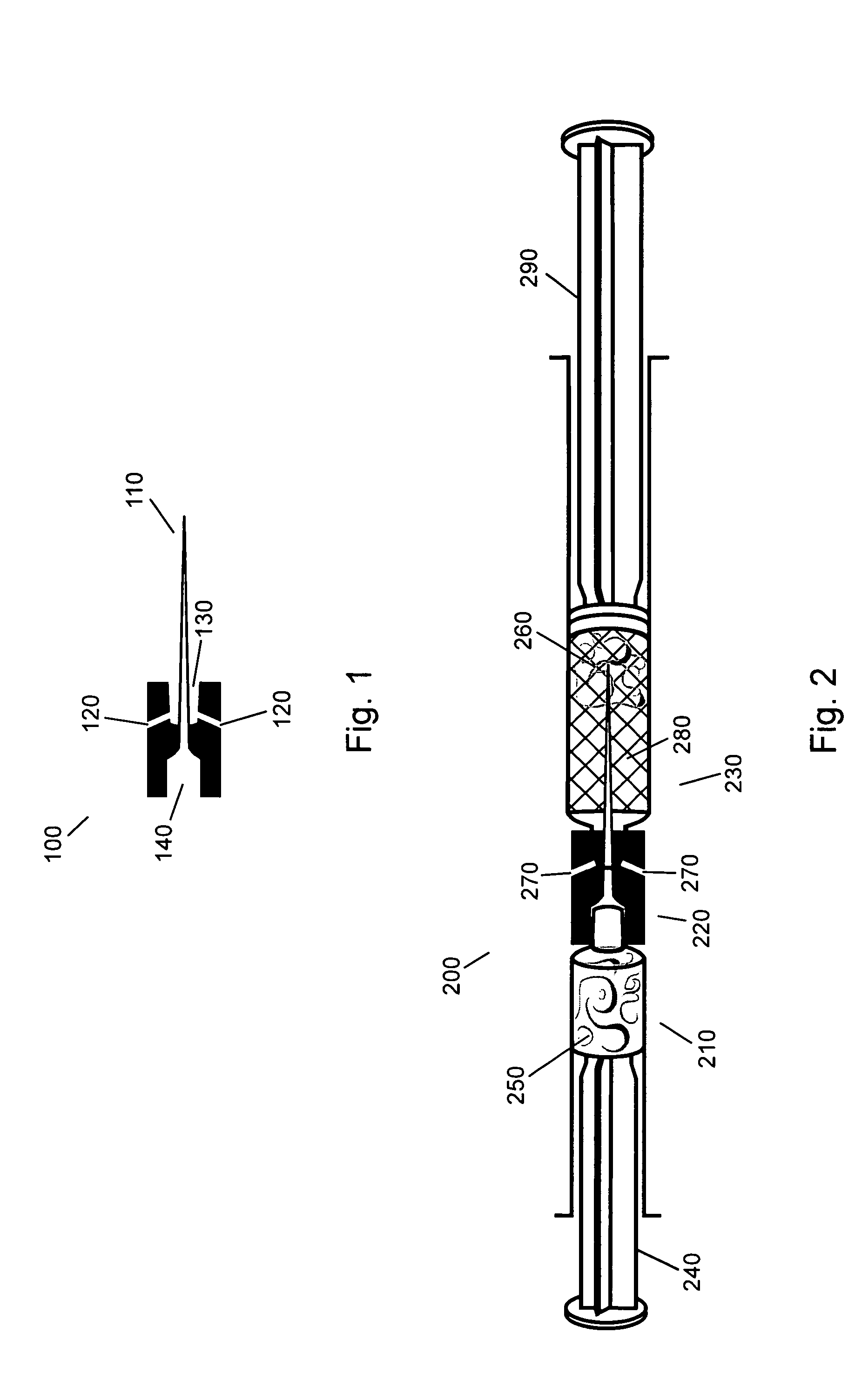
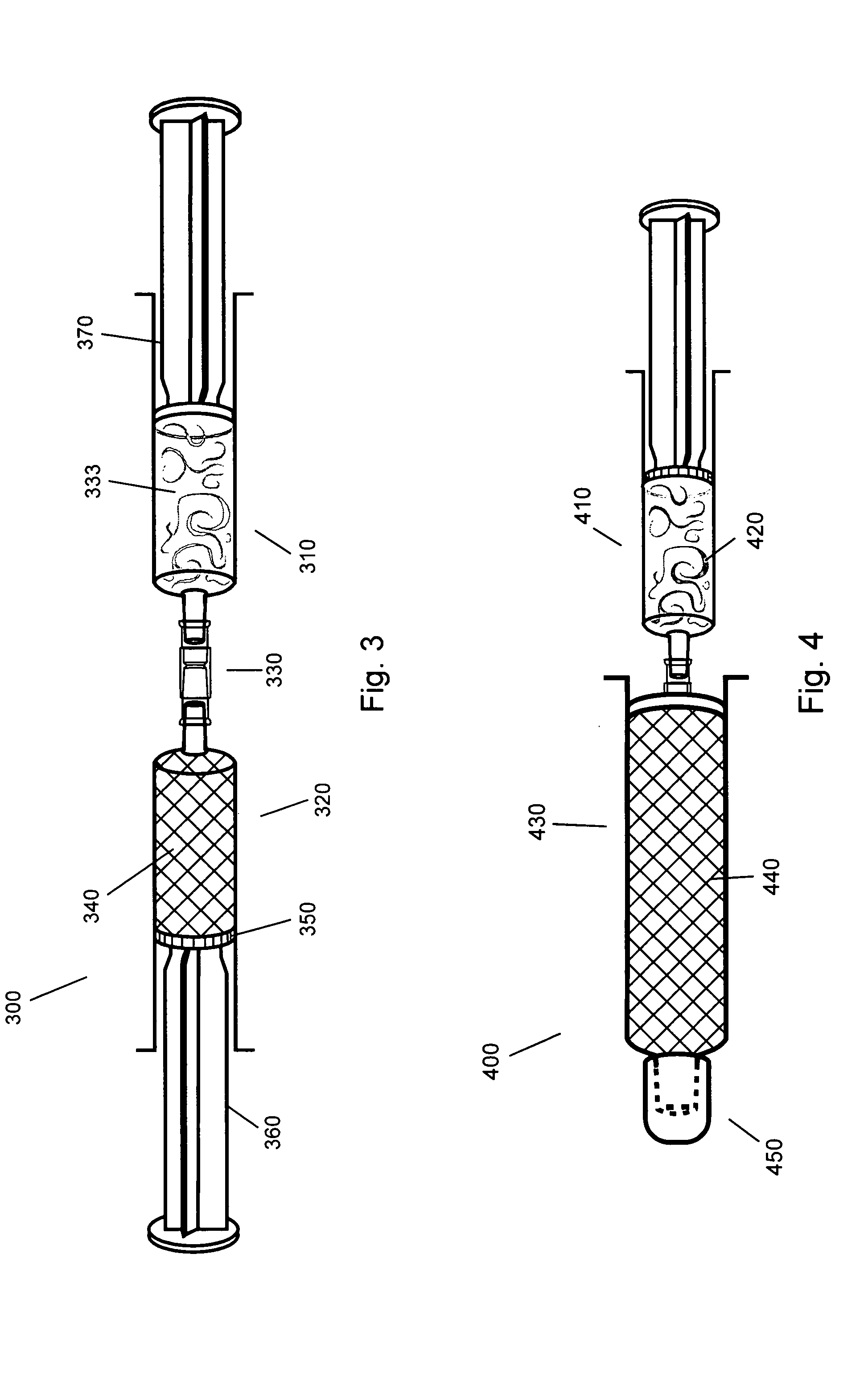
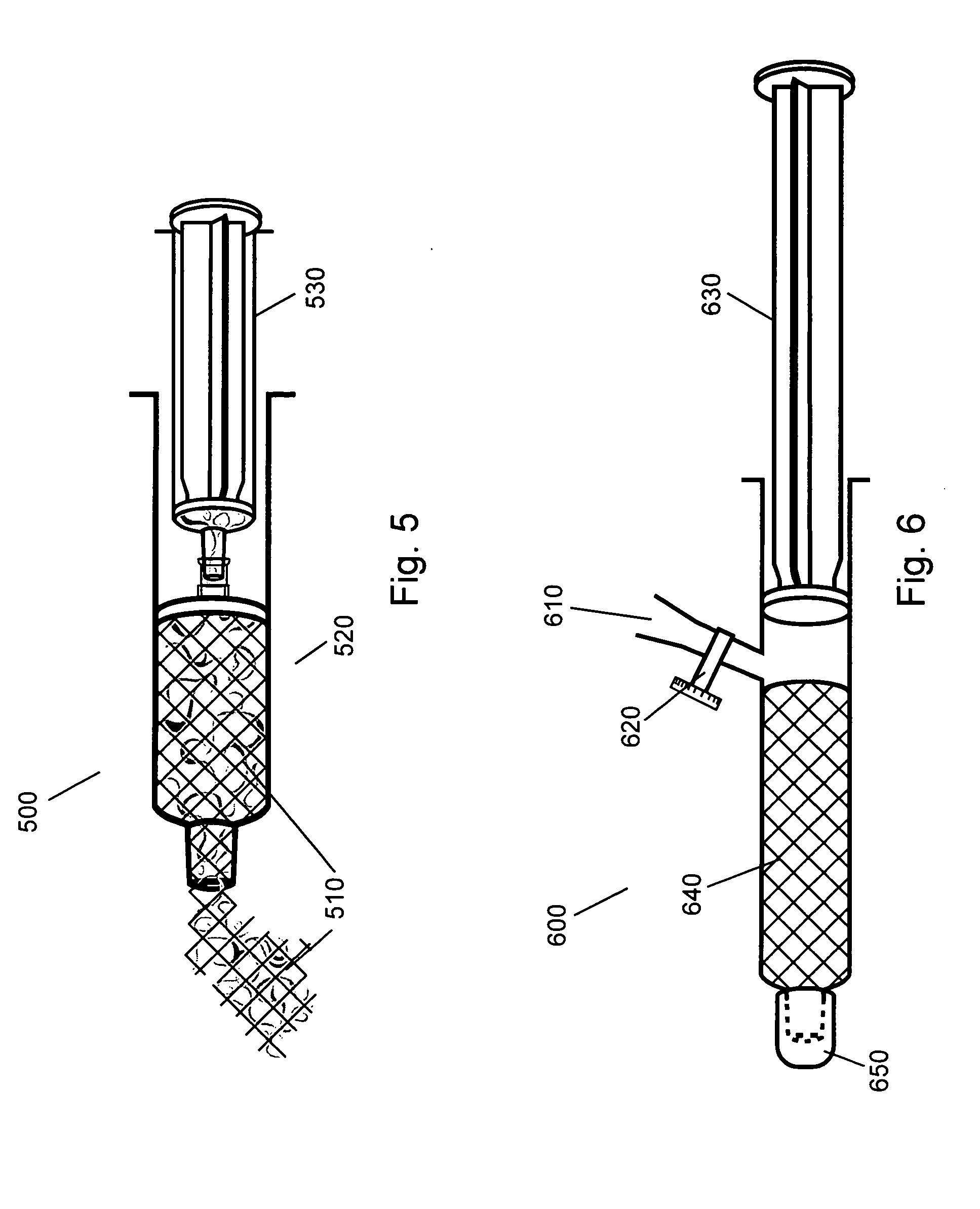
Gel suitable for implantation and delivery system
a gel and implantation technology, applied in the field of medical implant devices, can solve the problems of inability to rehydrate or resolve, change to polymers, undesirable final products, etc., and achieve the effects of convenient cellular ingrowth, high viscosity, and easy cellular ingrowth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0097] A single 0.1-gram porous collagen sheet of matrix material is placed in a shallow dish and covered with 1.9 grams of buffered saline at a pH of 7.4 that is allowed to soak in and spread across the internal surfaces of the pores by capillary rehydration. After 1 minute the sheet is kneaded and