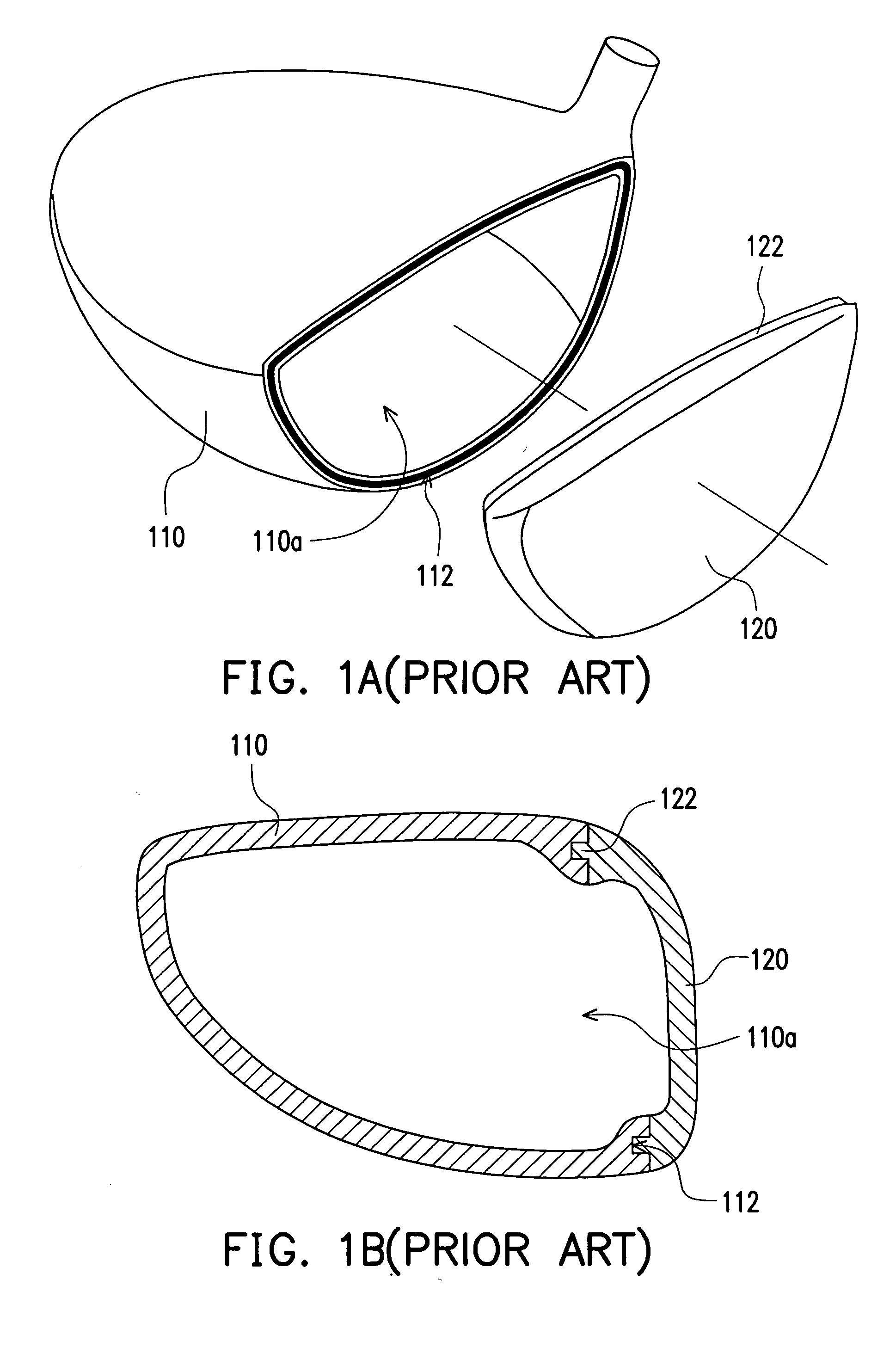
Golf club head
a golf club and head technology, applied in the field of golf club head, can solve the problems of reducing the shearing strength of the bonded surface, reducing the precision requirement and fabrication cost, and increasing the separation of the striking plate from the shell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
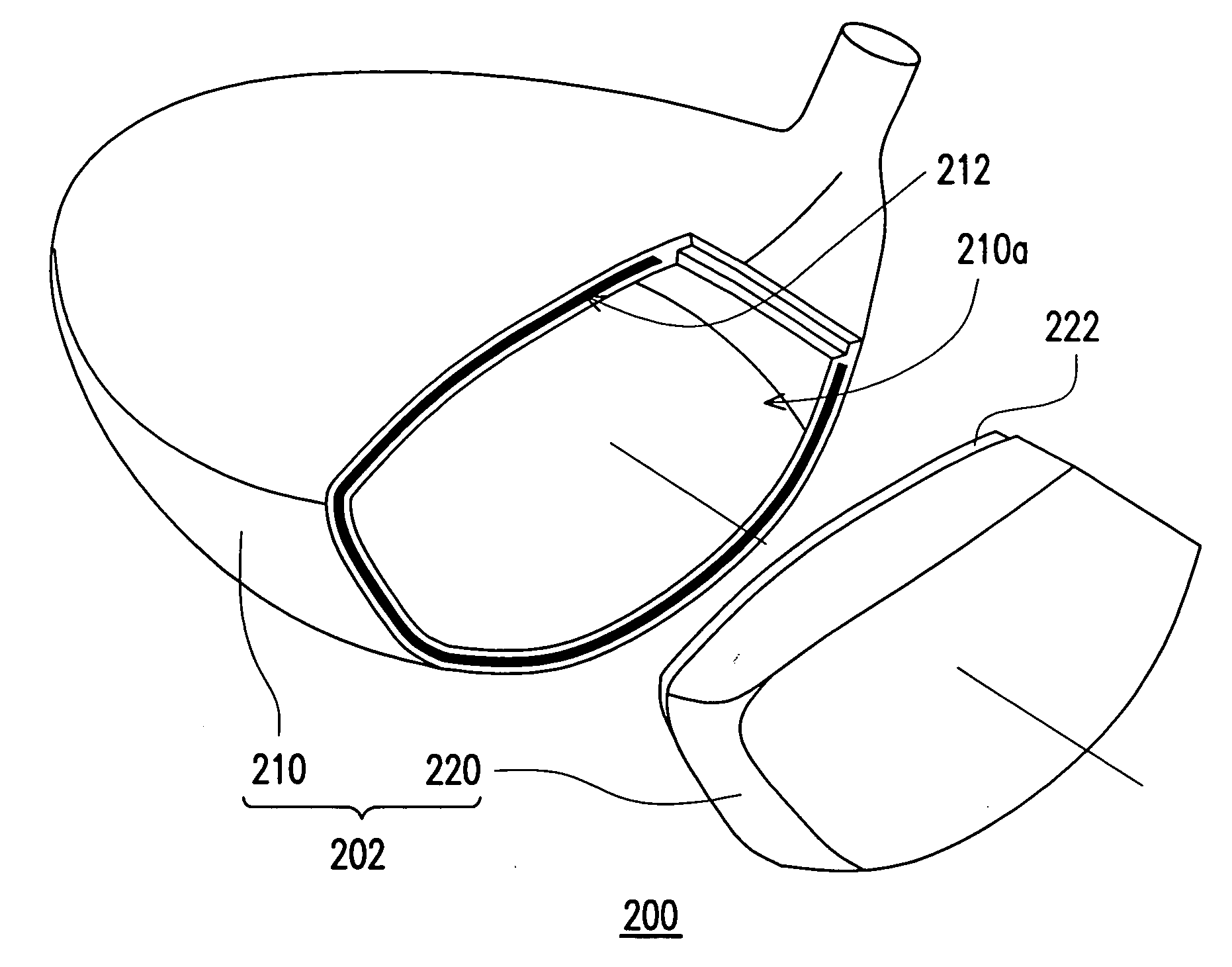
[0024] A three dimensional exploded view and a cross-sectional view of a first embodiment of the present invention respectively illustrates a golf club head, as in FIG. 2A and FIG. 2B. As illustrated in FIG. 2A and FIG. 2B, the golf club head 200 has a club head body 202, in which the club head body 202 is mainly formed from a shell 210 and a striking plate 220. In the present embodiment, the club head body 202 can be, for example, selected from typical metallic materials (such as stainless steel or other metallic materials) to use casting method to form a unibody construction. Furthermore, the shell 210 has an opening 210a. And the edge of the opening 210a at a portion of the shell 210 has a first engagement portion 212. In the present embodiment, the first engagement portion 212, for example, is a notch. And the notch, for example, is from the top portion of the shell 210, along a side portion, and extended to the bottom portion of the shell 210.
[0025] Referring again to FIG. 2A ...
second embodiment
[0029]FIG. 3A and FIG. 3B respectively illustrates a three dimensional exploded view and a cross-sectional view of a golf club head, according to a second embodiment of the present invention. The engagement location for the shell and the striking plate of the present embodiment is above the top portion and the