Process for producing activated carbon for electrode of electric double-layer capacitor
a technology of double-layer capacitors and activated carbon, which is applied in the direction of hybrid capacitor electrolytes, capacitors, pigmenting treatment, etc., can solve the problems of excessive oxidization, difficult activation of carbonized powders, and difficult activation, so as to reduce the amount of polarizing electrode expansion during charging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment-i
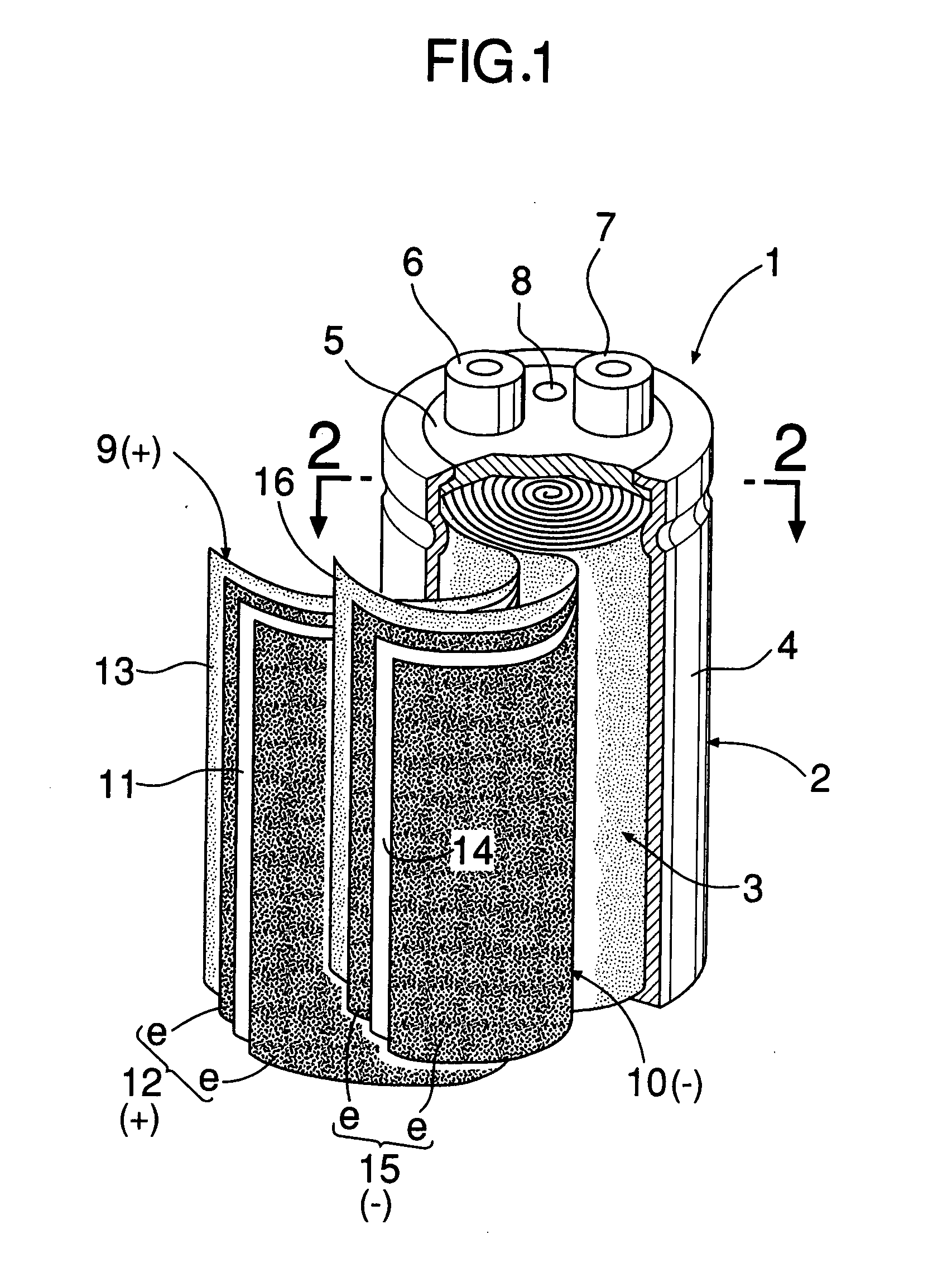
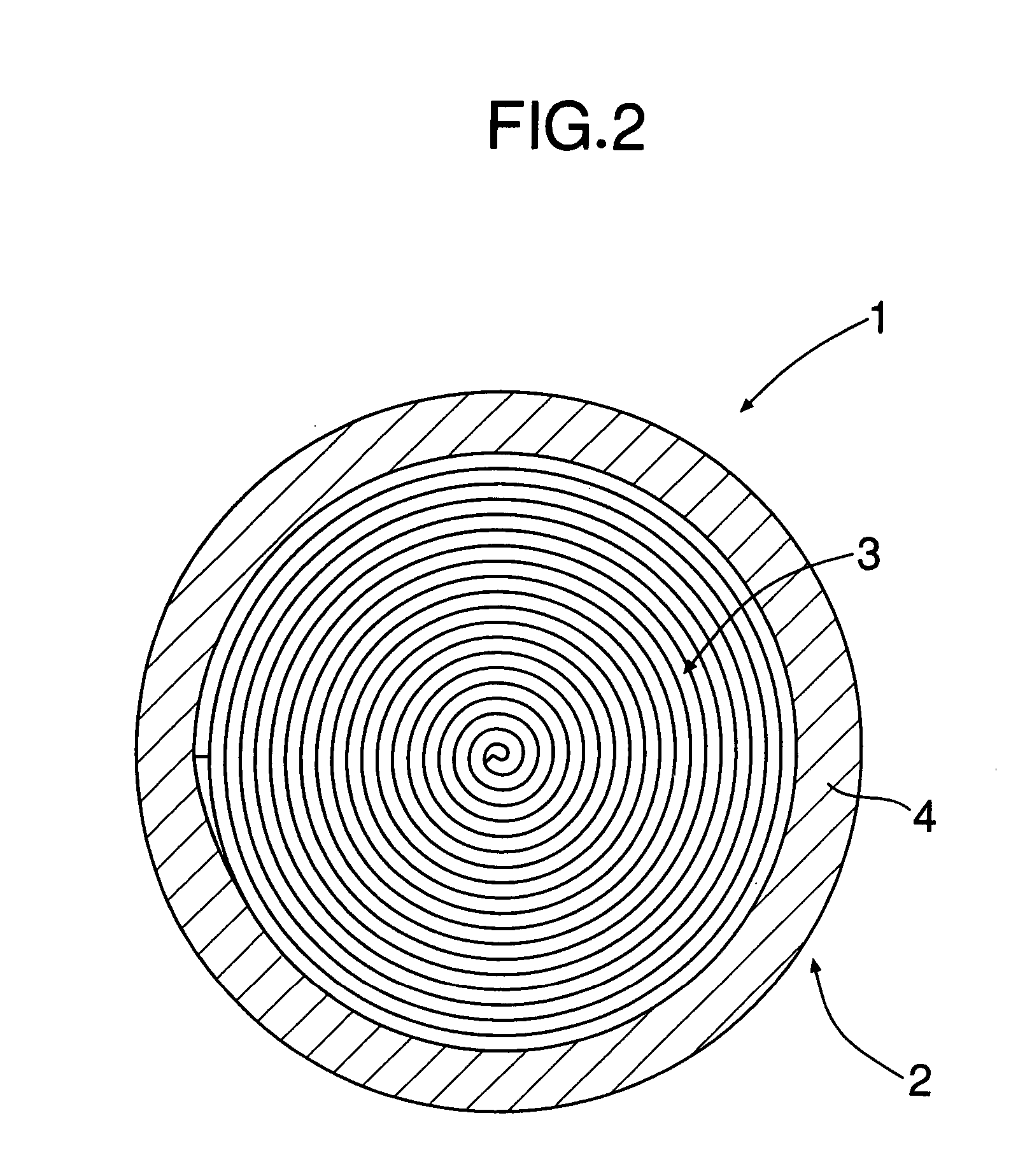
[0039] Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, a cylindrical electric double-layer capacitor 1 comprises a vessel 2 made of aluminum, an electrode roll 3 accommodated in the vessel 2, and a liquid electrolyte poured into the vessel 2. The vessel 2 comprises a bottomed cylindrical body 4, and a terminal plate 5 which closes an opening in one end of the cylindrical body 4. The terminal plate 5 is provided with positive and negative terminals 6 and 7 and a safety valve 8.
[0040] The electrode roll 3 includes a positive-pole laminated band 9 and a negative-pole laminated band 10. The positive-polar laminated band 9 comprises a band-shaped collector 11 formed of an aluminum foil, band-shaped polarizing electrodes e adhered to opposite sides of the band-shaped collector 11 with a conductive adhesive, respectively, and a first separator 13 made of PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) and superposed on one of the band-shaped polarizing electrodes e. A band-shaped positive pole 12 is formed by the pair of the...
example-1
[0048] First, alkali-activated carbon using a starting material of mesophase pitch, i.e., KOH-activated carbon in Example-1 was produced in the following manner:
