Assembly with osmolality-increasing fluid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
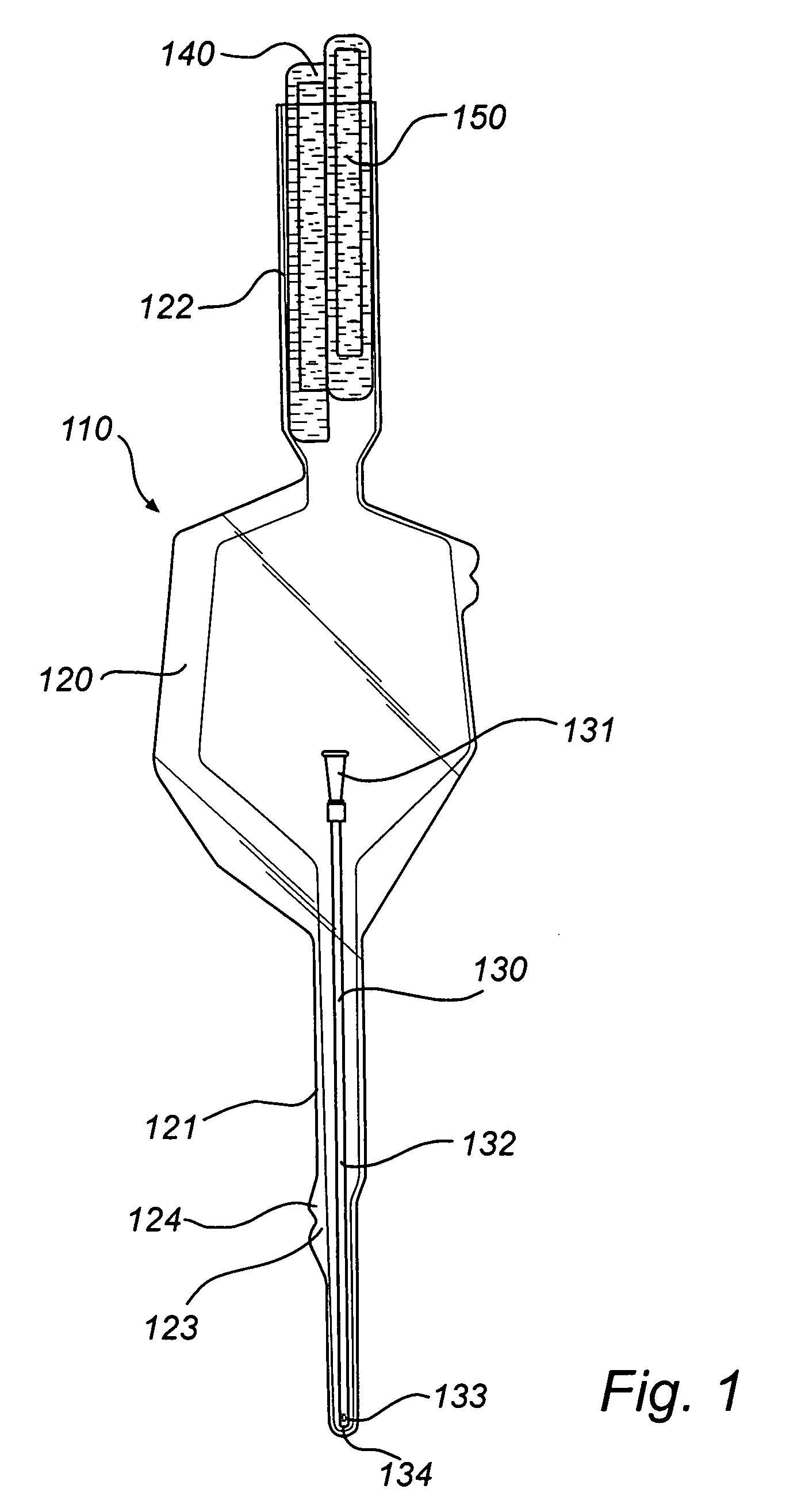
[0054] With reference to FIG. 1, a catheter assembly will now be described, the structure of which generally resemblings embodiments previously disclosed in WO 97 / 26937, hereby incorporated by reference.
[0055] The catheter assembly 110 comprises a wetting receptacle or bag 120, preferably of a transparent flexible plastics material. The receptacle 120 has an elongate pocket 121 at its forward end. At its rearward end 122 the receptacle presents an opening. The wetting receptacle 120 is adapted for accommodation of at least the insertable lenght of the catheter tube 132 in the elongate pocket 121.
