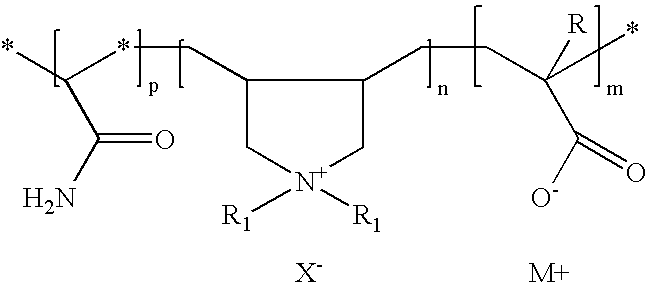
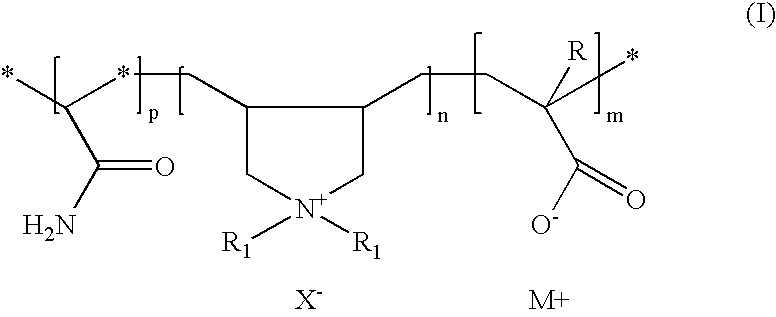
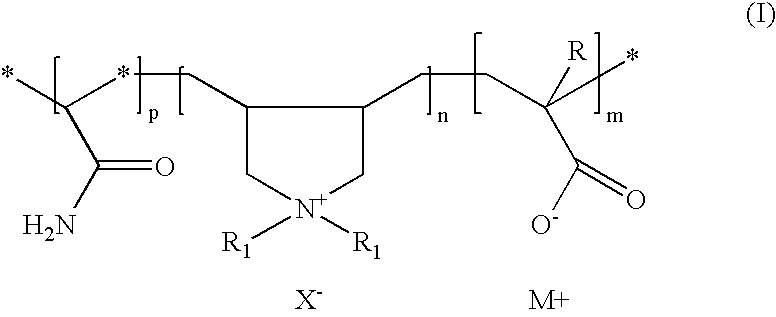
Amphoteric cationic polymers for controlling deposition of pitch and stickies in papermaking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of Amphoteric DADMAC Polymers 1-10 and DADMAC homopolymer Control
[0100] The procedure for making Polymer 1 is described in this example. Other polymers are made following the same procedure, but using different monomer ratios, initiator feeds and temperature to obtain polymers with different compositions and molecular weights. Molecular weights of the polymers are measured using the bulk viscosity or Brookfield viscosity (BV) at 20% polymer solids. A high 20% BV value indicates a high MW. Properties of the polymers synthesized are shown in Table 1.
[0101] A 1-liter reactor equipped with a condenser, a thermometer, a nitrogen inlet, and an overhead agitator is charged with 453.86 g of 66% monomer DADMAC, 15.8 g of acrylic acid, 59 g of deionized water and 0.15 g of Versene (Na4EDTA). 35 g of a 25% NaOH solution is added slowly to the reactor at room temperature to neutralize the acrylic acid. The polymerization mixture is purged with nitrogen and heated with agitation to a...
example 2
[0113] The samples tested in this example all have a relatively low molecular weight expressed by the 20% BV of about 400 cps. Testing is performed on 100% recycled old corrugated container (OCC) furnish from a linerboard mill experiencing serious stickies deposit problem. This example shows that with similar MW, the amphoteric DADMAC copolymer Polymer 1 performs better in the turbidity reduction than the DADMAC homopolymer control. Results in Table 2B for the Control, Polymer 1 and Polymer 2, demonstrate that the performance improvement with incorporation of the AA anionic component is diminished when the M content is above 10%.
TABLE 2B100% recycled Old Corrugated Container(OCC) furnishblank Turbidity, 379 NTUDosage, kg / ton1.02.05.0Turbidity, NTUControl 1 (homopolymer 0% AA)574943Polymer 1 (5% AA)574639Polymer 2 (10% AA)605442
example 3
[0114] The samples tested in this example all have a higher molecular weight expressed by the 20% BV of above 600 cps. Testing is performed on 100% recycle deinked pulp furnish from a paper mill. This example further demonstrates that the performance improvement with incorporation of AA anionic component is diminished when the AA content is above 10%. See Table 3A. A commercial fixative (Alcofix 159, a medium MW polyamine) commonly used for deposit control in paper mills is also included in the testing. Polymer 3 of the present invention gives significantly better performance in turbidity reduction than the commercial fixatives.
TABLE 3A100% recycled furnish deinked pulp (DIP)furnishblank turbidity, 578 NTUDosage, kg / ton0.20.40.8Turbidity, NTUCommercial fixative (Alcofix 159)1267350Polymer 3 (5% AA)996341Polymer 4 (10% AA)17610449Polymer 5 (20% AA)14910551Polymer 6 (40% AA)15910150
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com