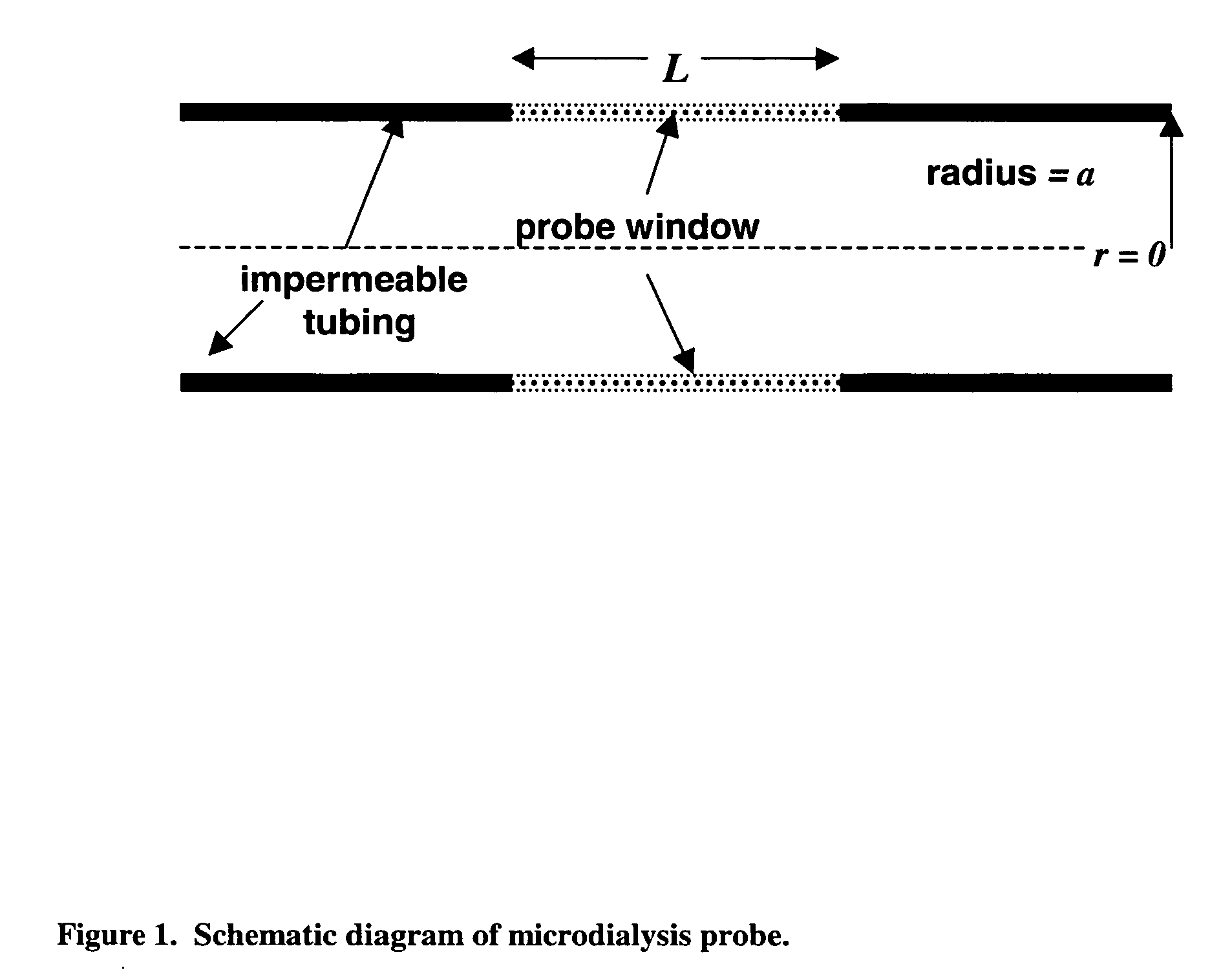
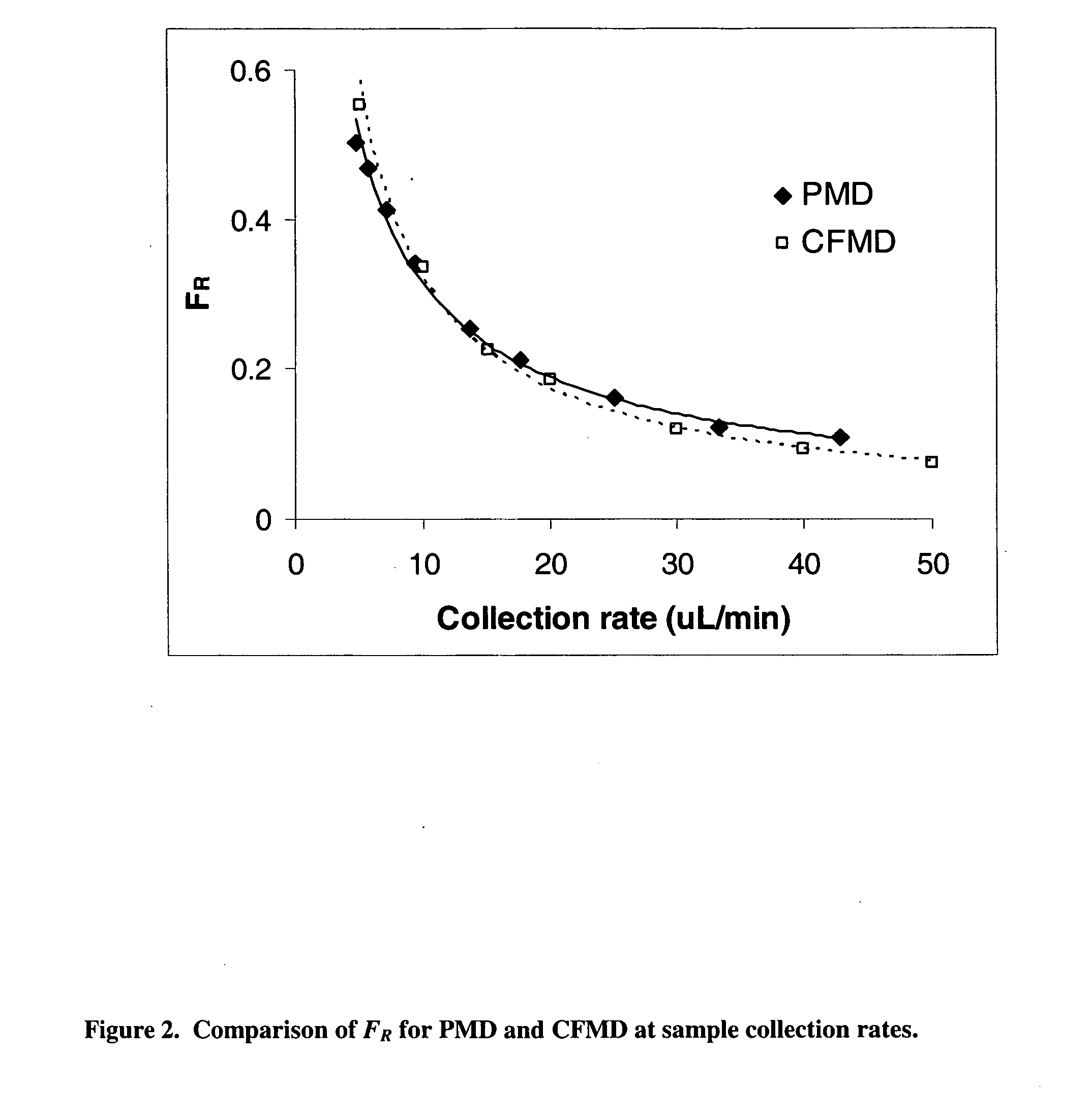
Method for use of microdialysis
a microdialysis and mass transfer technology, applied in the field of improving the method of mass transfer effect and measurement, can solve the problems of optimum application, and inability to associate, etc., and achieve the effect of long time required for sampling and reduced time requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Determination of RFO When the Donor Medium is Inside the Probe and Concentration Outside the Probe is Zero
[0134] Here, RFQ will be obtained using PMD data. In this application, the dialysate serves as the donor and the medium surrounding the probe is the receiver with a constant concentration. (In other words, the mass lost by the dialysate does not significantly change the receiver concentration.)
[0135] An example of a method that uses PMD to determine RFQ is as follows: [0136] a) Immerse a probe in a solution (medium outside the probe) containing a known concentration of drug. The volume of the external solution should be large enough (at least ˜25 mL) so drug transfer to the dialysate will not change the external medium concentration. [0137] b) Pump dialysate containing a known concentration of drug C0 into the probe window. The dialysate should be the same liquid as the external medium. It is preferable that the flow rate Q be relatively high (at least ˜100 μL / min), so that RF...
example 3
Determination of the Probe Window Volume
[0144] Measuring the window volume in this way is preferred since done in the context of the way the probe would actually be used, and also inherently takes into account any irregularities in the probe geometry which would give somewhat erroneous results using other methods, such as optical measurements.
