Surface mount LED
A technology of LED chips and mounting parts is applied to LEDs. It can solve the problems of inability to apply the optical system, cracks and warping of the resin molding part, and it is difficult to obtain the light distribution characteristics of complete scattering distribution, so as to achieve uniform light distribution characteristics and eliminate the effects of deterioration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
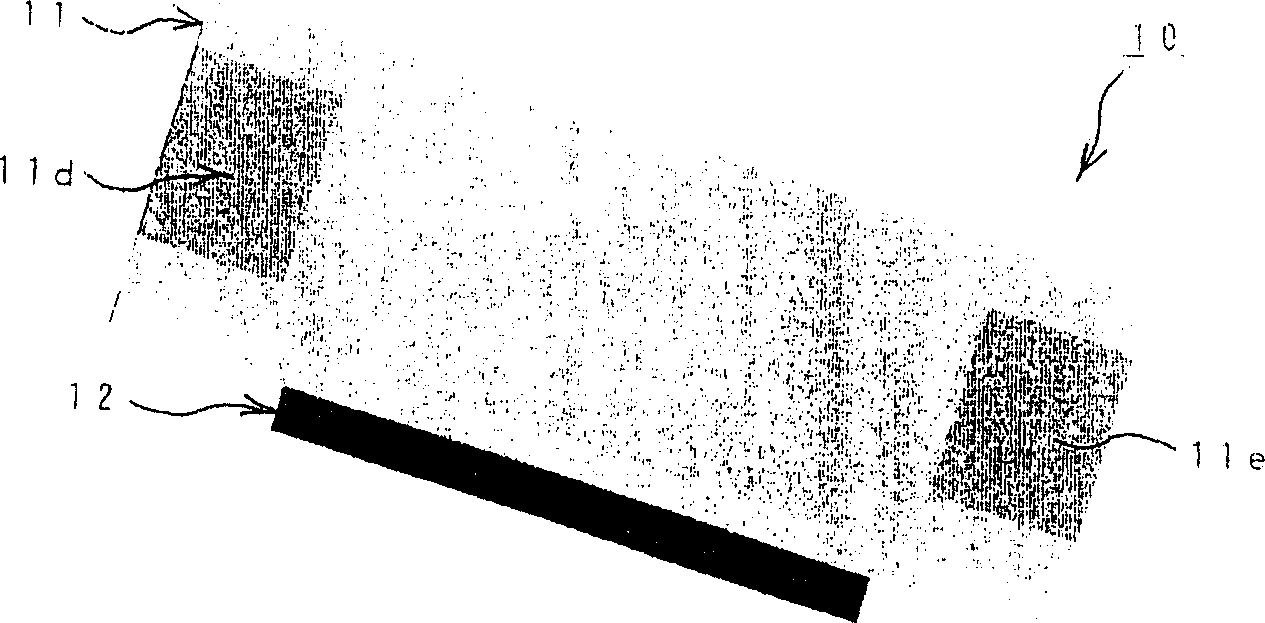
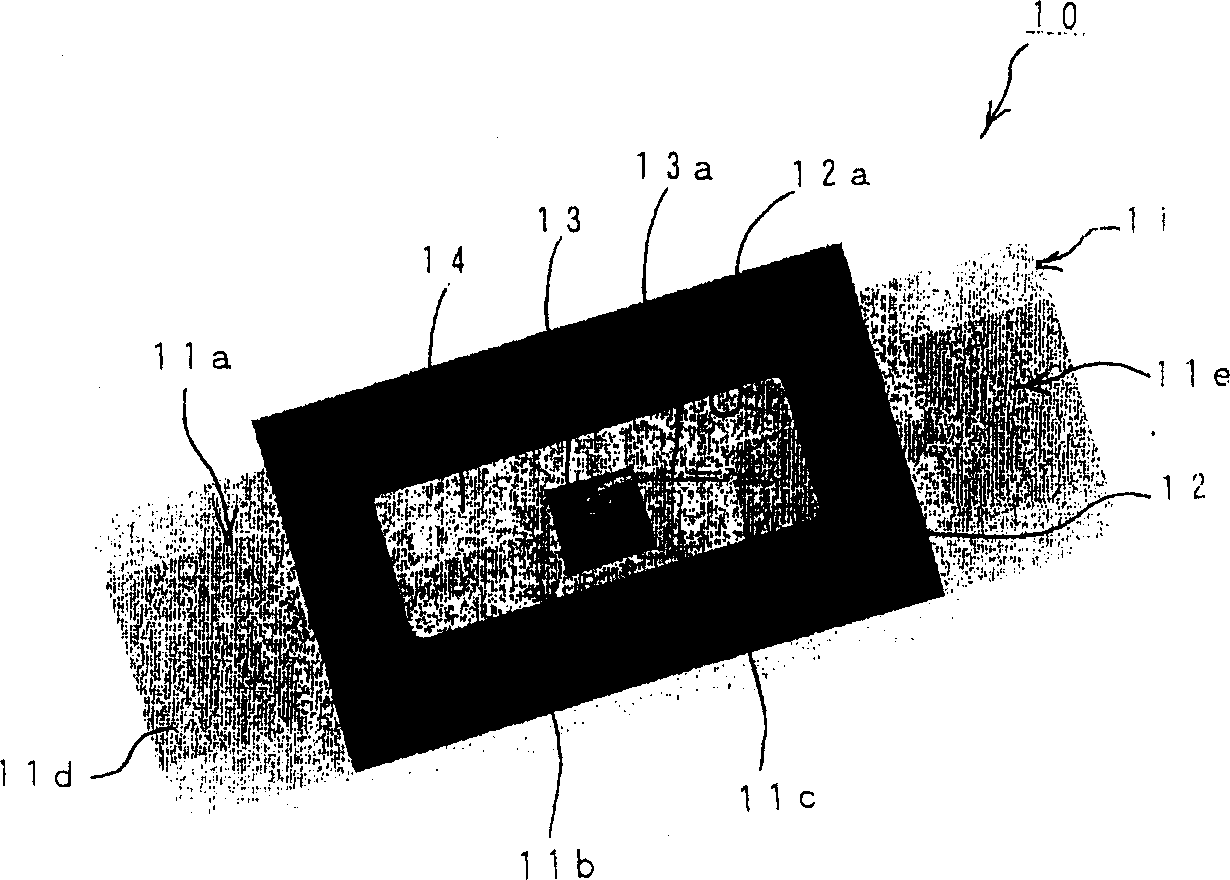
[0056] figure 1 and figure 2 The structure of the first embodiment of the LED of the present invention is shown. exist figure 1 and figure 2 Among them, the LED 10 is composed of the following parts: a silicon substrate 11; a glass frame 12 mounted on the silicon substrate 11; an LED chip 13 mounted on the silicon substrate 11 in the through hole 12a of the glass frame 12; The plastic sealing part 14 in the through hole of the glass frame body 12 .
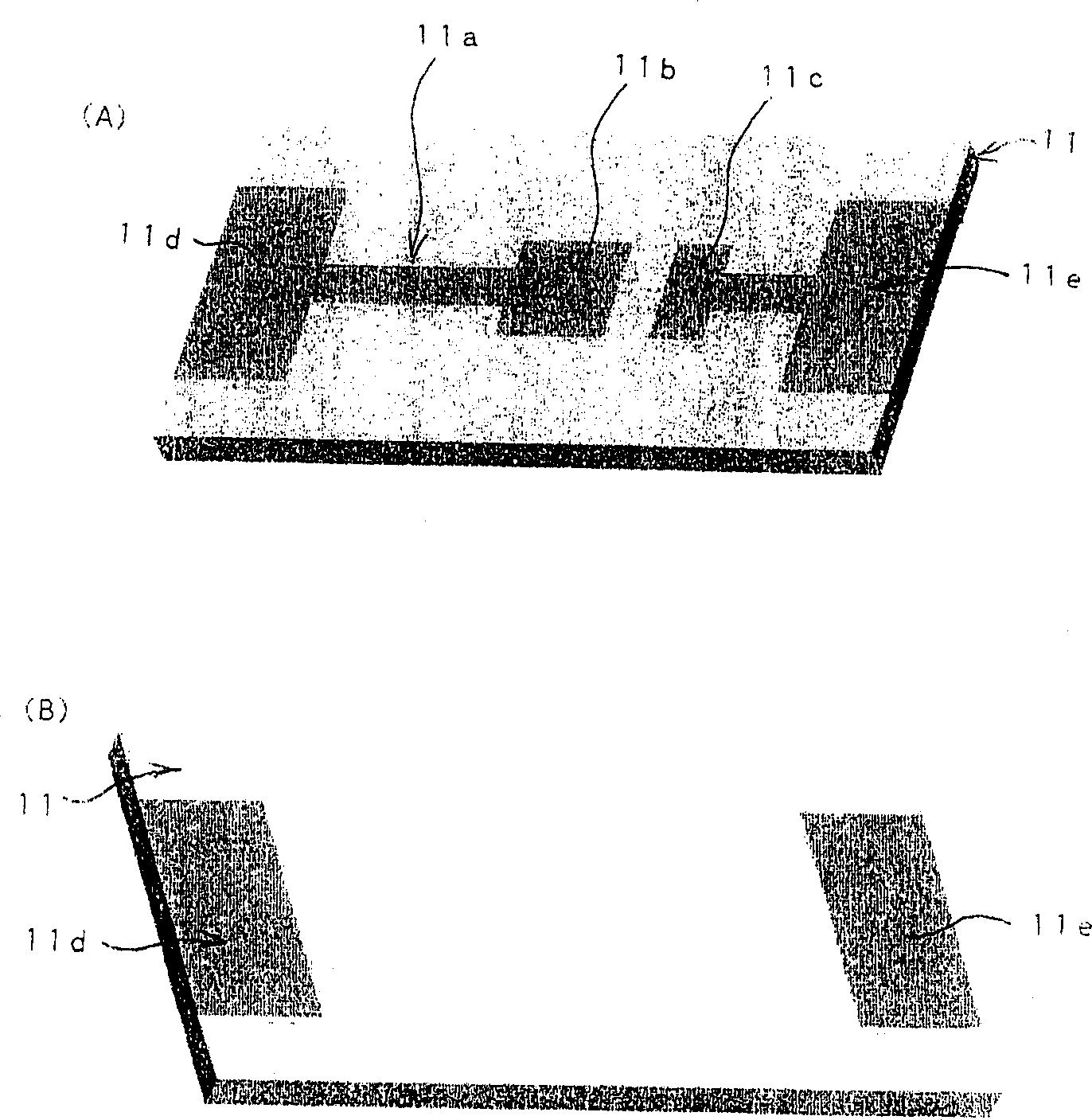
[0057] The above-mentioned silicon substrate 11 is made of plate-shaped silicon, and is formed with a image 3 (A) and image 3 (B) Conductive layer 11a of a predetermined pattern.
