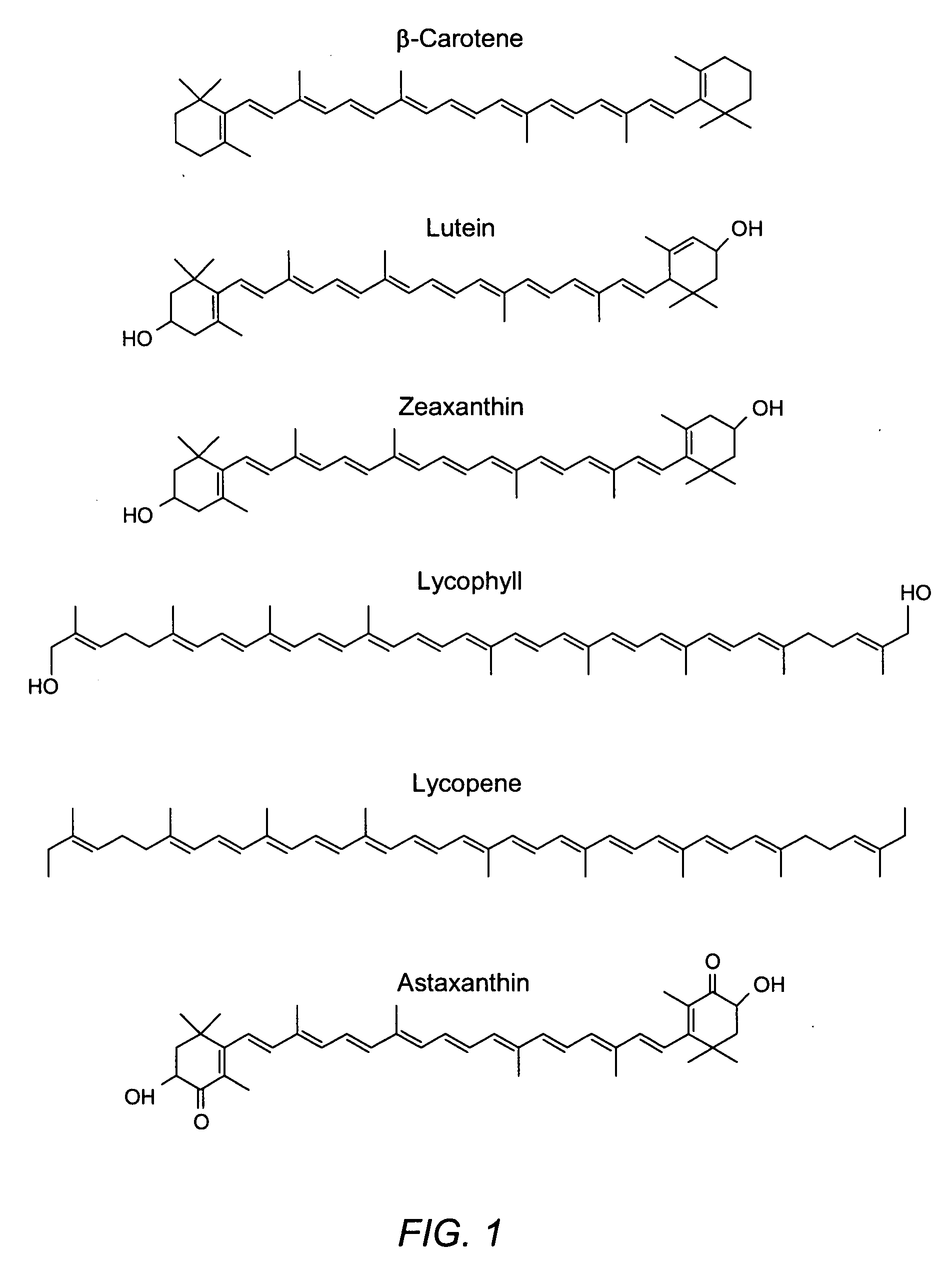
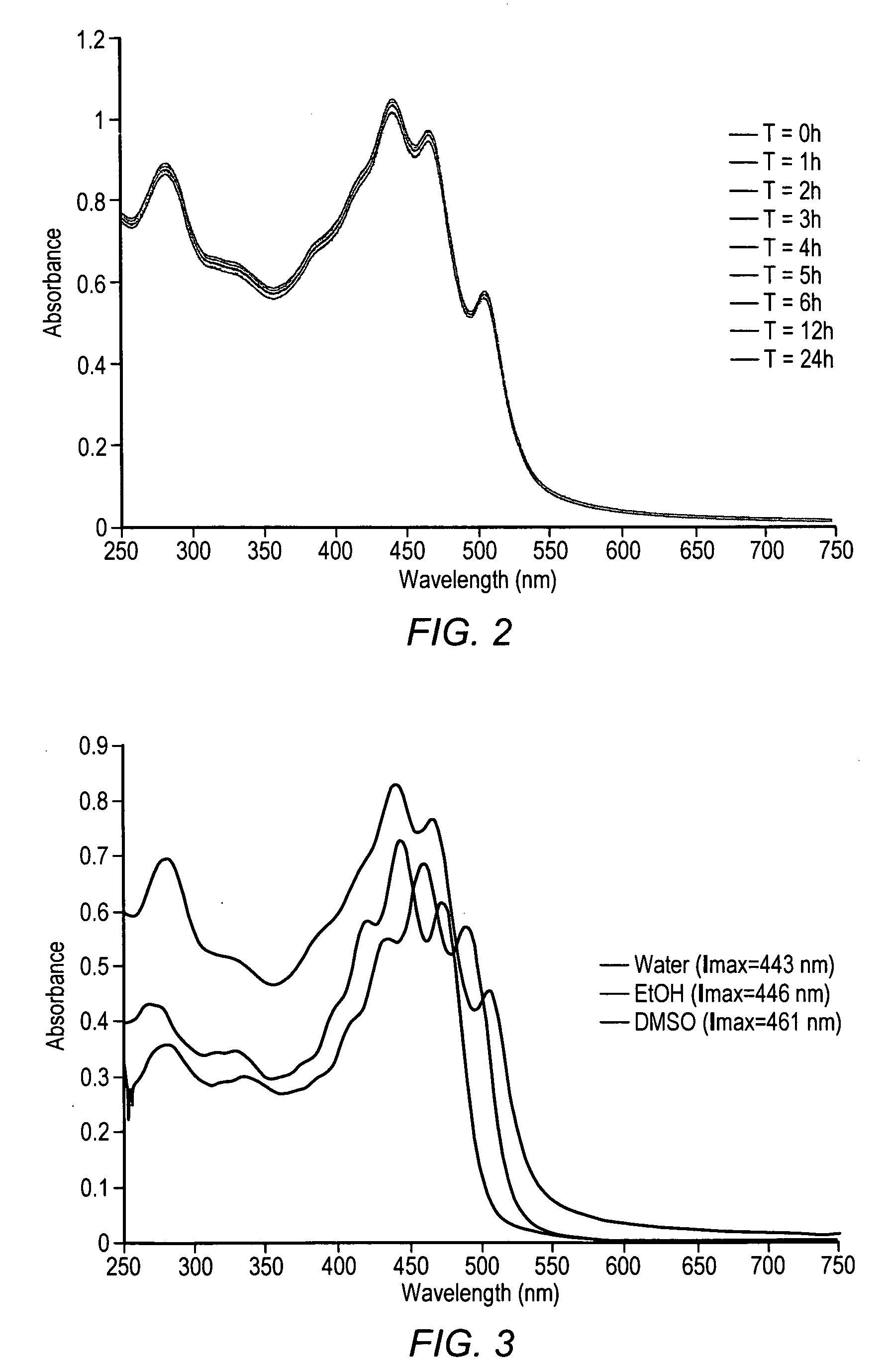
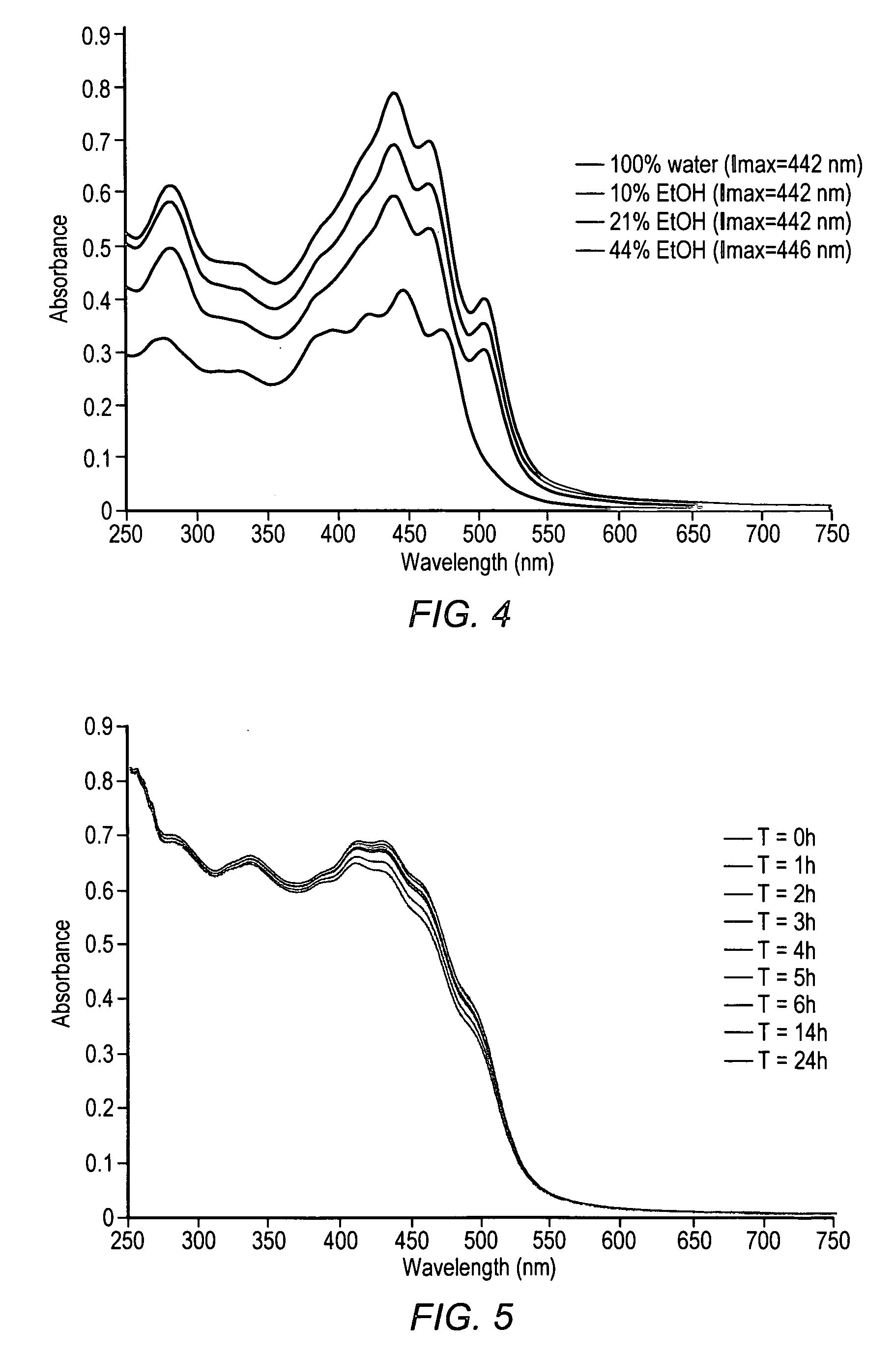
Reduction in complement activation and inflammation during tissue injury by carotenoids, carotenoid analogs, or derivatives thereof
a technology of carotenoids and complement, applied in the field of medicinal and synthetic chemistry, can solve the problems of high cost of safety and efficacy tests, increased crp in the absence of acute infection or acute tissue injury, and increased risk of adverse effects of acute infection and tissue injury
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0239] Determination of test animal vital signs. No differences in heart rate, blood pressure, or blood gases at baseline or throughout the experimental protocol performed on day 5 between the two groups was observed (data not shown). Turning to FIG. 11, no significant differences in areas at risk were observed between the animals treated with DDA or with saline, indicating that both groups were subjected to similar degrees of ischemia.
example 2
