Memory subsystem and its method for generating latch clock
A generation method and memory technology, which are applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., to ensure the timing and the effect of reading and writing operations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
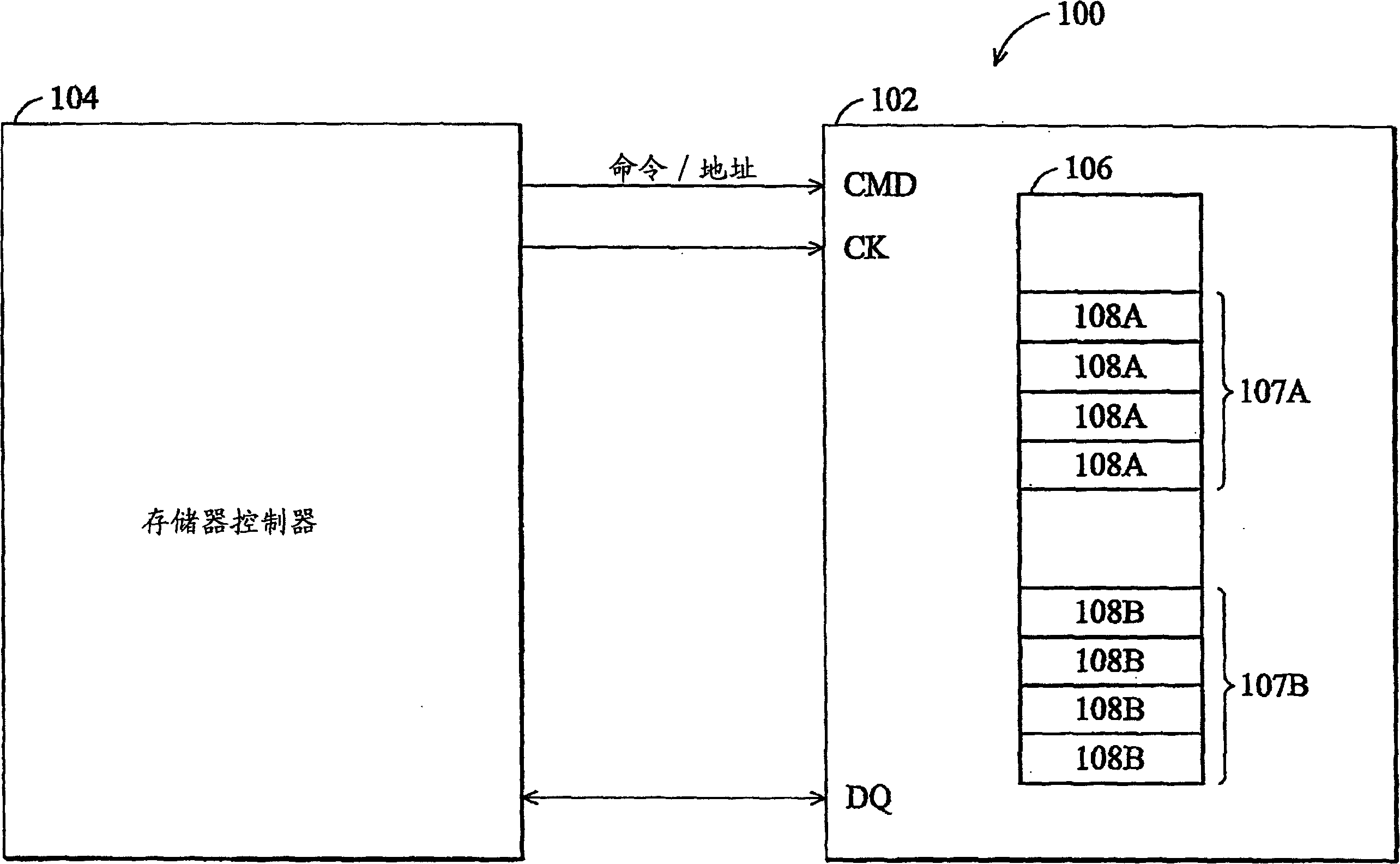
[0036] figure 1 It is a simplified functional block diagram showing a memory subsystem 100 according to an embodiment of the present invention, including a memory controller 104 and a memory 102 . The memory 102 typically has a memory array 106 of multiple banks. figure 1 The memory array 106 is shown as an example of two sets of banks 107A and 107B. The memory array 106 also includes a plurality of memory elements (not shown) for storing data, and the memory elements are generally arranged in addressable rows and columns respectively. Those skilled in the art typically refer to a commonly addressable subset of memory array 106 as a memory page. In general, memory cells in the same column within a bank in the memory array 106 constitute a particular memory page. exist figure 1 A plurality of memory pages (labeled 108A and 108B) corresponding to banks 107A and 107B, respectively, are shown.
[0037] Those skilled in the art understand that specific locations in memory arra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com