Diagnostic agents for pancreatic exocrine function
a technology of pancreatic exocrine function and diagnostic agent, which is applied in the field of compounds, can solve the problems of increased pancreatic exocrine enzymes in the blood, inability to be used repeatedly or for screening, and inability to meet the needs of patients,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
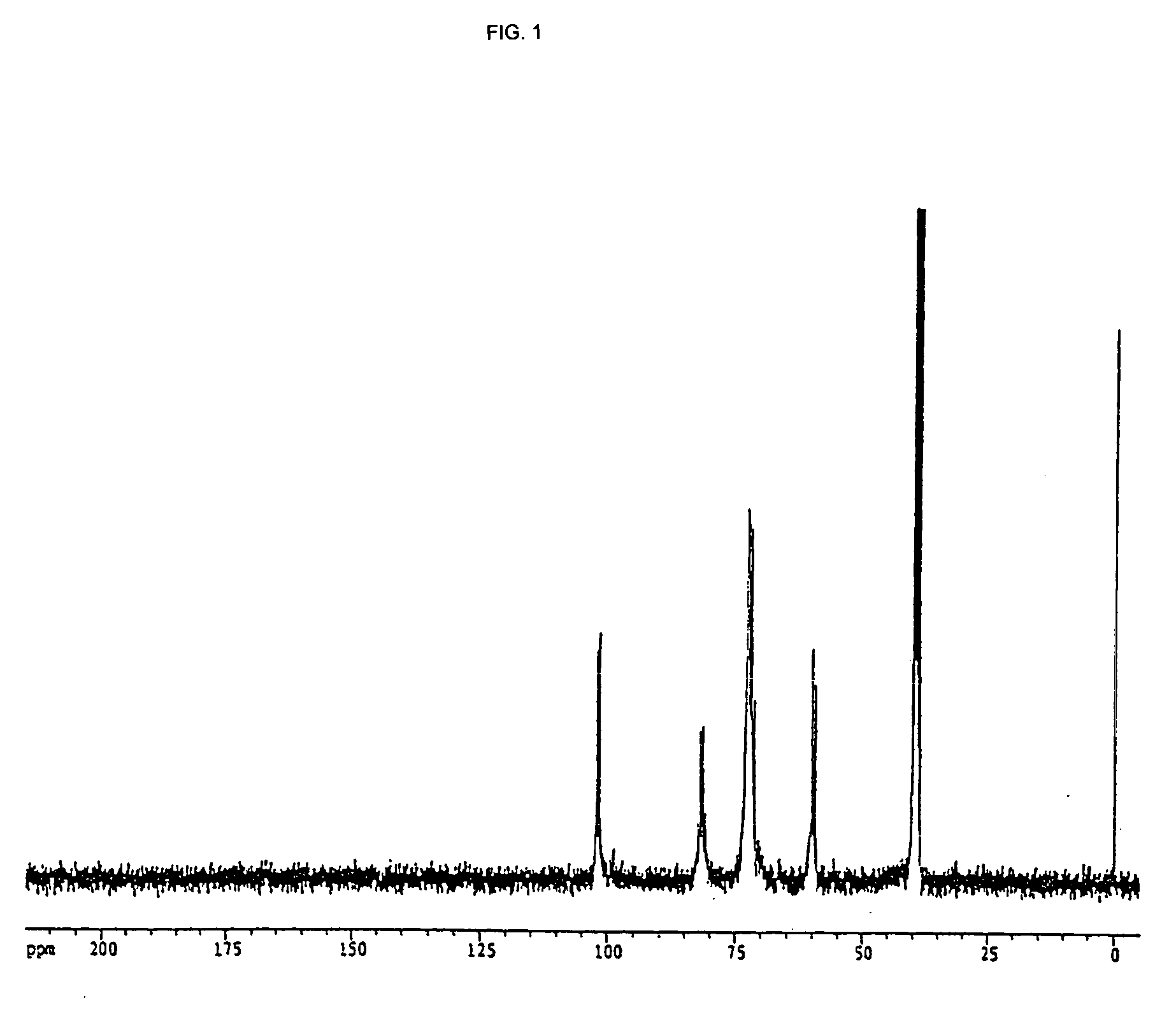
Preparation of 13C-labeled Cyclodextrin
13C-labeled starch (Chlorella Industry, Algal Starch (water-soluble), Lot No. 8031,S, U-13C:98.6 atom %, Starch Content: 93.5%) was dissolved in 50 mM acetate buffer (pH 5.4) at a concentration of 5% (w / v) and 100 Units of cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase (Hayashibara) was added thereto and reacted at 40° C. for 24 hours. After the enzyme was inactivated with the treatment at 100° C. for 15 minutes, glucoamylase was added and reacted at 40° C. for 1 hour to decompose components other than 13C-labeled cyclodextrin into glucose. After the reaction was completed, the reaction mixture was treated at 100° C. for 15 minutes to inactivate the glucoamylase.
