Inorganic micro filtering membrane vacuum emulsion breaking method and equipment
A microfiltration membrane and inorganic technology, applied in the field of microfiltration membrane vacuum demulsification, can solve the problems of easy clogging of membrane pores, high energy consumption, low membrane flux, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the degree of membrane fouling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Liquid Membrane Separation Technology Treatment of Phenol-Containing Wastewater
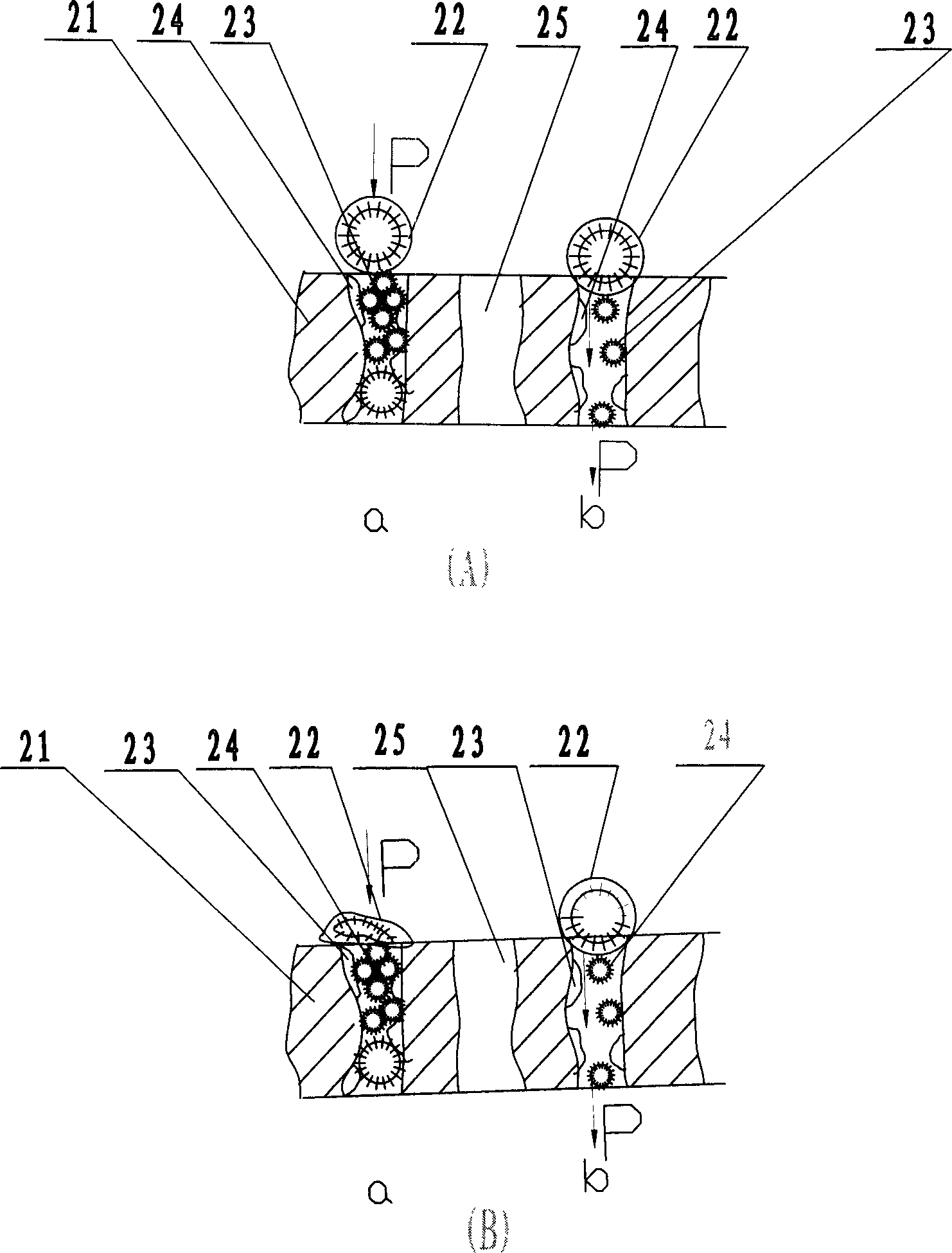
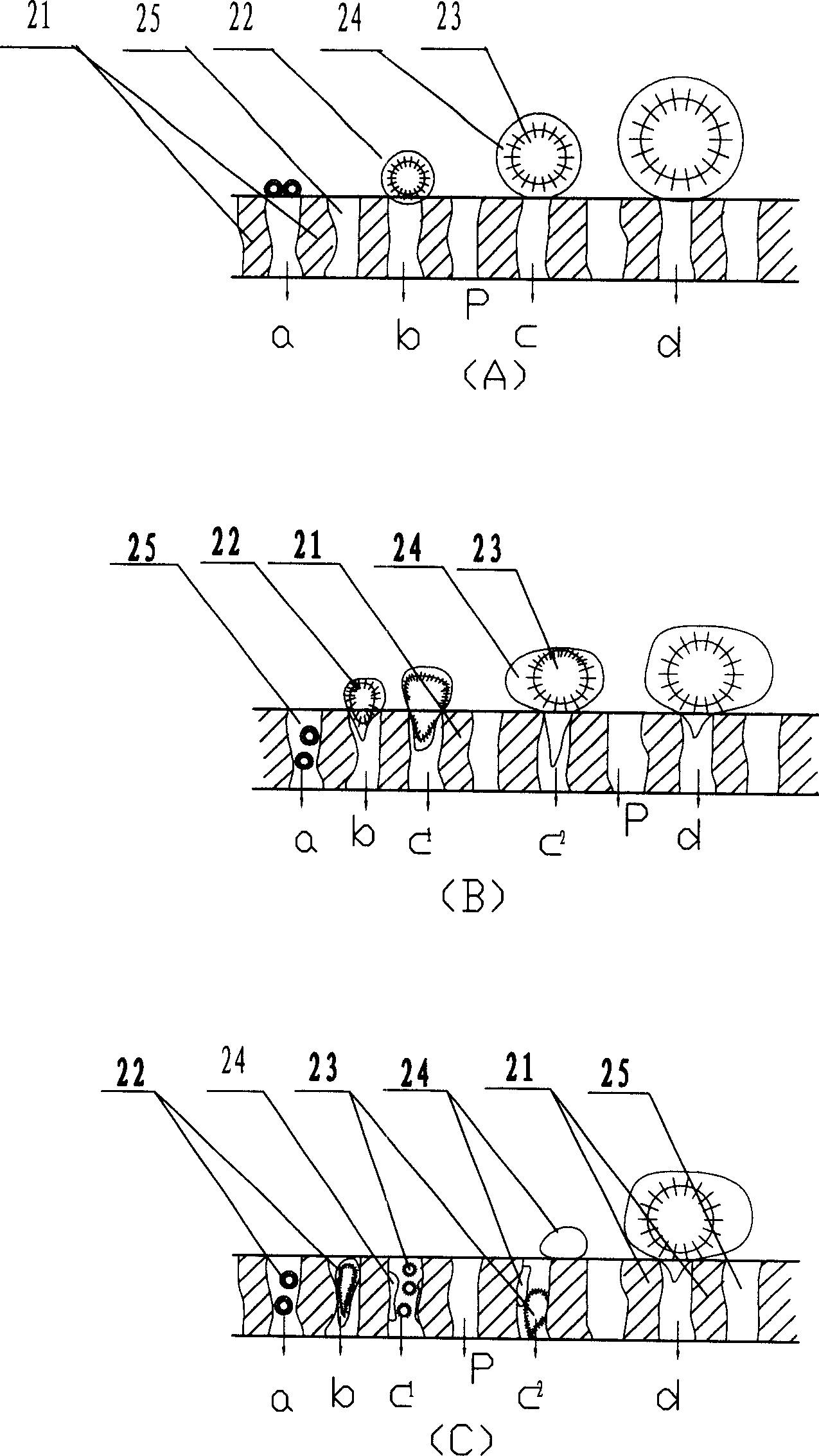
[0035] Emulsion breaking after liquid membrane extraction of phenol-containing wastewater - the average droplet diameter of the emulsion is about 3.5 times the average pore diameter of the membrane.
[0036] The mass percentage composition of emulsion film is as follows:
[0037] The content of surfactant span-80 (Span-80) in the oil phase is 4%, the content of kerosene in the oil phase is 93%, the content of liquid paraffin in the oil phase is 3%, and the NaOH concentration in the water phase For 5%, the oil phase in the emulsion is compared with the water R oi 1:1 to 1:1.5.