bottom portion of the club head body. As illustrated in FIG. 3A and FIG. 3B, the club head body 302 of the golf club head 300 of the present embodiment is similarly formed from a shell 310 and a striking plate 320. In comparison to the first embodiment, the first engagement portion 312 is also located at the edge of the opening 310a at a portion of the shell 310, and is also, for example, a notch. However, the difference is that the first engagement portion 312 is at the top portion and the bottom portion of the shell 310.
[0030] Furthermore, a second engagement portion 322 corresponding to the first engagement portion 312 is on the edge of a portion of the striking plate 320,...
third embodiment
[0032] Later, in reference to FIG. 4A and FIG. 4B, in which a three dimensional exploded view and a cross-sectional view of a golf club head of a third embodiment of the present invention are respectively illustrated. The engagement location of the shell and the striking plate of the present embodiment is only at the top portion of the club head body. As illustrated in FIG. 4A and FIG. 4B, the golf club head body 402 of the golf club head 400 is formed from a shell 410 and a striking plate 420, in which the first engagement portion 412 is disposed at the edge of the opening 410a at the top portion of the shell 410.
[0033] Futhermore, a second engagement portion 422 corresponding to the first engagement portion 412 is on the edge of the top portion of the striking plate 420. The second engagement portion 422, in which for example, is a raised edge, for allowing the shell 410 and the striking plate 420 to mutually engage respectively using the first engagement portion 412 and the seco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com