[0049] (a) Massive mesophase pitch was subjected to a pulverizing treatment at room temperature to produce a pulverized powder having an average particle size of 300 μm. Then, the powder was subjected to an infusibilizing treatment at 350° C. for 2 hours in the atmospheric air current and then to a carbonizing treatment at 700° C. for 1 hour in the current of nitrogen gas to provide a carbonized powder. (b) The carbonized powder and an amount of KOH two times the weight of carbon in the powder were mixed together, and the resulting mixture was subjected to a potassium activating treatment as an alkali activating treatment at 800° C. for 5 hours in the nitrogen atmosphere, followed by the post treatments such as the neutralization by hydrochloric acid, washing and drying, thereby providing KOH-activated carbon as activated c...
embodiment-ii
[0062] Referring to FIG. 9, a button-type electric double-layer capacitor 17 includes a case 18, a pair of polarizing electrodes 19 and 20 accommodated in the case 18, a spacer 21 sandwiched between the polarizing electrodes 19 and 20, and a liquid electrolyte filled in the case 18. The case 18 comprises a vessel body 23 made of aluminum and having an opening 22, and a lid plate 24 made of aluminum and closing the opening 22. An outer periphery of the lid plate 24 and an inner periphery of the vessel body 23 are sealed from each other by a seal material 25. Each of the polarizing electrodes 19 and 20 is made of a mixture comprising activated carbon, a conductive filler and a binder.
[0063] Activated carbon for the electrode is produced by subjecting a starting material having a metal compound incorporated therein to a carbonizing treatment and then to an activating treatment. Examples of the starting material for the activated carbon, which may be used, are various synthetic resins,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com