakage) power dissipation becoming a significant component of limiting the performance of integrated circuit chips, and high total chip power dissipation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
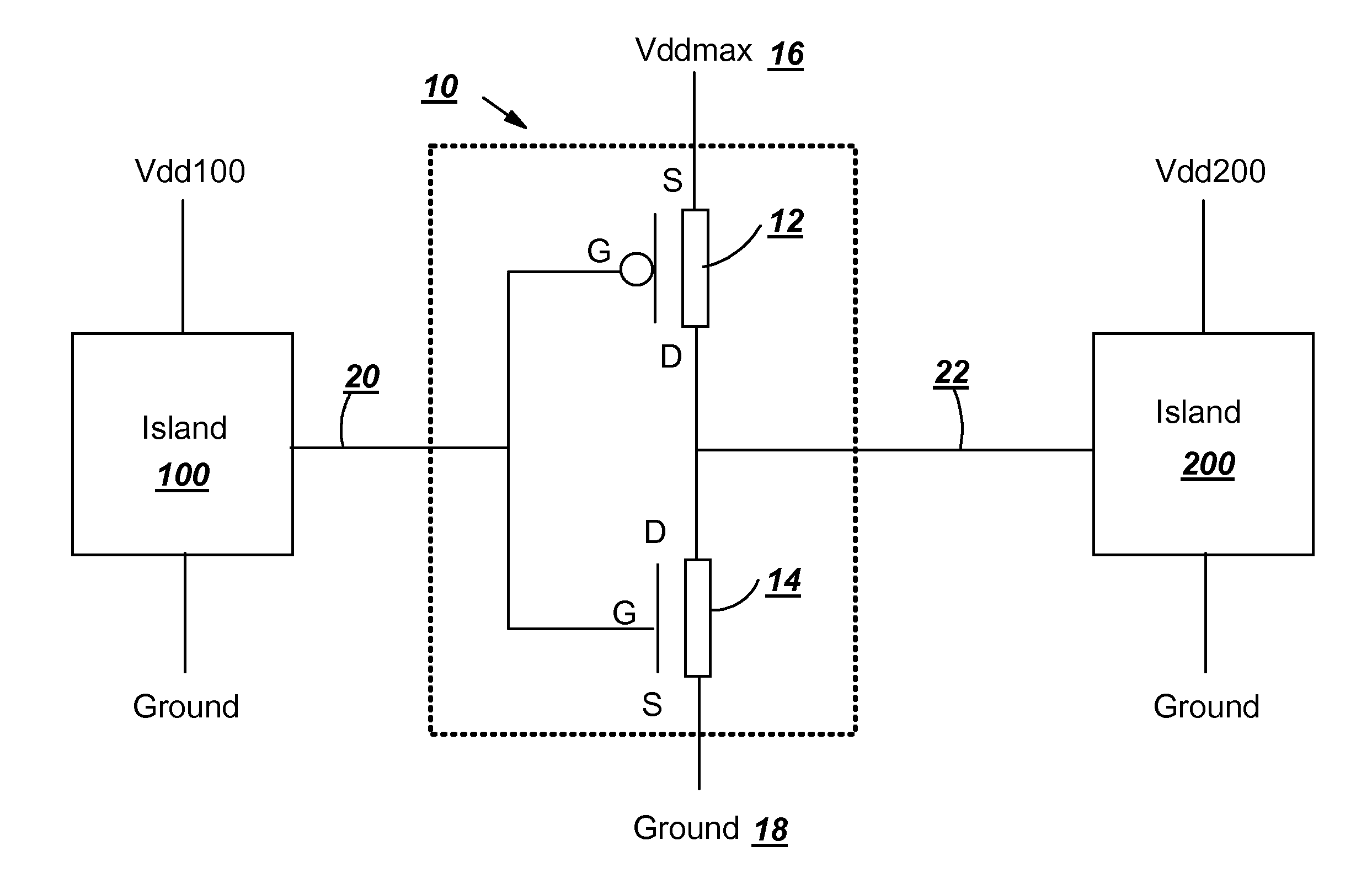
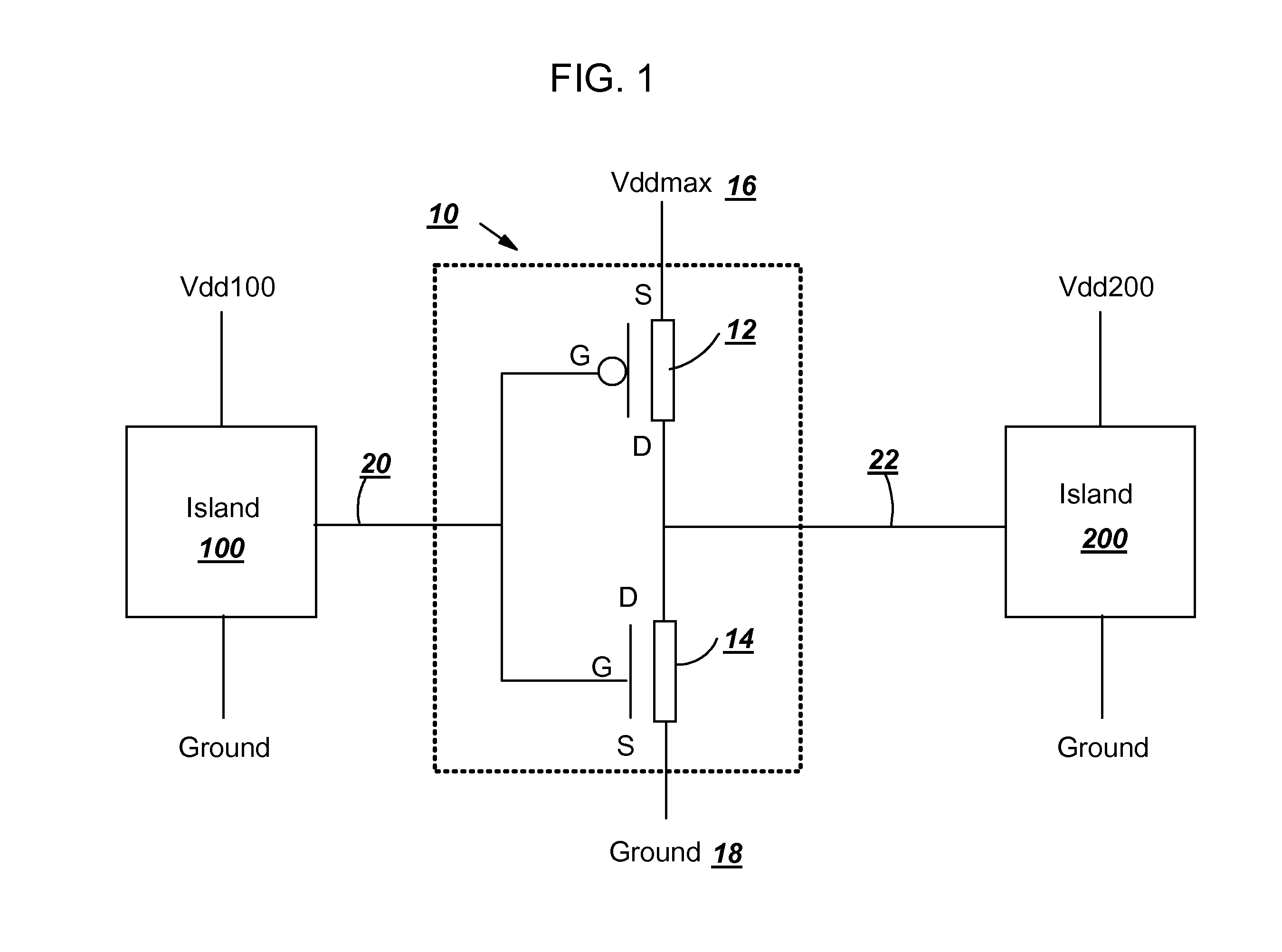
[0015] Turning to the drawings, FIG. 1 shows a block diagram of one embodiment of a driver 10 for a multi-voltage island / core of an integrated circuit (IC) chip (not shown). Driver 10 includes a high threshold voltage (hi-Vt) p-channel field-effect transistor (PFET) 12 and a regular threshold voltage n-channel field-effect transistor (NFET) 14, which are coupled together to form a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) inverter. Specifically, source pin of hi-Vt PFET 12 is coupled to Vddmax 16, which is the maximum positive voltage supply (Vdd) on the IC chip; source pin of NFET 14 is coupled to chip ground 18; gate pins of hi-Vt PFET 12 and NFET 14 are coupled to form an input terminal 20 of driver 10; and drain pins of hi-Vt PFET 12 and NFET 14 are coupled to form an output terminal 22 of driver 10.
[0016] In FIG. 1, two voltage islands / cores (islands) 100 and 200 are coupled to driver 10 such that output of island 100 controls driver 10 to provide logic state to island 20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com