Optical fiber base material ingot and method for producing the same
a technology of optical fiber and base material, which is applied in the direction of glass deposition burners, manufacturing tools, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as splicing loss, and achieve the effect of excellent ingot roundness and core portion eccentricity, and short period of tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0019] The present invention will be explained with reference to the following example and comparative example.
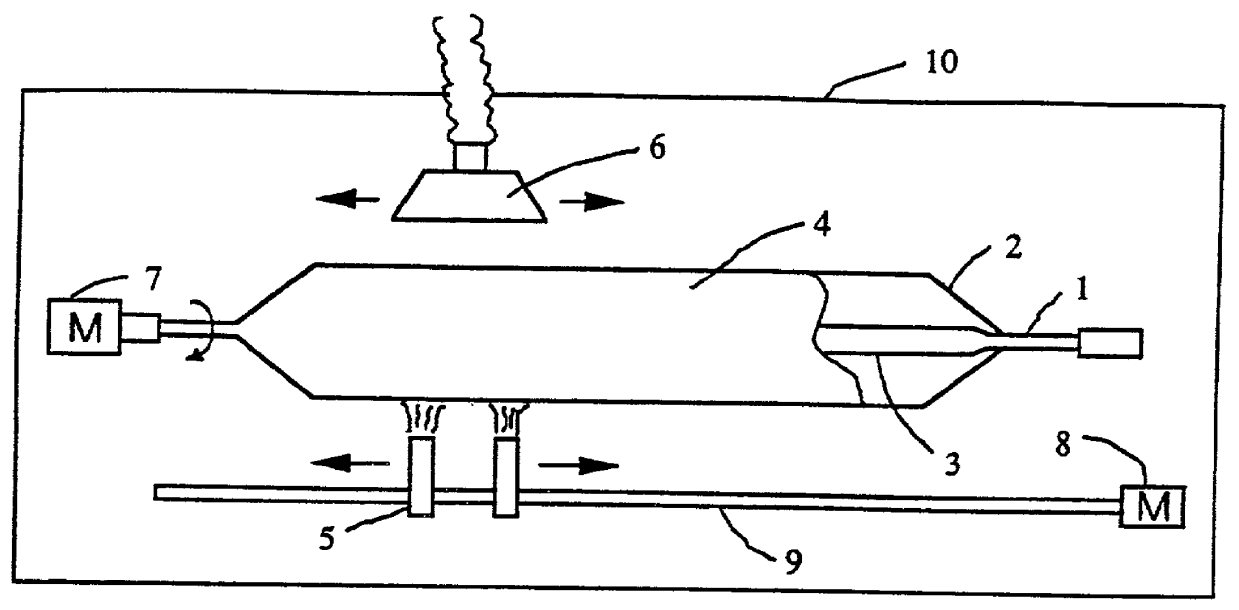
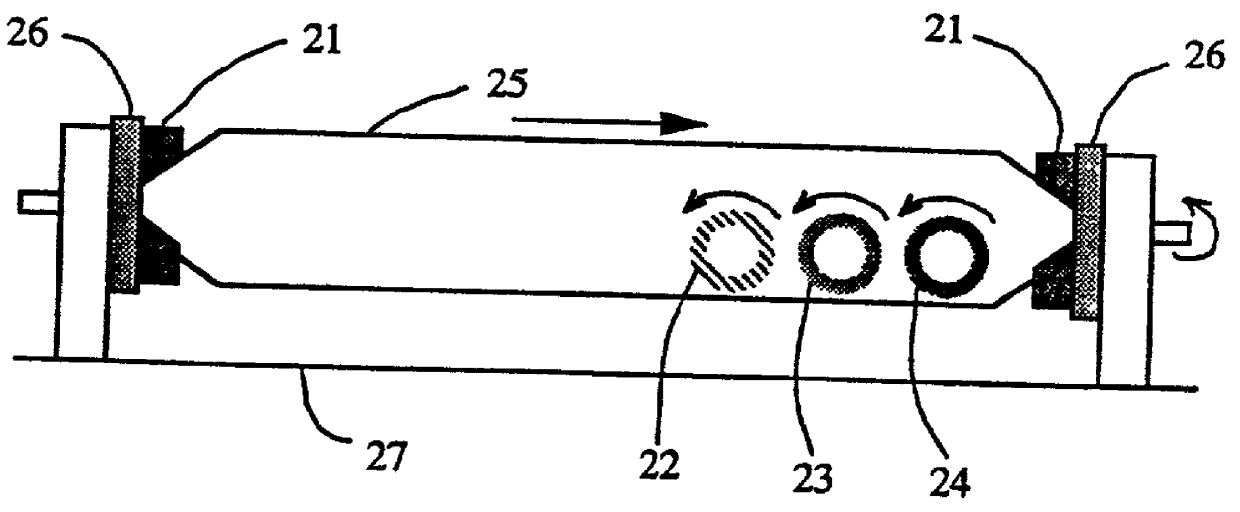
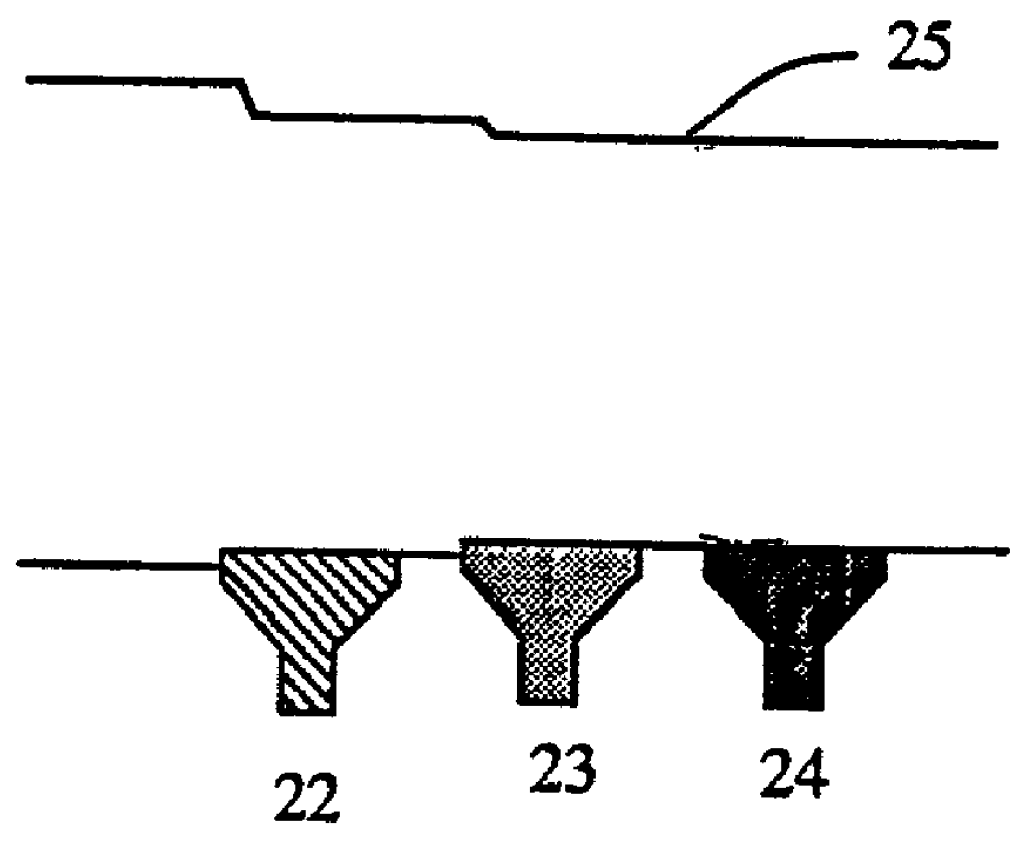
[0020] (Example) As a starting core member 3, quartz glass for single mode optical fibers, which had an outer diameter of 25 mm .phi. and a length of 1200 mm, was used. This was welded with a dummy quartz bar, attached to a revolution driving part 7 in a closed type reactor 10, and rotated at 40 rpm. Subsequently, oxygen gas of 75 L / min, hydrogen gas of 150 L / min, oxygen gas of 9 L / min as a carrier gas, and SiCl.sub.4 of 40 g / min as a material gas were introduced into the multi-pipe oxyhydrogen flame burners 5 having an opening diameter of 28 mm .phi. from a material supplying apparatus not shown. These burners 5 were reciprocated on a burner guiding mechanism 9 at a speed of 150 mm / min within a length of 1600 mm by a motor 8, so that glass microparticles formed from hydrolysis of SiCl.sub.4 in flame should be deposited on the core member 3. The exhaust was ejected from an ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com