[0240] Effect of DDA on Myocardial Infarct Size. Remaining with FIG. 11, each treatment group consisted of 9 animals in which either DDA or saline placebo was administered for 4 days before commencing the experimental protocol involving myocardial ischemia / reperfusion. The mean size of the area at risk expressed as a percentage of the total left ventricle was similar in both groups. Rabbits treated with DDA (50 mg / kg / day) exhibited significantly smaller mean infarcts expressed as a percentage of the area at risk (25.8±4.2%) compared with rabbits treated with placebo (52.5±7.5%, **p<0.01). This represented mean myocardial salvage of 51%. These results therefore demonstrate that disodium disuccinate astaxanthin treatment can significantly reduce the size of an infarct relative to the area of myocardium at risk in rabbits subjected to 30 minutes of coronary artery occlusion followed by a three hour period of reperfusion. DDA produced a mean myocardial salvage of approximately 51% when ...
example 3
[0241] Plasma and tissue levels of non-esterified, free astaxanthin. Turning to FIG. 12, the mean plasma concentration of non-esterified, free astaxanthin at the end of 3 hours of reperfusion is presented. Pretreatment with DDA at 50 mg / kg for 4 days resulted in a mean plasma concentration of 222±51 nM. However, the mean myocardial tissue concentration of DDA was several orders of magnitude greater than that observed in the plasma (FIG. 12), revealing highly favorable mean myocardium / serum ratios in the rabbit after intravenous subchronic administration. We were able to achieve plasma concentrations of non-esterified astaxanthin that were roughly equal to those previously found in other species using the same intravenous dosage regimen (Gross and Lockwood, 2004; Gross and Lockwood, In Press). We also observed a marked accumulation of non-esterified astaxanthin in the myocardium (mean>10 μM) in the rabbits utilized in this study. Rapid plasma clearance of free astaxanthin, and excell...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| protein concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com