Fiber containing boride microparticle and textile product therefrom
A technology of borides and fibers, which is applied in the field of fiber products, can solve the problems of large amount of necessary additions, high specific gravity of fibers, and heavy clothes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
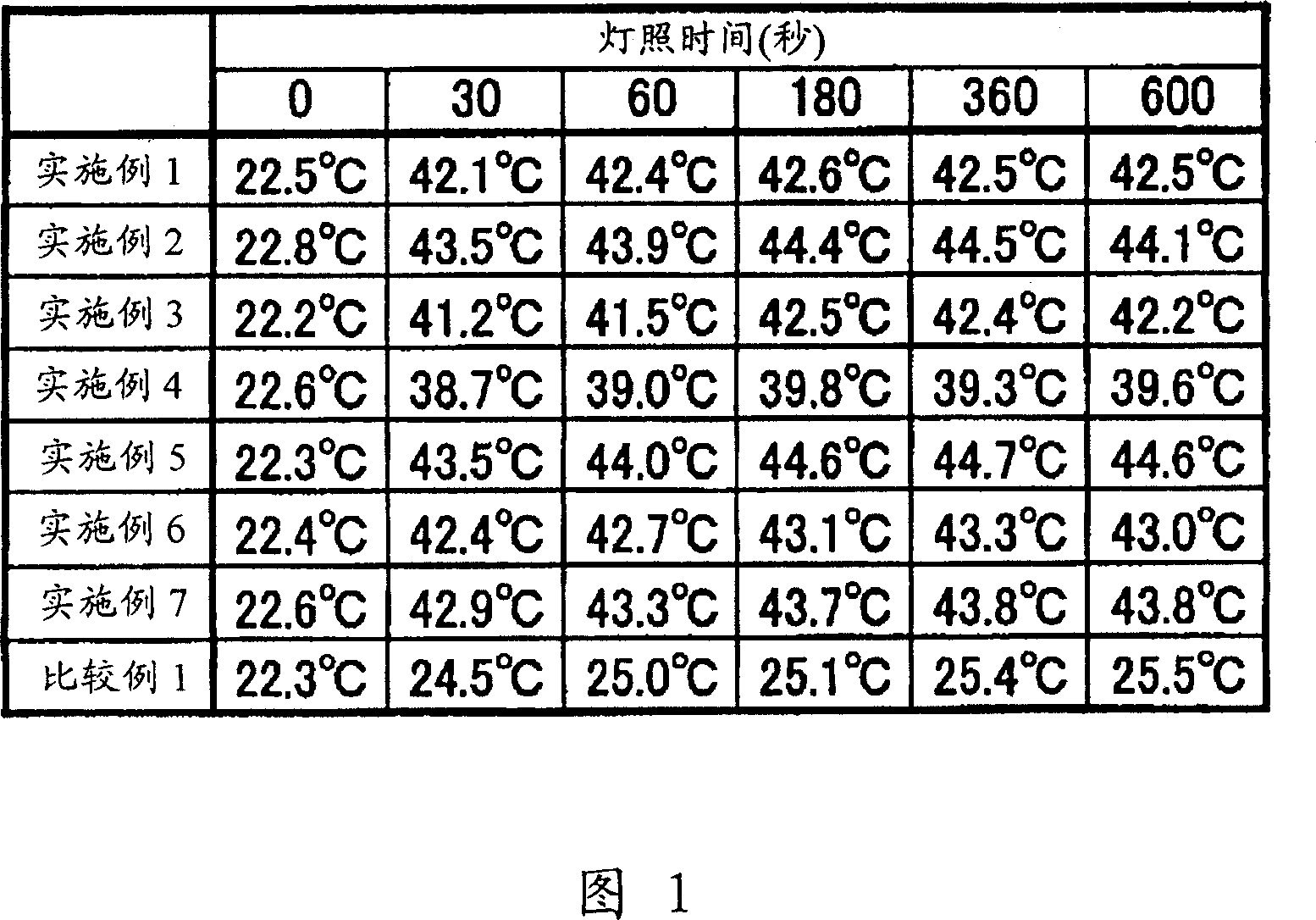
[0060] Mix 200g of LaB as boride particles 6 Particles (specific surface area 30m 2 / g), 730g of toluene as dispersant and 70g of dispersant for dispersing microparticles, carry out dispersing process with media agitation mill, prepare 1kg of LaB 6 The dispersion liquid of fine particles is referred to as (liquid A). Then use a spray dryer to remove the toluene in (liquid A) to obtain LaB 6 Dispersible powder (A powder). The obtained (A powder) is added to polyethylene terephthalate particles as a thermoplastic resin, uniformly mixed with a stirrer, melted and kneaded with a twin-screw extruder, and the extruded strands (strand ) was cut into pellets to obtain LaB containing 30% by weight as a heat-absorbing component 6 Microparticle masterbatch. 30% by weight of the LaB are mixed in a weight ratio of 1:1 6 The microparticle polyethylene terephthalate masterbatch and the polyethylene terephthalate masterbatch without adding inorganic microparticles were prepared by the s...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Make the LaB that contains 10% by weight with the ratio of 1: 1.5 with the same method as Example 1 6 Microparticles and ZrO 2 Microparticle polyethylene terephthalate masterbatch. LaB 6 Microparticles and ZrO 2 The average particle diameters of the fine particles were observed to be 20 nm and 30 nm, respectively, by the dark field method using TEM. Multifilament yarns were produced in the same manner as in Example 1 using a masterbatch containing the above two fine particles. The obtained multifilaments were cut to produce polyester staple fibers, and staple yarns were produced in the same manner as in Example 1. Knitted articles are obtained using the spun yarn. Using the same method as in Example 1, the spectral properties of the fabricated woven product were measured, and the sunlight absorption rate was 43.38%. Furthermore, the temperature rise effect on the back side of the base fabric was measured by the same method as in Example 1. The result is shown in ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The same method as in Example 1 was used to make CeB containing 30% by weight at a ratio of 1: 1.5. 6 Microparticles and ZrO 2 Microparticle polyethylene terephthalate masterbatch. CaB 6 Microparticles and ZrO 2 The average particle diameters of the microparticles were observed to be 25 nm and 30 nm, respectively, by the dark field method using TEM. Multifilament yarns were produced in the same manner as in Example 1 using a masterbatch containing the above two fine particles. The obtained multifilaments were cut to produce polyester staple fibers, and staple yarns were produced in the same manner as in Example 1. Knitted articles are obtained using the spun yarn. Using the same method as in Example 1, the spectral properties of the fabricated woven product were measured, and the sunlight absorption rate was 39.21%. Furthermore, the temperature rise effect on the back side of the base fabric was measured by the same method as in Example 1. The result is shown in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com