The solution was applied to a carbon column (2.5 cm×25 cm) and the column was washed with 500 ml of water. A 15% ethanol solution and a 40% ethanol solution were sequentially applied to recover the 13C-labeled cyclodextrin in the 40% ethanol solution eluted fractions. The resulting 13C-labele...
example 2
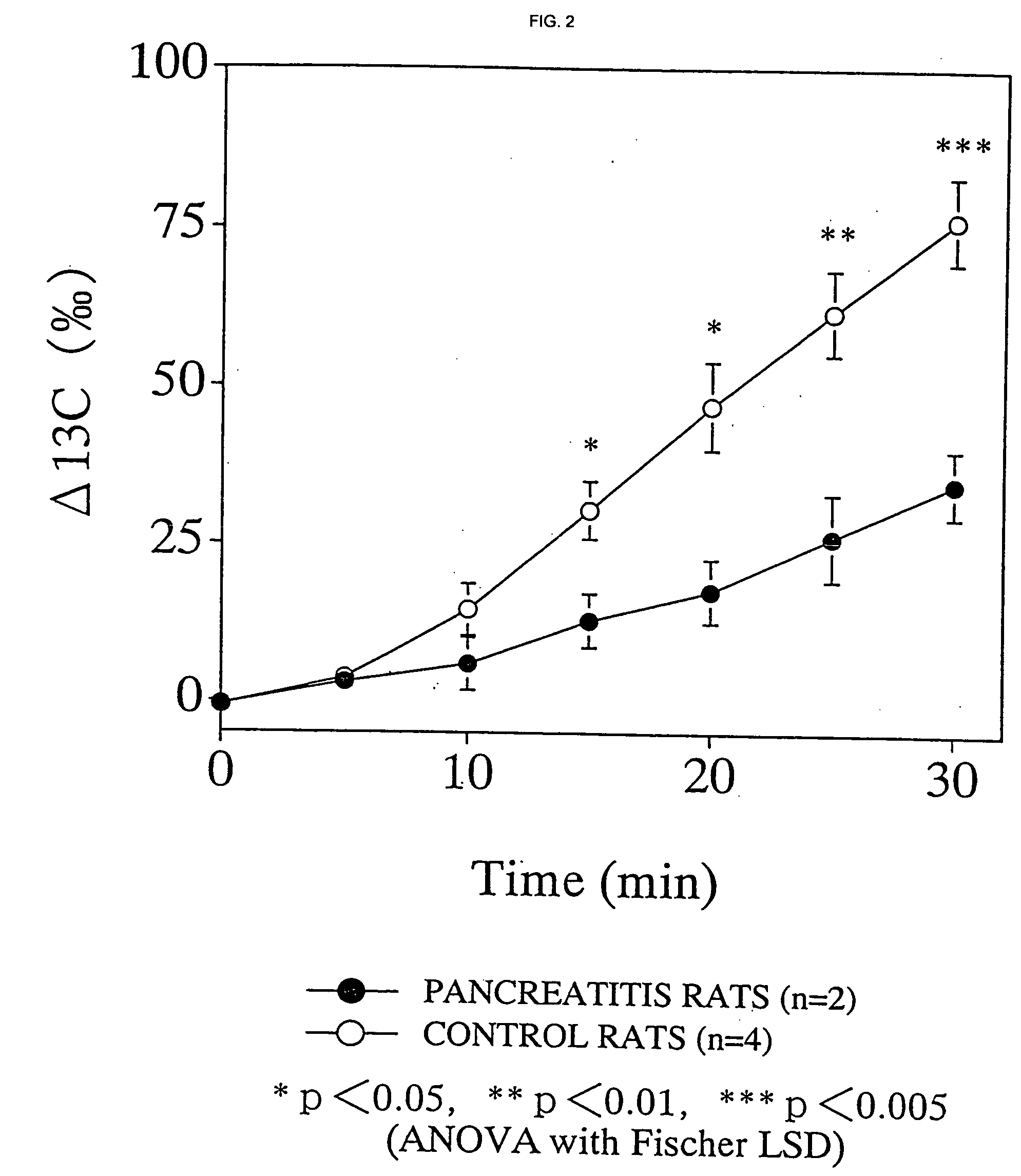
13C-labeled Cyclodextrin Breath Test
13C-labeled cyclodextrin breath test was carried out wherein 13C-labeled cyclodextrin prepared in Example 1 was orally administered to chronic pancreatitis and control rats and the time course of the 13C concentration in the exhaled CO2 after the administration was measured.
According to Mundlos et al. (Mundlos et al., Pancreas, 1:29 (1986)), the chronic pancreatitis rats were prepared by injecting oleic acid into the pancreatic duct of Wistar male rats of 5 weeks old and kept for 3 weeks. Rats in which midline incision was made on the abdomen were used as the control.
The chronic pancreatitis and control rats of 8 weeks old, which fasted overnight, were fixed without anesthesia in a rat holder for a microwave irradiation apparatus. The breath was collected at a rate of about 100 to 300 ml / min using a stroke pump (Variable Stroke Pump VS-500, Shibata Kagaku Kogyo) and introduced directly to a flow cell of a 13CO2 analyzer EX-130S (Nihon Bunko) ...
example 3
Preparation of C-labeled Galactosylmaltohexaose
13 C-labeled starch (Chlorella Industry, 4.65 g) was dissolved in a 50 mM acetate buffer (pH 5.4) at a concentration of 0.5% (w / v) and 186 Units of cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase (Hayashibara) was added thereto and reacted at 40° C. for 2 hours and 20 minutes. The enzyme was inactivated with the treatment at 95° C. for 15 minutes and the product was purified by Sephadex G-25. This procedure was repeated 4 times to yield 4.39 g of 13C -α-cyclodextrin (yield 23.6%).
Pyridine (200 mL) was added to 4.39 g of the resulting 13C-α-cyclodextrin and ice cooled. Acetic anhydride (100 mL) was added thereto. After 30 minutes, the reaction mixture was removed out of the ice bath and then stirred at room temperature for 36 hours. To the residue obtained by concentration under reduced pressure, toluene was added and azeotropically distilled. This procedure was repeated three times. Ethyl acetate and water were added to the residue to extract....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com