[0058] The conductive layer 11a includes an LED chip mounting portion 11b, adjacent connection pads 11c, and electrode portions 11d, 11e surrounding the silicon substrate 11 from both ends to the back surface near the center of the silicon substrate 11.
[0059] The conductive layer 11a is formed, for example, as described below.
[0060] ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Figure 5 The structure of the second embodiment of the LED of the present invention is shown.
[0080] exist Figure 5 , the structure of LED20 and figure 1 and figure 2 The illustrated LEDs 10 are substantially the same, so the same components are assigned the same symbols and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0081] The above LED20 with figure 1 and figure 2 Compared with the LED 10 shown, the difference is that the silicon substrate 21 is used instead of the silicon substrate 11 .
[0082] Here, the above-mentioned silicon substrate 21 is made of a slightly thick plate-shaped silicon, and has slopes 21a, 21b that become lower toward the outside at both end edges.
[0083] Such slopes 21a, 21b are formed by, for example, scribing and cutting, or the surface of the silicon substrate 21 is used as (100 plane) and (110 plane) is formed as a slope by, for example, KOH series alkaline wet etching.
[0084] And, for this silicon substrate 21, the conductive la...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Figure 6 The structure of the 3rd embodiment of the LED of this invention is shown.
[0090] exist Figure 6 , the structure of LED30 and figure 1 and figure 2 The illustrated LEDs 10 are substantially the same, so the same components are assigned the same symbols and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0091] The above LED30 with figure 1 and figure 2 Compared with the LED 10 shown, the difference is that the silicon substrate 31 is used instead of the silicon substrate 11 .
[0092] Here, the silicon substrate 31 is made of silicon, has a trapezoidal gap on the back side, and has spacer surfaces 31a, 31b widening from the center of the back side toward both end edges.
[0093] Such a silicon substrate 31 such as Figure 7 As shown in (A), it consists of a lower part 32 that divides the partition surface into 31a and 31b, and a plate-shaped upper part 33, and is formed by joining the upper part 33 to the upper surface of the lower part 32.
[0094] Here, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com