[0145] An example of a method that uses PMD to determine VW is as follows: [0146] a) Immerse a probe in a solution (medium outside the probe) containing a known concentration of drug. The volume of the external solution should be large enough (at least ˜25 mL) so drug transfer to the dialysate will not change the external medium concentration. [0147] b) Pump fresh dialysate (i.e., containing no drug) into the probe window. The dialysate should be the same liquid as the external medium. It is preferable that the flow rate Q be relatively high (at least ˜100 μL / min), so that FRQ is much smaller than 1. [0148] c) Allow the dialysate to occupy th...
example 4
Determination of γ1
[0154] Measuring the value of γ1 in this way is one of the preferred ways because it does not require a knowledge of VW. However, knowledge of VW is still desirable because it can be used to improve the accuracy of the method.
[0155] An example of a method that uses PMD to determine γ1 is as follows: [0156] a) Immerse a probe in a solution (medium outside the probe) containing a known concentration of drug. The volume of the external solution should be large enough (at least ˜25 mL) so drug transfer to the dialysate will not change the external medium concentration. [0157] b) Pump fresh dialysate (i.e., containing no drug) into the probe window. The dialysate should be the same liquid as the external medium. It is preferable that the flow rate Q be relatively high (at least ˜100 μL / min), so that FRQ is much smaller than 1. [0158] c) Allow the dialysate to occupy the probe at rest for a known time tR. [0159] d) Flush and collect a known sample volume VS of the dia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com