Thermal cushion and device comprising such a cushion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
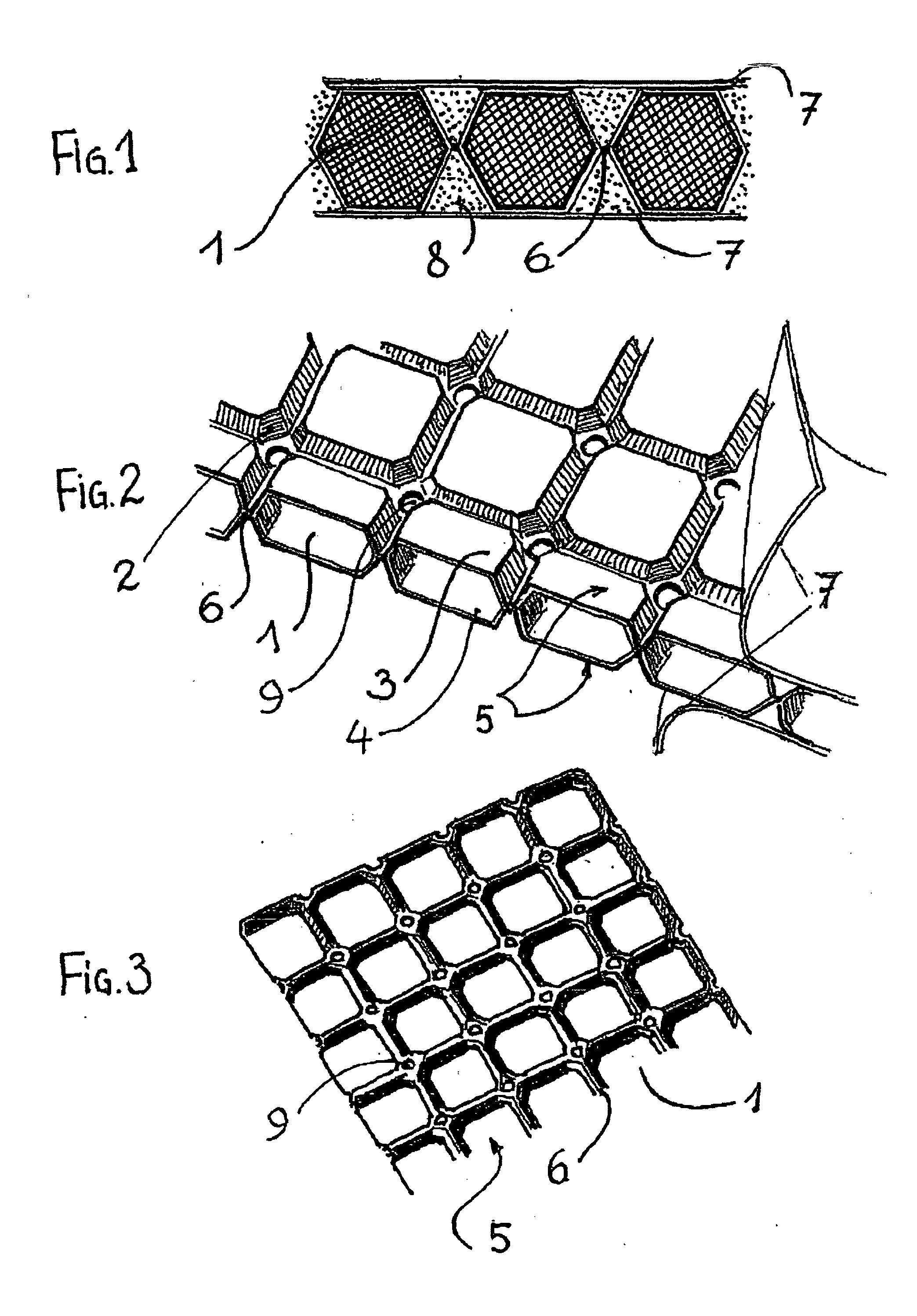
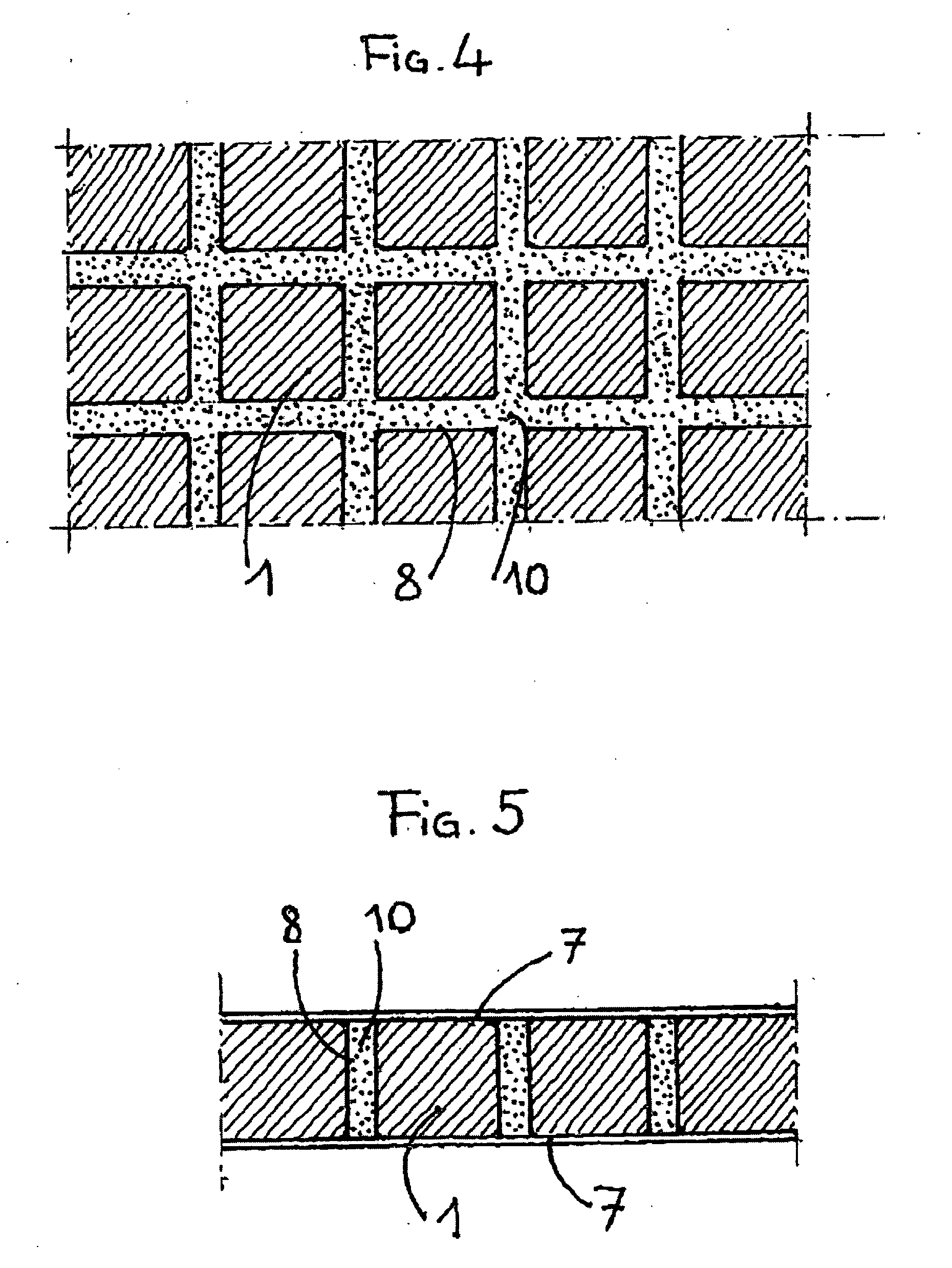
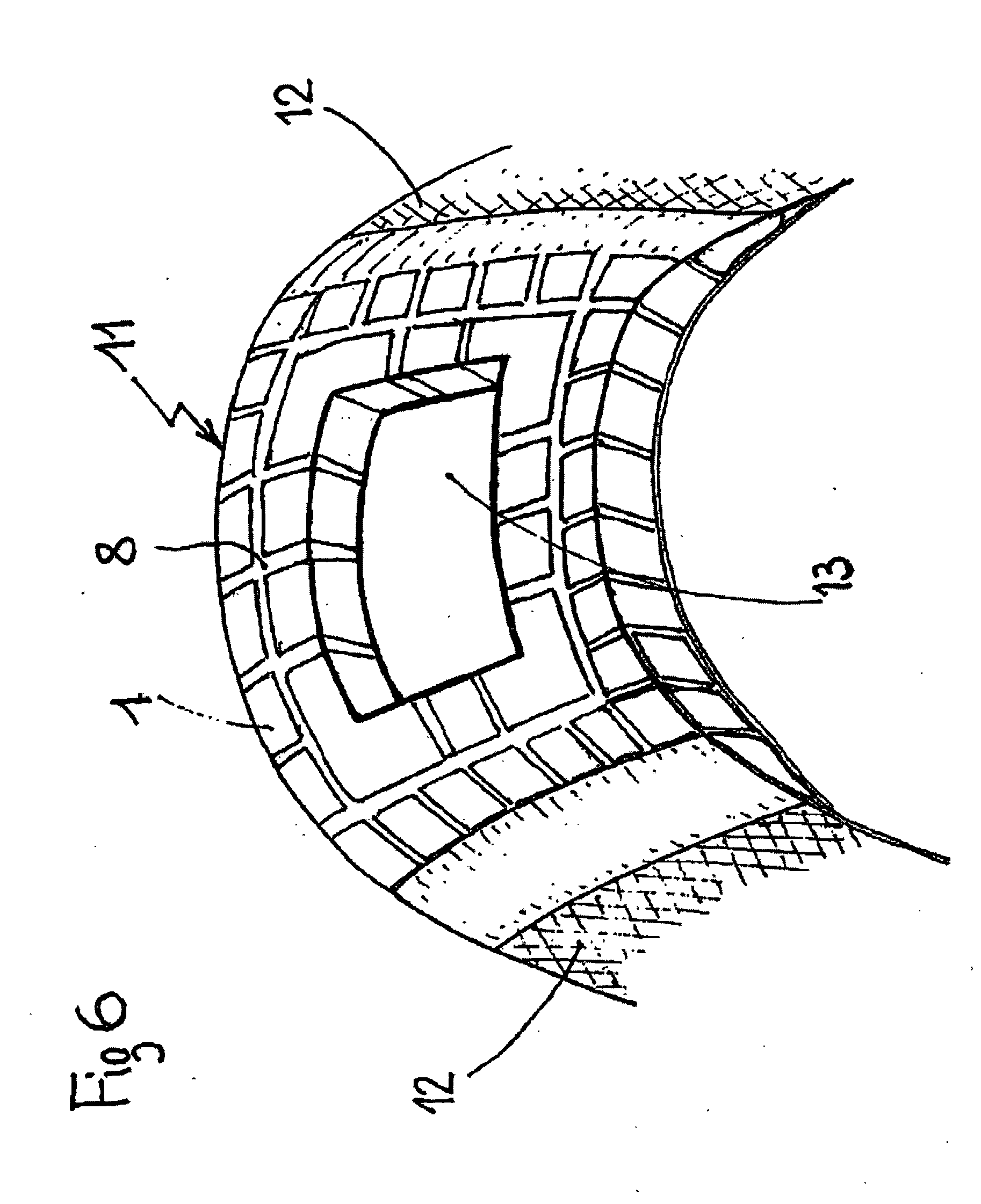
[0089] The thermal cushion shown in FIG. 1 and 2 comprises a network of blocks 1, formed by hollow cells. The blocks or cells 1 have the shape of prisms with square bases. Each cell 1 is formed by two truncated pyramids 3 and 4, attached along their long square bases. The side ridges of the two truncated pyramids have bevelled edges (2). The network of cells 1 is formed by the assembly of two corrugated sheets 5 in a flexible polymer material (for example in plastified polyvinyl chloride or in styrene-ethylene-butyl-styrene copolymer) pre-drawn and welded to each other along tongues 6 between the cells (a corrugated sheet 5 is shown in FIG. 3). The tongues 6 are flexible and elastic and they act as articulations between the cells 1. They are pierced by apertures 9 whose function will be explained later on. By bending or twisting the assembly of sheets 5, the cushion of cells may thus adopt complex profiles to fit an appropriate body, for example part of the anatomy of a human being ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com