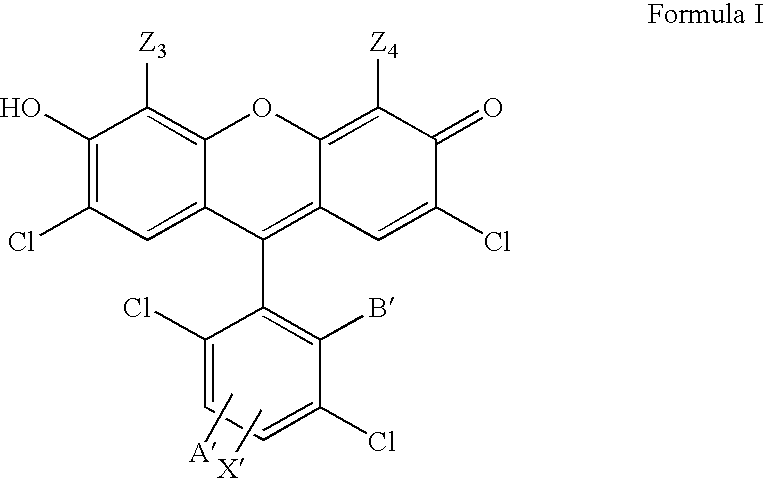
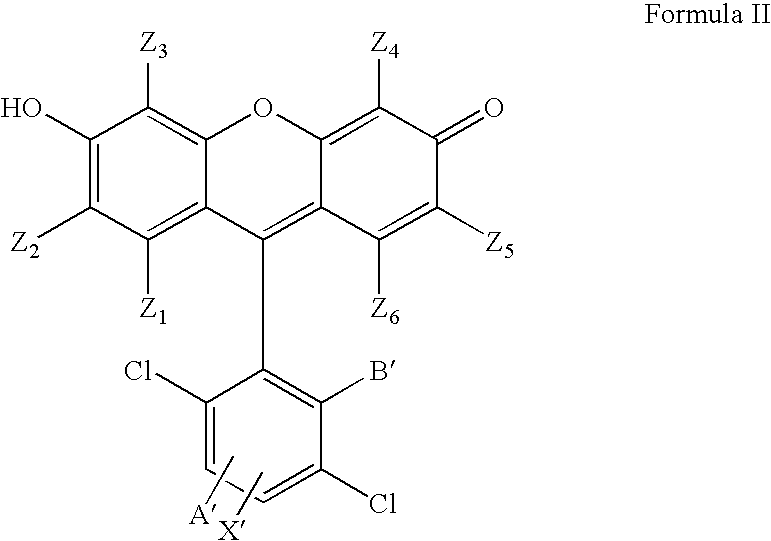
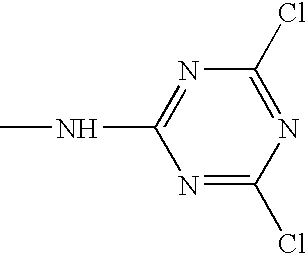
4,7-dichlorofluorescein dyes as molecular probes
a technology of dimerization and fluorescence, which is applied in the field of fluorescent labelling techniques, can solve the problems of difficult to find three or more dyes with no significant overlap of emission bands, and the requirement is particularly difficult to satisfy, and achieves high fluorescence efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
4,7-dichloro-5- (and 6-)carboxyfluorescein (“ALF”)
[0044] 0.58 g of 3,6-dichlorotrimellitic acid, 0.72 g of resorcinol, 0.5 ml concentrated sulfuric acid, and 3 ml of propionic acid were refluxed 12 hours under argon. The reaction mixture was poured into 150 ml water; the precipitate was dried, taken into 3 ml pyridine and acetylated with 2 ml acetic anhydride for 1 hour. The acetylation mixture was taken into 100 ml ethyl acetate, washed with 1 N hydrochloric acid, water, and evaporated to dryness. The residue was placed on 15 grams of silica gel and eluted with 50 ml ethyl acetate, then 4:1 ethyl acetate:methanol. Fractions containing UV active material with Rf of about 0.2 (4:1 ethyl acetate:methanol / silica gel) were evaporated to dryness. This residue was dissolved in 10 ml methanol and then 1 ml of 4 N sodium hydroxide was added. After 10 minutes, the reaction mixture was diluted to 200 ml with water and then 0.5 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added. The total mixture...
example 2
4,7-dichloro-5- (and 6-)carboxyfluorescein N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester
[0045] 13.7 mg of fluorescein from Example 1. 3.3 mg of 30 NHS, 6,4 mg DCC, and 1 ml ethyl acetate were stirred 0.5 hours. The solid was filtered, and the supernatant was washed three times with 1:1 brine:water, dried with sodium sulfate, and evaporated to dryness yielding 15 mg of NHS ester.
example 3
Conjugation of 4,7-dichloro-5- (and 6-)carboxyfluorescein with aminoalkyloligonucleotides
[0046] 5 mg of NHS ester from Example II were dissolved 5 in 20 ul of DMSO: 3 ul of this solution were added to a solution consisting of 20 ul of 1.0 mM 5′-aminohexylphosphate oligonucleotide (an 18-mer) in water and 10 ul of 1 M sodium bicarbonate / sodium carbonate buffer, pH 9.0. After one hour in the dark, the solution was passed through a 10 ml Sephadex G-25 (medium) column with 0.1 M triethylammonium acetate buffer, pH 7.0. The band of colored material eluting in the exclusion volume was collected. Reverse phase HPLC showed two major fluorescent peaks, corresponding to the 5- and 6-isomers of the dye conjugated onto the DNA. The peaks were collected, and the fluorescence spectra in 50% urea at pH 8.0 showed full width at half max of 34 nm with the emission maxima at 528 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com