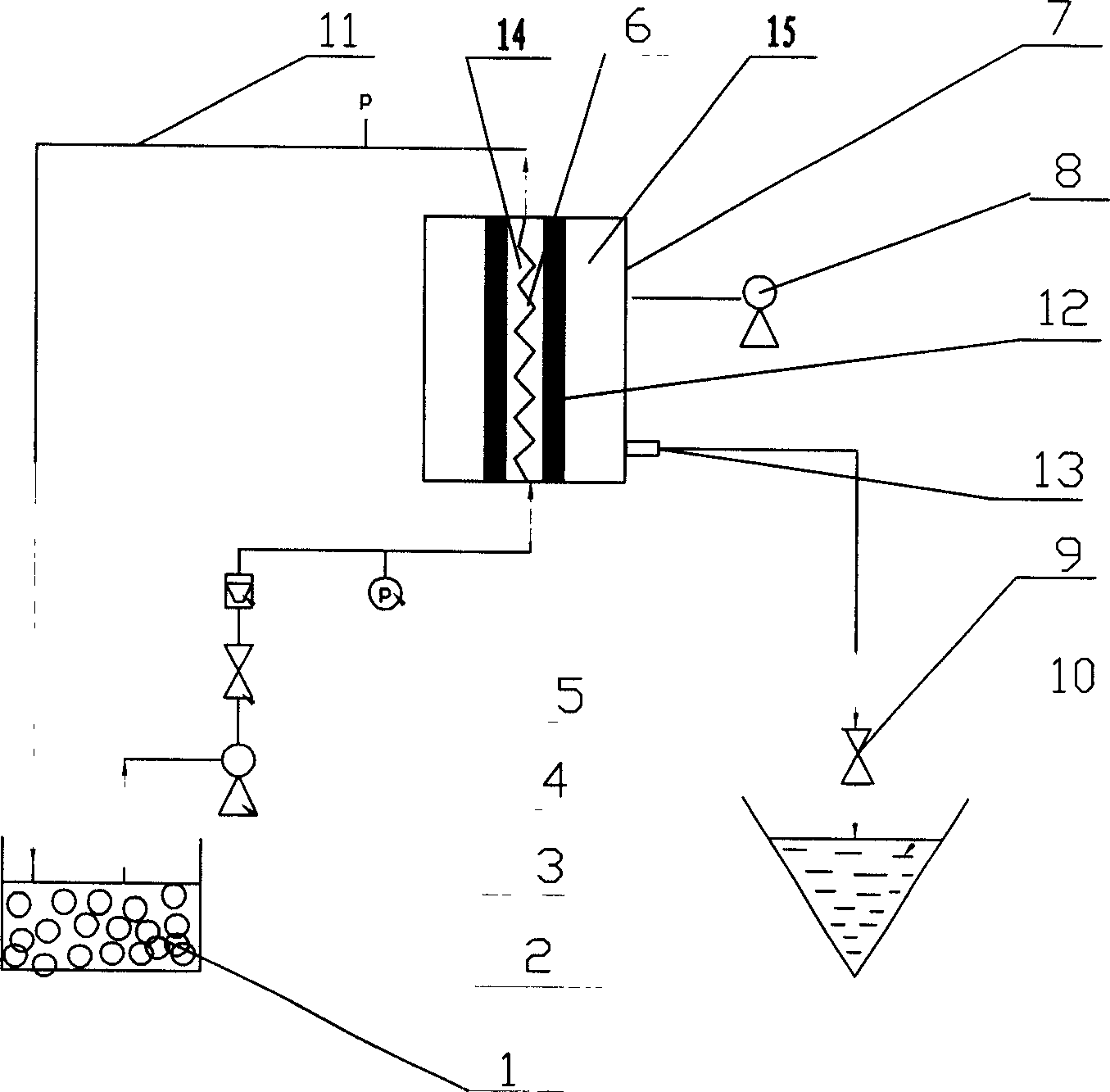
[0038] The conditions for making milk are as follows: the rotation speed of the mixer is 10000 rpm, and the emulsification time is 3 minutes to prepare an emulsion, which is mixed and stirred with wastewater containing phenol, left to stand for separation, and the extracted emulsion is obtained. It was ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Emulsion demulsification after liquid membrane extraction of phenol-containing wastewater - the average droplet diameter is 4.5-5 times the average pore diameter of the membrane
[0043] The mass percent composition of the emulsion liquid film and the milk-making conditions are the same as in Example 1.
[0044] The demulsification process is the same as in Example 1, and the demulsification conditions are different from those in Example 1: the degree of vacuum is (75-85) kPa, the average membrane pore size is about 2.5 μm, and the membrane pore size distribution is mainly concentrated at (1.2-4.5) μm Between, other demulsification conditions are identical with embodiment 1. The demulsification rate is over 96%, and the membrane flux is up to (1350-1450) L / m 2 .h. And compared with the conventional demulsification of the external permeation membrane method without disturbance elements (other operating conditions are the same), it is concluded that the best operating e...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Emulsion demulsification after liquid membrane extraction of ammonia nitrogen wastewater - the average droplet diameter of the emulsion is about 3.5 times the average pore diameter of the membrane
[0047] The mass percentage composition of emulsion film is as follows:
[0048] The content of surfactant span-80 (Span-80) in the oil phase is 4%, the content of kerosene in the oil phase is 89%, the content of liquid paraffin in the oil phase is 7%, in the water phase H 2 SO 4 The concentration is 18%, the oil phase in the emulsion is compared with water R oi 1:1 to 1:1.5.
[0049] Milking conditions and demulsification conditions are the same as in Example 1. The particle size and distribution of the extracted emulsion are basically the same as in Example 1, mainly because the material ratio and operating conditions of the two are basically the same or nearly the same. The demulsification rate reaches about 95%, and the membrane flux reaches (1600-1700) L / m 2 .h.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average membrane pore diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com