Novel polyurea photochromic material with azobenzene lateral group
A photochromic material and azobenzene technology are applied in the field of polyurea-type photochromic polymer materials and their preparation, which can solve the problems of reducing the optical properties of the polymer, low content of azobenzene groups, etc., and achieve photochromic properties. Excellent discoloration performance and thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The raw materials used are as follows:
[0033] 1 part of p-nitroazo m-phenylenediamine (moles)
[0034] 1 part of MDI (number of moles)
[0035] Under nitrogen protection, add 1.25g MDI and 15ml DMAc to a vacuum-baked three-necked flask, stir rapidly at 65°C under reflux and nitrogen, and slowly add 10ml of DMAc solution containing 1.28g of azo m-phenylenediamine After the dropwise addition, the temperature was raised to 75°C and 85°C for 4 hours respectively. Cool down to terminate the reaction. After washing with water, it is extracted with ethanol to obtain a polyurea photochromic material containing p-nitroazobenzene side groups.
[0036] Characterization of Photochromic Monomers and Polymers:
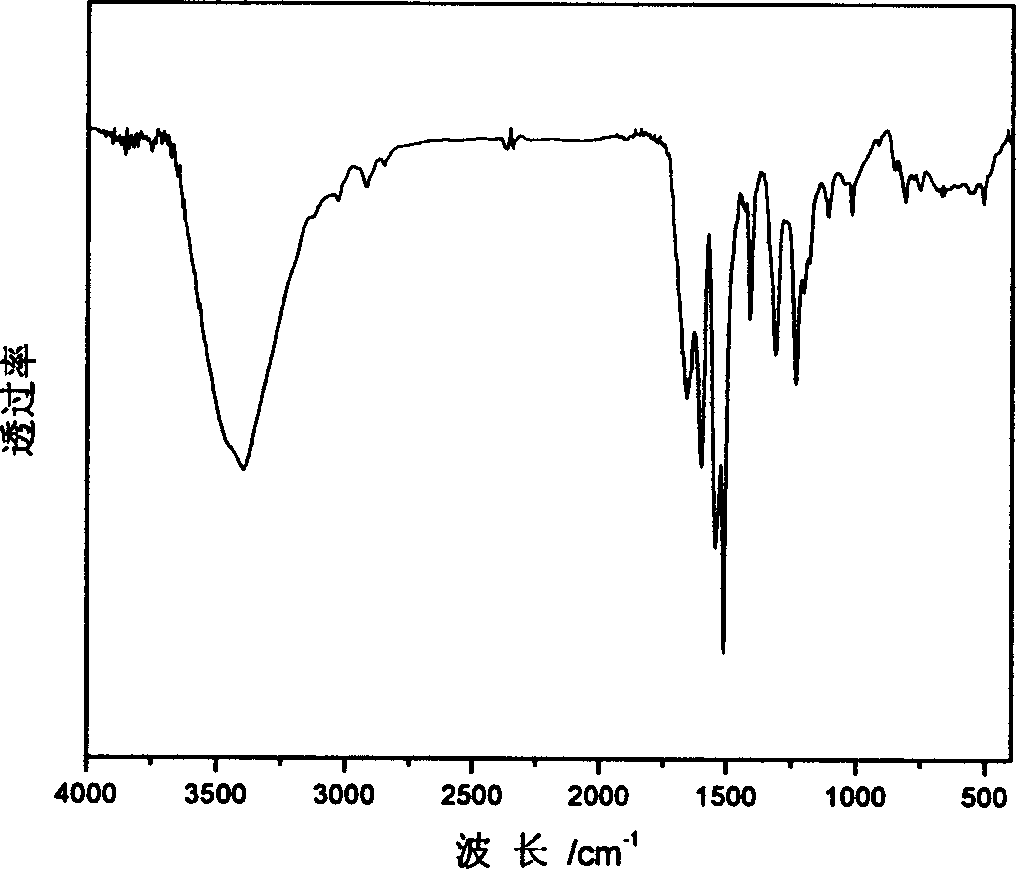
[0037] (1) The structure of the synthesized polyurea containing p-nitroazobenzene side groups is characterized by FTIR spectroscopy, and the infrared spectrum of polyurea containing p-nitroazobenzene side groups is shown in figure 1 shown.
[0038] (2) The polyurea co...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The raw materials used are as follows:
[0042] 0.8 parts of p-methylazo m-phenylenediamine (moles)
[0043] 1 part of MDI (number of moles)
[0044] The synthetic method of polyurea is similar to embodiment 1.
[0045] Characterization of photochromic azo-m-phenylenediamine and polyurea:
[0046] (1) p-methylazo-m-phenylenediamine has good photochromic properties. See Figure 4 shown.
[0047] (2) The polyurea containing p-methylazobenzene side groups has good photochromic performance, and the photochromic phenomenon is obvious when the solution is irradiated with ultraviolet light. The relationship between the change in absorbance of the polyurea solution containing p-methylazobenzene side groups and the irradiation time of ultraviolet light is shown in Figure 5 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The raw materials used are as follows:
[0050]0.5 parts of p-nitroazo m-phenylenediamine (moles)
[0051] Disperse Red 19 0.5 parts (moles)
[0052] 1 part of MDI (number of moles)
[0053] 2.5g of MDI and 30ml of DMAc were stirred rapidly under reflux and nitrogen, and 10ml of DMAc solution containing 1.65g of DR19 was added dropwise. Raise the temperature to 40°C and 75°C for 1 hour respectively, and react at 90°C for 2 hours. The above reaction system was cooled to 65° C. in an ice bath, and 10 ml of a DMAc solution containing 1.28 g of p-nitroazo-m-phenylenediamine was added dropwise. After completion, the temperature was raised to react at 70° C. for 5 hours, and at 90° C. for 3 hours each, and the temperature was lowered to terminate the reaction. After washing with water and extracting with ethanol, the photochromic material containing p-nitroazobenzene pendant norcarbamate urea can be obtained.
[0054] Characterization of Photochromic Monomers and Polymer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com