[0056] The catheter assembly 110 further comprises a hydrophilic urinary catheter 130, as is discussed in more detail in the foregoing.
[0057] The catheter assembly 110 comprises a wetting fluid 150 forming part of the assembly 110, i.e. the wetting fluid is not provided completely separate from the assembly. More specifically, in the embodiment in FIG. 1, the catheter assembly 110 further ...
second embodiment
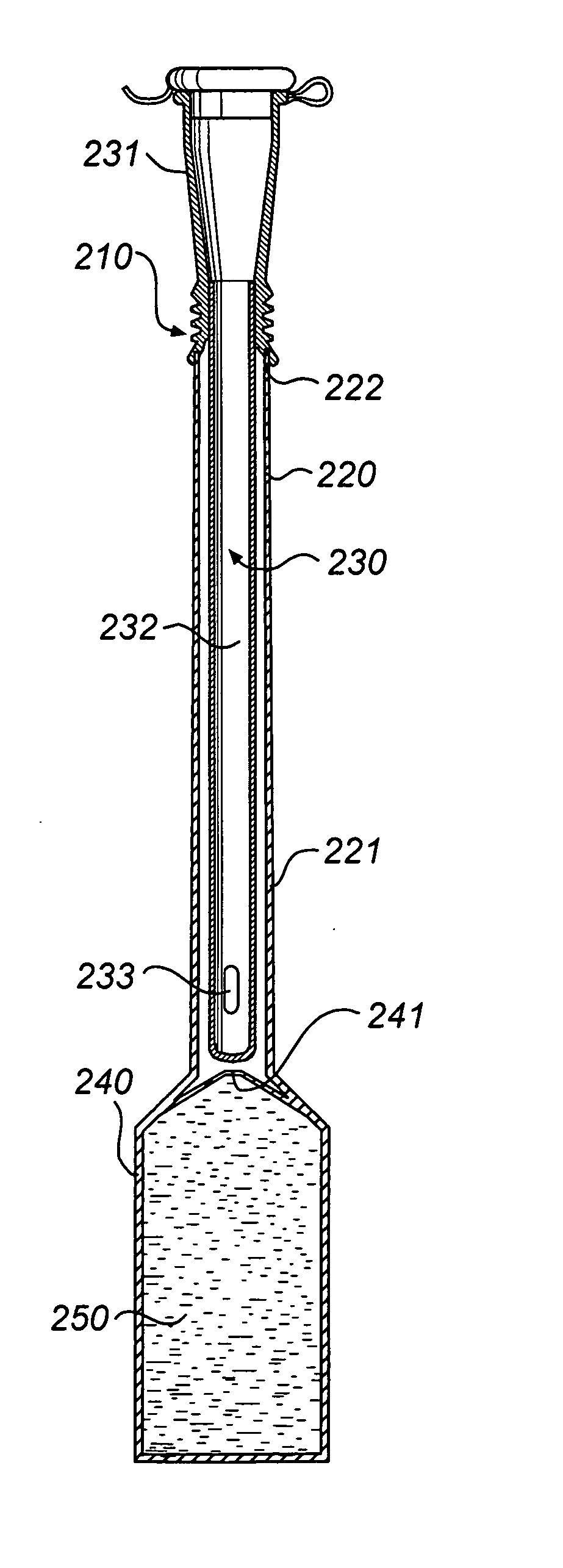
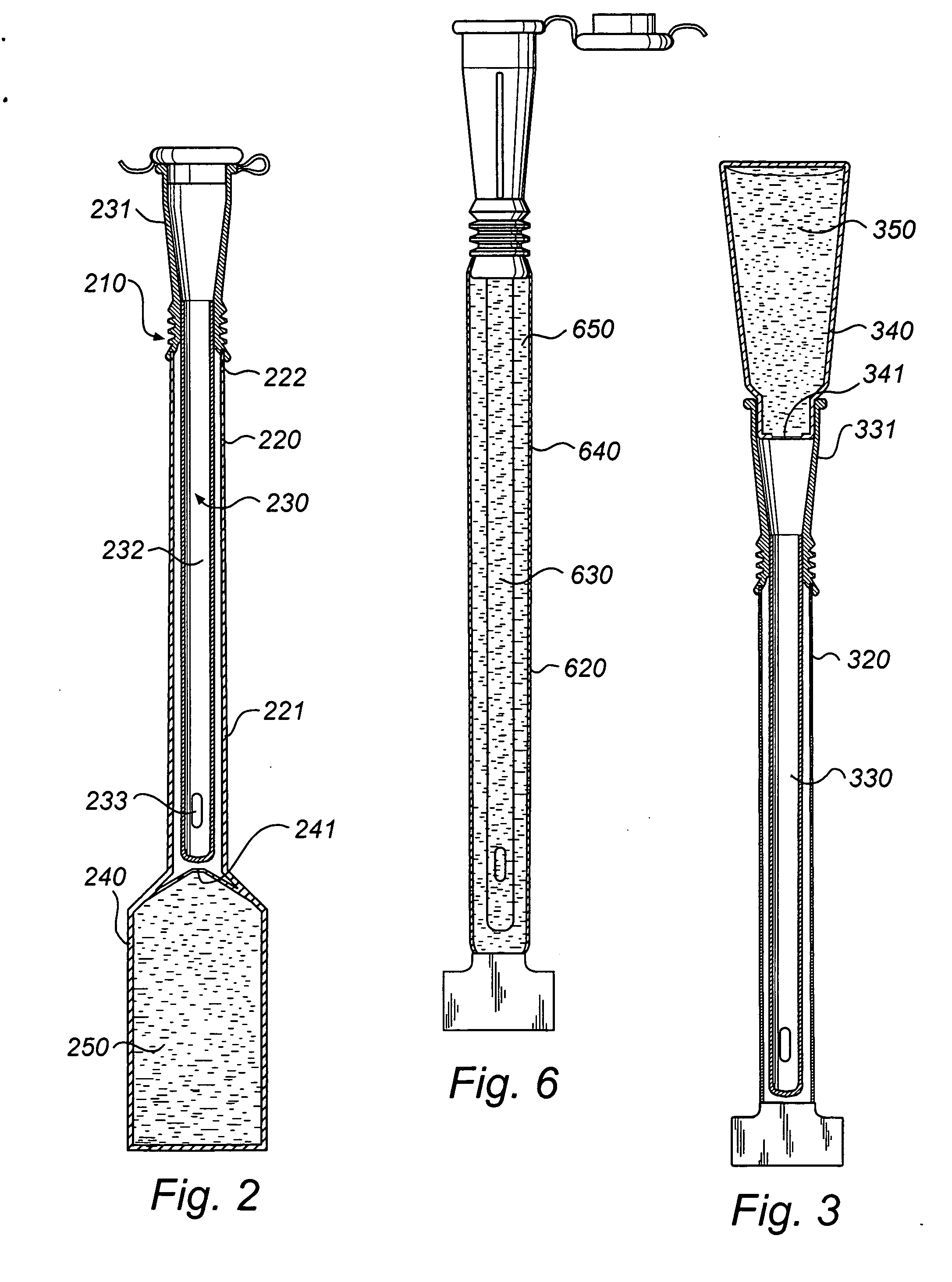
[0063] With reference to FIG. 2, a catheter assembly will now be described, the structure of which resembling catheter assemblies disclosed in WO 01 / 43807, hereby incorporated by reference.
[0064] In this embodiment, the wetting receptacle 220 is adapted for accommodation of only the catheter tube 232 in the elongate pocket 221, whereas the opening end 222 of the wetting receptacle 220 is sealingly connected to and closed by the connector or rearward end 231 of the catheter 230. Hereby, the receptacle 220 encloses the insertable length of the catheter 230, but leaves a part of the catheter 230 outside the receptacle 220.
[0065] In the embodiment in FIG. 2, the wetting fluid container 240 enclosing the wetting fluid 250 is formed as a separate compartment of the wetting receptacle 220. A rupturable separation wall 241 is arranged between this receptacle compartment 240 holding the wetting fluid 250 and the receptacle compartment holding the catheter 230, i.e. the elongate pocket 221. ...
fourth embodiment
[0069] With reference to FIGS. 4a and 4b, the catheter assembly will now be described. Also in this embodiment, the catheter assembly in structure resembles catheter assemblies disclosed in WO 01 / 43807. The catheter assembly 410 comprises a wetting receptacle or bag 420. As in the previously discussed embodiments, the catheter assembly comprises a hydrophilic catheter, and preferably a urinary catheter 430. The wetting receptacle encloses at least the insertable length of the catheter 430, but leaves at least part of the catheter 430 outside the wetting receptacle 420, said part comprising the connection interface. The assembly also comprises a wetting fluid container 440 containing a wetting fluid 450. In this embodiment, the wetting fluid container 440 is formed in a compartment of the wetting receptacle being separated from the compartment accommodating the catheter 430. The wetting fluid container 440 is arranged in a part of the receptacle extending rearward from the catheter 4...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com