Rice stripe virus immune detection reagent kit
A technology for rice streak virus and immune detection, applied in the field of agricultural science, can solve the problems of high cost and inappropriate detection of samples in large quantities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] To detect the virus-carrying condition of the transmission medium SBPH, the steps at room temperature are as follows:
[0047] 1) Dilute the washing solution 10 times to 0.01M with pure water, and prepare the blocking solution for later use.
[0048] 2) Draw 0.25cm on the nitrocellulose membrane (NC) membrane with a pencil 2 left and right squares.
[0049] 3) Add 2 drops of sample treatment solution to a 0.2ml centrifuge tube, mash it with a toothpick, take a small drop of supernatant (about 3 μL) and apply it to the center of the nitrocellulose membrane grid, and dry it at room temperature.
[0050] 4) Immerse the dried membrane in blocking solution for 1 h at room temperature.
[0051] 5) Add one unit of monoclonal antibody to 10 ml of blocking solution, take out the membrane and immerse it, and place it at room temperature for 3 hours.
[0052] 6) Take out the membrane and wash with lotion 3 times, each time for 3-5 minutes.
[0053] 7) Add one unit of secondary...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Sample dilution test
[0060] Single-headed SBPH and diseased leaves were diluted into 11 gradients starting from 100 times, and the non-toxic SBPH was used as a negative control at the same dilution.
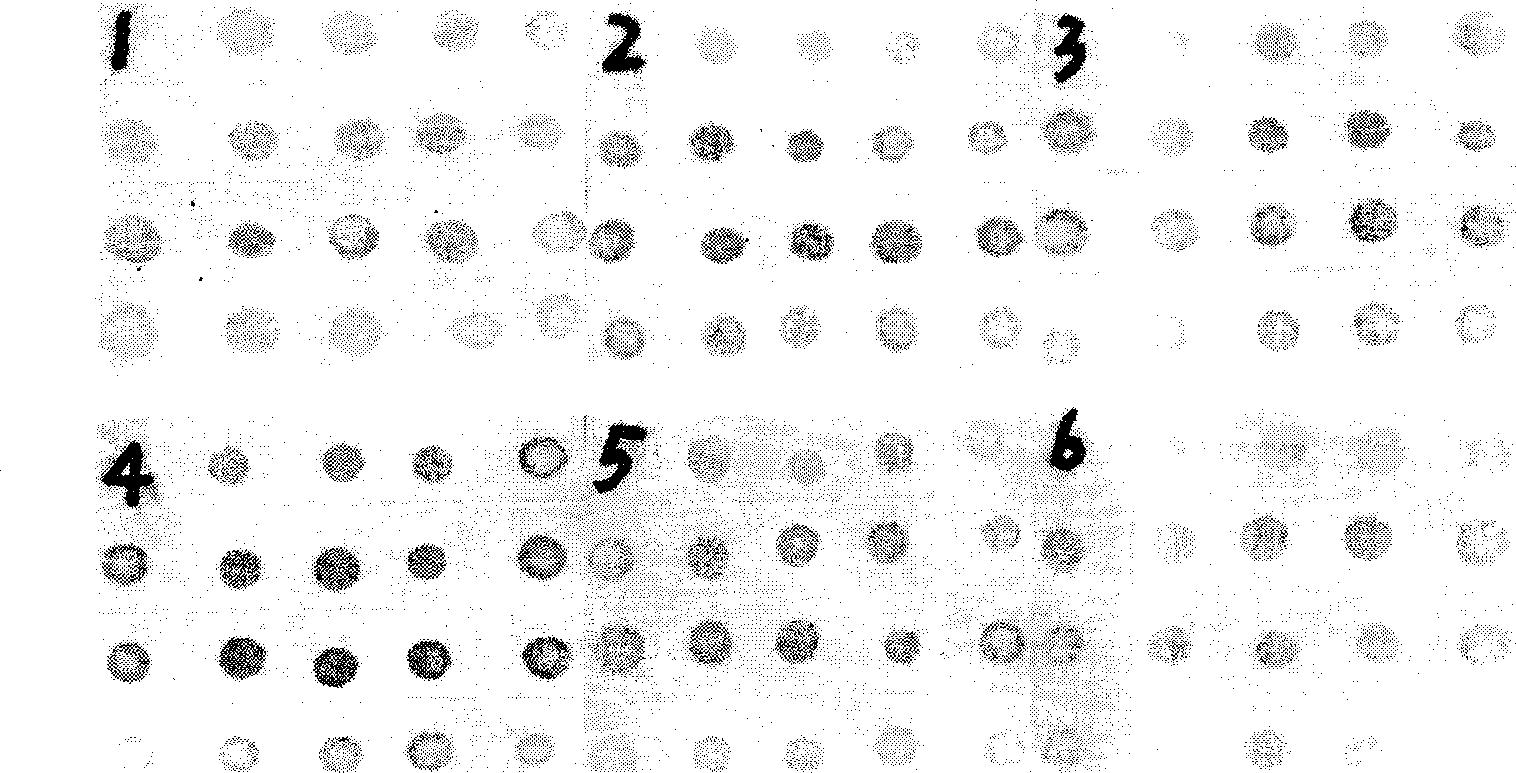
[0061]The results show that a weak positive reaction can still be seen when diluted to 25,600 times, but the strongest positive reaction can be seen at a dilution of 100 times, and a dilution of 100-200 times is usually used for routine detection; weak positive reactions can still be seen when the diseased leaves are diluted to 51,200 times , but 400-fold dilution is better for visual inspection, and 200-500-fold dilution ( figure 2 ). But it is best to use fresh diseased leaves or use the method of detecting plant tissue.
Embodiment 3
[0063] Antibody Incubation Time Test
[0064] Monoclonal antibody working concentration 1:20000, incubate at 37°C for 0.5h, 1h, 1.5h, 2h, 2.5h, 3h (secondary antibody concentration 1:2500, secondary antibody incubation 1.5h) to determine the change of monoclonal antibody incubation time impact on test results. The results showed that when incubated at 37°C for 0.5h, positive samples could be detected, the color of the spots when incubated for 1h was basically the same as when incubated for 1.5h, 2h, and 2.5h, and the color decreased slightly when incubated for 3h ( image 3 ). Therefore, it is determined that incubation of monoclonal antibody at 37°C for 1-1.5h is the best incubation time.
[0065] Determine the monoclonal antibody concentration of 1:20000, and incubate at 37°C for 1.5h; use the concentration of secondary antibody at 1:2500, and incubate at 37°C for 0.5h, 1h, 1.5h, 2h, 2.5h, and 3h, respectively, to determine whether to change the secondary antibody Effect ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com