compressed by hand while folding any dry areas into the moist center of the mass to create approximately 2 cc of 5% putty. A putty made in this manner has a viscoelastic property similar to soft tissue, and thus makes an ideal augmentation material.
example 2
[0098] The 5% putty from Example 1 was placed into a small container and covered with 40 cc of buffered saline at a pH of 7.4. After 4 hours the material is still intact with no sign of softening, swelling or taking on moisture. The putty is then kneaded and compressed while in contact with 1 gram of buffered saline at a pH of 7.4 to create approximately 3 cc of 3.3% putty. A putty made in this manner is easily injected through long needles and thus makes an ideal deep injection augmentation material.
example 3
[0099] A single 0.1-gram porous collagen sheet of matrix material is rolled and placed into a 10 cc syringe. Using a 14 g I.V. needle, 1.9 grams of buffered saline at a pH of 7.4 is injected from a separated delivery syringe into the bottom of the syringe containing the rolled collagen sheet. After removing the needle, the plunger to the syringe containing the rolled collagen and saline is depressed, crushing the porosity of the hydrated region of the sponge and forcing the fluid into the non-hydrated portions of the sponge. Once fully hydrated, a syringe cap is placed over the opening and the plunger compressed to pressurize the interior of the syringe and solvate the polymer. The cap is removed and smooth, homogeneous 5% putty is expelled from the syringe. This material has physical properties identical to example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com